Y-27632ROCK inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 146986-50-7 |
- Fasudil (HA-1077) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2542
CAS No.:105628-07-7
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- GSK429286A
Catalog No.:BCC2532
CAS No.:864082-47-3
- SLx-2119
Catalog No.:BCC1954
CAS No.:911417-87-3
- AS 1892802
Catalog No.:BCC6335
CAS No.:928320-12-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 146986-50-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 448042 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H21N3O | M.Wt | 247.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (202.15 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 5 mg/mL (20.22 mM; ultrasonic and warming and heat to 60°C) | ||
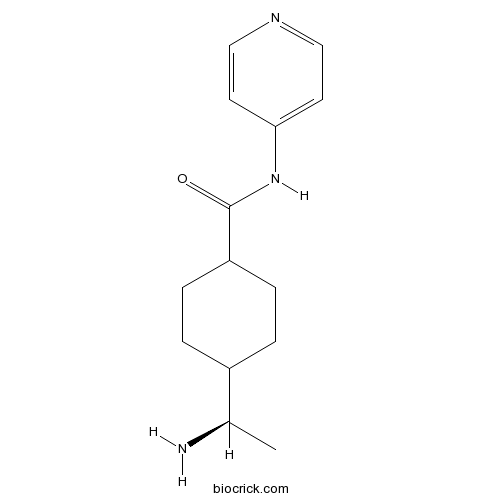
| Chemical Name | 4-[(1R)-1-aminoethyl]-N-pyridin-4-ylcyclohexane-1-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C1CCC(CC1)C(=O)NC2=CC=NC=C2)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IYOZTVGMEWJPKR-VOMCLLRMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H21N3O/c1-10(15)11-2-4-12(5-3-11)14(18)17-13-6-8-16-9-7-13/h6-12H,2-5,15H2,1H3,(H,16,17,18)/t10-,11?,12?/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Y-27632 2HCl is a selective inhibitor of ROCK1 (p160ROCK) with a Ki value of 140 nM. | |||||
| Targets | ROCK1 (p160ROCK) | ROCK2 | ||||
| IC50 | 140 nM(Ki) | 300 nM(Ki) | ||||

Y-27632 Dilution Calculator

Y-27632 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.043 mL | 20.2151 mL | 40.4302 mL | 80.8604 mL | 101.0754 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8086 mL | 4.043 mL | 8.086 mL | 16.1721 mL | 20.2151 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4043 mL | 2.0215 mL | 4.043 mL | 8.086 mL | 10.1075 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0809 mL | 0.4043 mL | 0.8086 mL | 1.6172 mL | 2.0215 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0404 mL | 0.2022 mL | 0.4043 mL | 0.8086 mL | 1.0108 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Y-27632 is a specific inhibitor of Rho-associated kinases(ROCK) family with Ki values of 0.22μM and 0.30μM for ROCK1 and ROCK2, respectively.
Y-27632 has shown selectivity of inhibition by comparing their Ki values for other Rho effector kinases, citron kinase and PKN, as well as PKCα. The Ki values of Y-27632 for citron kinase and PKN are least 20-fold higher, and Ki values for PKCα are about 200-fold higher than those for ROCK kinases. In addition, Y-27632 has been reported to inhibit ROCK1 and ROCK2 by competing with ATP for binding to the kinase in HeLa cells. Besides, Y-27632 has also shown the inhibition of stress fibers in Swiss 3T3 cells when the concentration of Y-27632 is 10μM [1].
References:
[1] Ishizaki T1, Uehata M, Tamechika I, Keel J, Nonomura K, Maekawa M, Narumiya S. Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. Mol Pharmacol. 2000 May;57(5):976-83.
