SLx-2119Selective ROCK2 inhibitor CAS# 911417-87-3 |
- RKI-1447
Catalog No.:BCC1903
CAS No.:1342278-01-6
- Y-27632
Catalog No.:BCC4301
CAS No.:146986-50-7
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- GSK269962A
Catalog No.:BCC5178
CAS No.:850664-21-0
- GSK429286A
Catalog No.:BCC2532
CAS No.:864082-47-3
- ROCK inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1905
CAS No.:867017-68-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 911417-87-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11950170 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H24N6O2 | M.Wt | 452.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | ROCK inhibitor; KD-025 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 29 mg/mL (64.09 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
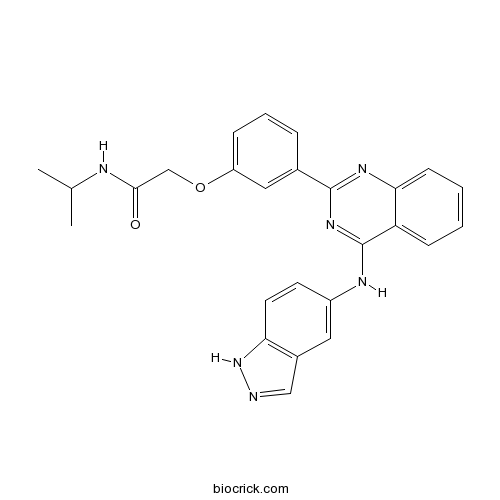
| Chemical Name | 2-[3-[4-(1H-indazol-5-ylamino)quinazolin-2-yl]phenoxy]-N-propan-2-ylacetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)NC(=O)COC1=CC=CC(=C1)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3C(=N2)NC4=CC5=C(C=C4)NN=C5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GKHIVNAUVKXIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H24N6O2/c1-16(2)28-24(33)15-34-20-7-5-6-17(13-20)25-30-23-9-4-3-8-21(23)26(31-25)29-19-10-11-22-18(12-19)14-27-32-22/h3-14,16H,15H2,1-2H3,(H,27,32)(H,28,33)(H,29,30,31) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | SLx-2119 is a selective inhibitor of ROCK2 with IC50 of 105 nM, more than 200 fold selecivity over ROCK1 (IC50=24 μM).In Vitro:SLx-2119 (40 µM) induces significant down-regulations of Tsp-1 and CTGF mRNA levels in PASMC. The microarray hybridized with aRNA from HMVEC treated with SLx-2119, shows a 5-times higher background than the other arrays[1].In Vivo:KD025 (100, 200 or 300 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently reduces infarct volume after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. KD025 is at least as efficacious in aged, diabetic or female mice, as in normal adult males[2]. References: | |||||
| Kinase experiment [1]: | |
| Inhibitory activities | Cell-free enzyme assays were performed to determine the selective inhibition of ROCK1 and ROCK2 by SLx-2119. Reactions were performed on non-binding surface microplates. Four mU of human ROCK1 and ROCK2 were used to phosphorylate 30 μM of the synthetic ROCK peptide substrate S6 Long (sequence: KEAKEKRQEQIAKRRRLSSLRASTSKSGGSQK), prepared at American Peptide (Sunnyvale, CA) with the addition of 10 μM ATP, containing 33P-ATP in the presence of 10 mM Mg2+, 50 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 0.1 mM EGTA and 1 mM DTT at room temperature. One unit is the amount of kinase needed to catalyze the transfer of 1 nmol phosphate/min to the peptide. The reactions were allowed to proceed for 45 minutes and then stopped with 3% phosphoric acid to a final concentration of 1%. The reactions were captured on phospho cellulose filtration microplates and washed with 75 mM phosphoric acid and methanol using a vacuum manifold. Phosphorylation was measured on a Perkin-Elmer MicroBeta 1450. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC; CC-2527, Cambrex). |
| Preparation method | Dissolved in DMSO to obtain a stock solution of 20 mM [1]. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 3 ml culture media containing 10 μM or 40 μM SLx-2119; 24 h. |