- Fmoc-Lys(Aloc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3515
CAS No.:146982-27-6
- Fmoc-Asp(OAll)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3089
CAS No.:146982-24-3
- Codaphniphylline
Catalog No.:BCN1652
CAS No.:14694-15-6
- Ziprasidone
Catalog No.:BCC2071
CAS No.:146939-27-7
- K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12
Catalog No.:BCC5562
CAS No.:1469337-95-8
- K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 9
Catalog No.:BCC6500
CAS No.:1469337-91-4
- 1,2-Diacetoxy-4,7,8-trihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)dibenzofuran
Catalog No.:BCN7691
CAS No.:146905-24-0
- Triptobenzene H
Catalog No.:BCN6784
CAS No.:146900-55-2
- 1,5-Dihydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7423
CAS No.:14686-65-8
- 2-Bromo-1-(3-thienyl)-1-ethanone
Catalog No.:BCN2657
CAS No.:1468-82-2
- Y-29794 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC5795
CAS No.:146794-84-5
- N-desmethyldauricine
Catalog No.:BCC8217
CAS No.:146763-55-5
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Atglistatin
Catalog No.:BCC5104
CAS No.:1469924-27-3
- QL47
Catalog No.:BCC3920
CAS No.:1469988-75-7
- Diphenhydramine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8947
CAS No.:147-24-0
- DL-Arabinose
Catalog No.:BCN8541
CAS No.:147-81-9
- Proline
Catalog No.:BCN1656
CAS No.:147-85-3
- Cytarabine
Catalog No.:BCC3759
CAS No.:147-94-4
- 3'-O-Demethylarctigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3544
CAS No.:147022-95-5
- Menthyl-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-2H-pyrimidin-1-yl)-[1,3]oxathiolane-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9019
CAS No.:147027-10-9
- MK591
Catalog No.:BCC1766
CAS No.:147030-01-1
- Cyclo(Phe-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN2416
CAS No.:14705-60-3
- Rocaglaol
Catalog No.:BCN1653
CAS No.:147059-46-9
Y-27632 Increases Sensitivity of PANC-1 Cells to EGCG in Regulating Cell Proliferation and Migration.[Pubmed:27694793]
Med Sci Monit. 2016 Oct 3;22:3529-3534.
BACKGROUND The study aimed to investigate the inhibitory effect of (1R,4r)-4-((R)-1-aminoethyl)-N-(pyridin-4-yl) cyclohexanecarboxamide (Y-27632) and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on the proliferation and migration of PANC-1 cells. EGCG, found in green tea, has been previously shown to be one of the most abundant and powerful catechins in cancer prevention and treatment. Y-27632, a selective inhibitor of rho-associated protein kinase 1, is widely used in treating cardiovascular disease, inflammation, and cancer. MATERIAL AND METHODS PANC-1 cells, maintained in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium, were treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (control) as well as different concentrations (20, 40, 60, and 80 mug/mL) of EGCG for 48 h. In addition, PANC-1 cells were treated separately with 60 mug/mL EGCG, 20 muM Y-27632, and EGCG combined with Y-27632 (60 mug/mL EGCG + 20 muM Y-27632) for 48 h. The effect of EGCG and Y-27632 on the proliferation and migration of PANC-1 cells was evaluated using Cell Counting Kit-8 and transwell migration assays. The expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) and Caspase-3 mRNA was determined by Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). RESULTS EGCG (20-80 mug/mL) inhibited cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. Y-27632 enhanced the sensitivity of PANC-1 cells to EGCG (by increasing the expression of PPARa and Caspase-3 mRNA) and suppressed cell proliferation. PANC-1 cell migration was inhibited by treatment with a combination of EGCG and Y-27632. CONCLUSIONS Y-27632 increases the sensitivity of PANC-1 cells to EGCG in regulating cell proliferation and migration, which is likely to be related to the expression of PPARa mRNA and Caspase-3 mRNA.
Additive effects of the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 and vardenafil on relaxation of the corpus cavernosum tissue of patients with erectile dysfunction and clinical phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor failure.[Pubmed:27763717]
BJU Int. 2017 Feb;119(2):325-332.
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the expression of the Rho/Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) pathway in the corpus cavernosum of patients with severe erectile dysfunction (ED) compared with healthy human corpus cavernosum, and to test the functional effects of two Rho kinase inhibitors (RKIs) on erectile tissue of patients with severe ED, which did not respond to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5Is). PATIENTS AND METHODS: Human corpus cavernosum samples were obtained after consent from men undergoing penile prosthesis implantation (n = 7 for organ bath experiments, n = 17 for quantitative PCR [qPCR]). Potent control subjects (n = 5) underwent penile needle biopsy. qPCR was performed for the expression of RhoA and ROCK subtypes 1 and 2. Immunohistochemistry staining against ROCK and alpha smooth muscle actin (alphaSMA) was performed on the corpus cavernosum of patients with ED. Tissue strips were precontracted with phenylephrine and incubated with 1 mum of the PDE5I vardenafil or with DMSO (control). Subsequently, increasing concentrations of the RKIs azaindole or Y-27632 were added, and relaxation of tissue was quantified. RESULTS: The expression of ROCK1 was unchanged (P > 0.05), while ROCK2 (P < 0.05) was significantly upregulated in patients with ED compared with controls. ROCK1 and ROCK2 protein colocalized with alphaSMA, confirming the presence of this kinase in cavernous smooth muscle cells and/or myofibroblasts. After incubation with DMSO, 10 mum azaindole and 10 mum Y-27632 relaxed precontracted tissues with 49.5 +/- 7.42% (P = 0.1470 when compared with vehicle) and 85.9 +/- 10.3% (P = 0.0016 when compared with vehicle), respectively. Additive effects on relaxation of human corpus cavernosum were seen after preincubation with 1 mum vardenafil. CONCLUSION: The RKI Y-27632 causes a significant relaxation of corpus cavernosum in tissue strips of patients with severe ED. The additive effect of vardenafil and Y-27632 shows that a combined inhibition of Rho-kinase and phosphodiesterase type 5 could be a promising orally administered treatment for severe ED.
The effects of Y-27632 on pial microvessels during global brain ischemia and reperfusion in rabbits.[Pubmed:28270098]
BMC Anesthesiol. 2017 Mar 7;17(1):38.
BACKGROUND: Global brain ischemia-reperfusion during propofol anesthesia provokes persistent cerebral pial constriction. Constriction is likely mediated by Rho-kinase. Cerebral vasoconstriction possibly exacerbates ischemic brain injury. Because Y-27632 is a potent Rho-kinase inhibitor, it should be necessary to evaluate its effects on cerebral pial vessels during ischemia-reperfusion period. We therefore tested the hypotheses that Y-27632 dilates cerebral pial arterioles after the ischemia-reperfusion injury, and evaluated the time-course of cerebral pial arteriolar status after the ischemia-reperfusion. METHODS: Japanese white rabbits were anesthetized with propofol, and a closed cranial window inserted over the left hemisphere. Global brain ischemia was produced by clamping the brachiocephalic, left common carotid, and left subclavian arteries for 15 min. Rabbits were assigned to cranial window perfusion with: (1) artificial cerebrospinal fluid (Control group, n = 7); (2) topical infusion of Y-27632 10(-6) mol . L(-1) for 30 min before the initiation of global brain ischemia (Pre group, n = 7); (3) topical infusion of Y-27632 10(-6) mol . L(-1) starting 30 min before ischemia and continuing throughout the study period (Continuous group, n = 7); and, (4) topical infusion of Y-27632 10(-6) mol . L(-1) starting 10 min after the ischemia and continuing until the end of the study (Post group, n = 7). Cerebral pial arterial and venule diameters were recorded 30 min before ischemia, just before arterial clamping, 10 min after clamping, and 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, and 120 min after unclamping. RESULTS: Mean arterial blood pressure and blood glucose concentration increased significantly after global brain ischemia except in the Continuous group. In the Pre and Continuous groups, topical application of Y-27632 produced dilation of large (mean 18-19%) and small (mean; 25-29%) pial arteries, without apparent effect on venules. Compared with the Control and Pre groups, arterioles were significantly dilated during the reperfusion period in the Continuous and Post groups (mean at 120 min: 5-8% in large arterioles and 11-12% in small arterioles). CONCLUSIONS: Y-27632 dilated cerebral pial arterioles during reperfusion. Y-27632 may enhance recovery from ischemia by preventing arteriolar vasoconstriction during reperfusion.
Y-27632, a Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, inhibits systemic lupus erythematosus.[Pubmed:28122300]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Apr;88:359-366.
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate whether Rho-kinase inhibition (Y-27632) modulated the expressions of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) in systemic lupus erythematosus. 20 wild type mice and 20 MRL/lpr mice were applied for the research. The animals were randomly assigned to wild type, wild type+Y-27632 group, MRL/lpr group and MRL/lpr+Y-27632 group. 5mg/kg Y-27632 was intravenously injected to inhibit the ROCK expressions.Y-27632 significantly decreased the serum levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and increased IL-10 level in serum of MRL/lpr mice. Flow cytometry (FCM) studies also showed that Y-27632 remarkably increased Regulatory cells(Treg) cell percentage in spleen cells. Western blot analysis demonstrated Y-27632 downregulated the expressions of ROCK1, ROCK2, upregulated the expression of forkhead/winged helix transcription factor(Foxp3), and inhibited the phosphorylations of NF-kappaBp65 and IkappaBalpha. The findings showed that the inhibition of ROCK was beneficial for the prevention of systemic lupus erythematosus, which possibly by suppressing NF-kappaB activation.