| Applications | SLx-2119 at 40 μM significantly reduces the mRNA levels of Tsp-1 and CTGF. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
| Animal models | C57BL/6 mice. |
| Dosage form | 100, 200 or 300 mg/kg; administered every 12 h for 2 days via orogastric gavage. |
| Application | KD025 (formerly SLx-2119) reduces infarct volume by 30% and 40% at 100 and 200 mg/kg dose levels. KD025 (200 mg/kg 90 min before distal middle cerebral artery occlusion (dMCAO)) significantly reduces the area of perfusion defect, suggesting that ROCK2 inhibition improves cortical perfusion during acute cerebral arterial occlusion. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1]. Boerma M, Fu Q, Wang J, et al. Comparative gene expression profiling in three primary human cell lines after treatment with a novel inhibitor of Rho kinase or atorvastatin. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis, 2008, 19(7): 709-718. [2]. Lee JH, Zheng Y, von Bornstadt D, et al. Selective ROCK2 Inhibition In Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Ann Clin Transl Neurol, 2014, 1(1): 2-14. | |

SLx-2119 Dilution Calculator

SLx-2119 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2099 mL | 11.0495 mL | 22.099 mL | 44.1979 mL | 55.2474 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.442 mL | 2.2099 mL | 4.4198 mL | 8.8396 mL | 11.0495 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.221 mL | 1.1049 mL | 2.2099 mL | 4.4198 mL | 5.5247 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0442 mL | 0.221 mL | 0.442 mL | 0.884 mL | 1.1049 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0221 mL | 0.1105 mL | 0.221 mL | 0.442 mL | 0.5525 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SLx-2119(KD-025) is a selective inhibitor of ROCK2 with IC50 of 105 nM [1].
Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) is a serine-threonine kinase and is involved in regulating cytoskeletal dynamics. It is associated with many intracellular processes, which are relevant to stroke. ROCK2 is the predominant isoform mainly expressed in vasculature and neurons [2].
In smooth muscle cells isolated from human intestine with radiation-induced fibrosis (RE-SMC), SLx-2119 reduced mRNA level of CTGF. Over-expression of which is associated with fibrotic diseases. While, in SMC isolated from normal human intestine (N-SMC), SLx-2119 didn’t change CTGF mRNA level [1].
In focal cerebral ischemia mice, after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion, KD025 reduced infarct volume in a dose-dependant way. And the efficacy maintained for at least 4 weeks. In aged male and female mice, as well as in type 2 diabetes mice, KD025 reduced infarct volume by 34%, 42% and 32% in aged male mice, female mice and diabetic mice respectively compared to vehicle in mice [2].
References:
[1]. Boerma M, Fu Q, Wang J, et al. Comparative gene expression profiling in three primary human cell lines after treatment with a novel inhibitor of Rho kinase or atorvastatin. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis, 2008, 19(7): 709-718.
[2]. Lee JH, Zheng Y, von Bornstadt D, et al. Selective ROCK2 Inhibition In Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Ann Clin Transl Neurol, 2014, 1(1): 2-14.
- EC 144
Catalog No.:BCC5600
CAS No.:911397-80-3
- MPP dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7225
CAS No.:911295-24-4
- LY2603618
Catalog No.:BCC3923
CAS No.:911222-45-2
- Cefoselis hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4093
CAS No.:911212-25-4
- Adapalene sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC4285
CAS No.:911110-93-5
- SB 706504
Catalog No.:BCC5615
CAS No.:911110-38-8
- Isotussilagine
Catalog No.:BCN1985
CAS No.:91108-32-6
- Furowanin A
Catalog No.:BCN4790
CAS No.:911004-72-3
- 3,6,19,23-Tetrahydroxy-12-ursen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1310
CAS No.:91095-51-1
- 8-Epidiosbulbin E acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7812
CAS No.:91095-48-6
- Danshenol C
Catalog No.:BCN6681
CAS No.:910856-25-6
- BAY 60-6583
Catalog No.:BCC6197
CAS No.:910487-58-0
- Infractin
Catalog No.:BCN3652
CAS No.:91147-07-8
- Terbinafine
Catalog No.:BCC3865
CAS No.:91161-71-6
- 17-AAG Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1297
CAS No.:911710-03-7
- Chrysothol
Catalog No.:BCN4454
CAS No.:911714-91-5
- Lucyoside B
Catalog No.:BCN7811
CAS No.:91174-19-5
- Ophiopogonin C
Catalog No.:BCN5379
CAS No.:911819-08-4
- H-Met-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2996
CAS No.:91183-71-0
- Noscapine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3819
CAS No.:912-60-7
- Spantide I
Catalog No.:BCC5808
CAS No.:91224-37-2
- Karavilagenin A
Catalog No.:BCN4455
CAS No.:912329-03-4
- TCB-2
Catalog No.:BCC7421
CAS No.:912342-28-0
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
Selective ROCK2 Inhibition In Focal Cerebral Ischemia.[Pubmed:24466563]
Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2014 Jan 1;1(1):2-14.
OBJECTIVE: Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) is a key regulator of numerous processes in multiple cell types relevant in stroke pathophysiology. ROCK inhibitors have improved outcome in experimental models of acute ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. However, the relevant ROCK isoform (ROCK1 or ROCK2) in acute stroke is not known. METHODS: We characterized the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profile, and tested the efficacy and safety of a novel selective ROCK2 inhibitor KD025 (formerly SLx-2119) in focal cerebral ischemia models in mice. RESULTS: KD025 dose-dependently reduced infarct volume after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. The therapeutic window was at least 3 hours from stroke onset, and the efficacy was sustained for at least 4 weeks. KD025 was at least as efficacious in aged, diabetic or female mice, as in normal adult males. Concurrent treatment with atorvastatin was safe, but not additive or synergistic. KD025 was also safe in a permanent ischemia model, albeit with diminished efficacy. As one mechanism of protection, KD025 improved cortical perfusion in a distal middle cerebral artery occlusion model, implicating enhanced collateral flow. Unlike isoform-nonselective ROCK inhibitors, KD025 did not cause significant hypotension, a dose-limiting side effect in acute ischemic stroke. INTERPRETATION: Altogether, these data show that KD025 is efficacious and safe in acute focal cerebral ischemia in mice, implicating ROCK2 as the relevant isoform in acute ischemic stroke. Data suggest that selective ROCK2 inhibition has a favorable safety profile to facilitate clinical translation.
Genetic Interference With Endothelial PPAR-gamma (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma) Augments Effects of Angiotensin II While Impairing Responses to Angiotensin 1-7.[Pubmed:28674038]
Hypertension. 2017 Sep;70(3):559-565.
Pharmacological activation of PPAR-gamma (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma) protects the vasculature. Much less is known on the cell-specific impact of PPAR-gamma when driven by endogenous ligands. Recently, we found that endothelial PPAR-gamma protects against angiotensin II-induced endothelial dysfunction. Here, we explored that concept further examining whether effects were sex dependent along with underlying mechanisms. We studied mice expressing a human dominant-negative mutation in PPAR-gamma driven by the endothelial-specific vascular cadherin promoter (E-V290M), using nontransgenic littermates as controls. Acetylcholine (an endothelium-dependent agonist) produced similar relaxation of carotid arteries from nontransgenic and E-V290M mice. Incubation of isolated arteries with angiotensin II (1 nmol/L) overnight had no effect in nontransgenic, but reduced responses to acetylcholine by about 50% in male and female E-V290M mice (P<0.05). Endothelial function in E-V290M mice was restored to normal by inhibitors of superoxide (tempol), NADPH oxidase (VAS-2870), Rho kinase (Y-27632), ROCK2 (SLx-2119), NF-kappaB (nuclear factor-kappa B essential modulator-binding domain peptide), or interleukin-6 (neutralizing antibody). In addition, we hypothesized that PPAR-gamma may influence the angiotensin 1-7 arm of the renin-angiotensin system. In the basilar artery, dilation to angiotensin 1-7 was selectively reduced in E-V290M mice by >50% (P<0.05), an effect reversed by Y-27632. Thus, effects of angiotensin II are augmented by interference with endothelial PPAR-gamma through sex-independent mechanisms, involving oxidant-inflammatory signaling and ROCK2 (Rho kinase). The study also provides the first evidence that endothelial PPAR-gamma interacts with angiotensin 1-7 responses. These critical roles for endothelial PPAR-gamma have implications for pathophysiology and therapeutic approaches for vascular disease.
Comparative gene expression profiling in three primary human cell lines after treatment with a novel inhibitor of Rho kinase or atorvastatin.[Pubmed:18832915]
Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2008 Oct;19(7):709-18.
Inhibitors of Rho kinase (ROCK) are a relatively new class of drugs with potential benefits in oncology, neurology, and fibrotic and cardiovascular diseases. ROCK inhibitors modulate many cellular functions, some of which are similar to the pleiotropic effects of statins, suggesting additive or synergistic properties. Studies to date have used compounds that inhibit both isoforms of ROCK, ROCK1 and ROCK2. This study was designed to compare gene expression profiles of atorvastatin with the newly developed ROCK2 inhibitor SLx-2119 in primary cultures of normal human endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and fibroblasts. Cells were treated with each compound for 24 h, after which total RNA was isolated and genome-wide gene-expression profiles were obtained with Illumina arrays. Because of the known effect of statins on the actin cytoskeleton and on connective tissue growth factor, a prominent growth factor involved in tissue fibrosis, the effects of SLx-2119 and atorvastatin on the actin cytoskeleton and connective tissue growth factor mRNA were also examined in cultures of smooth muscle cells with a fibrotic phenotype, isolated from biopsies of human intestine with radiation-induced fibrosis. Although SLx-2119 and atorvastatin affected expression of genes belonging to the same biological processes, individual genes were mostly different, consistent with synergistic or additive properties. Both SLx-2119 and atorvastatin reduced connective tissue growth factor mRNA and remodeled the actin cytoskeleton in fibrosis-derived smooth muscle cells, suggesting that both compounds have antifibrotic properties. These results form the basis for further studies to assess the possible therapeutic benefit of combined treatments.
Heterogeneous Impact of ROCK2 on Carotid and Cerebrovascular Function.[Pubmed:27432870]
Hypertension. 2016 Sep;68(3):809-17.
Rho kinase (ROCK) has been implicated in physiological and pathophysiological processes, including regulation of vascular function. ROCK signaling is thought to be a critical contributor to cardiovascular disease, including hypertension and effects of angiotensin II (Ang II). Two isoforms of ROCK (1 and 2) have been identified and are expressed in vascular cells. In this study, we examined the importance of ROCK2 in relation to vessel function using several models and a novel inhibitor of ROCK2. First, incubation of carotid arteries with the direct RhoA activator CN-03 or Ang II impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation by approximately 40% to 50% (P<0.05) without altering endothelium-independent relaxation. Both CN-03- and Ang II-induced endothelial dysfunction was prevented by Y-27632 (an inhibitor of both ROCK isoforms) or the selective ROCK2 inhibitor SLx-2119. In contrast, SLx-2119 had little effect on contraction of carotid arteries to receptor-mediated agonists (serotonin, phenylephrine, vasopressin, or U46619). Second, in basilar arteries, SLx-2119 inhibited constriction to Ang II by approximately 90% without significantly affecting responses to serotonin or KCl. Third, in isolated pressurized brain parenchymal arterioles, SLx-2119 inhibited myogenic tone in a concentration-dependent manner (eg, 1 mumol/L SLx-2119 dilated by 79+/-4%). Finally, SLx-2119 dilated small pial arterioles in vivo, an effect that was augmented by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. These findings suggest that ROCK2 has major, but heterogeneous, effects on function of endothelium and vascular muscle. The data support the concept that aberrant ROCK2 signaling may be a key contributor to select aspects of large and small vessel disease, including Ang II-induced endothelial dysfunction.


