ROCK inhibitorROCK-1/ROCK-2 inhibitor,highly potent CAS# 867017-68-3 |
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- H-1152
Catalog No.:BCC1615
CAS No.:451462-58-1
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 867017-68-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11524200 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H13ClF2N6O | M.Wt | 402.79 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Azaindole-1 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (82.75 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
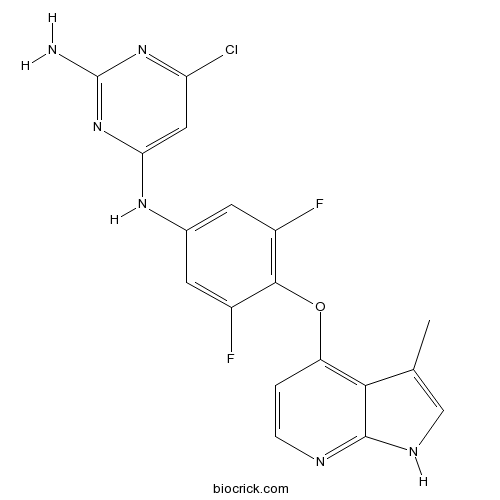
| Chemical Name | 6-chloro-4-N-[3,5-difluoro-4-[(3-methyl-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-yl)oxy]phenyl]pyrimidine-2,4-diamine | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CNC2=NC=CC(=C12)OC3=C(C=C(C=C3F)NC4=CC(=NC(=N4)N)Cl)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NRSGWEVTVGZDFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H13ClF2N6O/c1-8-7-24-17-15(8)12(2-3-23-17)28-16-10(20)4-9(5-11(16)21)25-14-6-13(19)26-18(22)27-14/h2-7H,1H3,(H,23,24)(H3,22,25,26,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and highly selective ROCK inhibitor (IC50 values are 0.6 and 1.1 nM for ROCK1 and ROCK2, respectively). Exhibits >200-fold selectivity over TRK and FLT3 receptors, and >900-fold selectivity over a panel of other kinases and cardiovascular relevent enzymes and receptors. Reduces blood pressure in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Orally active. |

ROCK inhibitor Dilution Calculator

ROCK inhibitor Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4827 mL | 12.4134 mL | 24.8268 mL | 49.6537 mL | 62.0671 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4965 mL | 2.4827 mL | 4.9654 mL | 9.9307 mL | 12.4134 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2483 mL | 1.2413 mL | 2.4827 mL | 4.9654 mL | 6.2067 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0497 mL | 0.2483 mL | 0.4965 mL | 0.9931 mL | 1.2413 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0248 mL | 0.1241 mL | 0.2483 mL | 0.4965 mL | 0.6207 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
ROCK inhibitor (Rho-kinase inhibitor) is useful for Anti-cancer.
- (S)-Methylisothiourea sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC6791
CAS No.:867-44-7
- (R)-(+)-2-Amino-3-methyl-1,1-diphenyl-1-butanol
Catalog No.:BCC8394
CAS No.:86695-06-9
- ARL 17477 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7647
CAS No.:866914-87-6
- BINA
Catalog No.:BCC7849
CAS No.:866823-73-6
- (1S)-4,5-Dimethoxy-1-[(methylamino)methyl]benzocyclobutane hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8383
CAS No.:866783-13-3
- Yuexiandajisu E
Catalog No.:BCN3775
CAS No.:866556-16-3
- Yuexiandajisu D
Catalog No.:BCN3774
CAS No.:866556-15-2
- [Ala2,8,9,11,19,22,24,25,27,28]-VIP
Catalog No.:BCC5973
CAS No.:866552-34-3
- 7-Hydroxy-3-prenylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN4415
CAS No.:86654-26-4
- Dorsomorphin
Catalog No.:BCC5131
CAS No.:866405-64-3
- DPPI 1c hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2363
CAS No.:866396-34-1
- 10-Aminocamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCC8111
CAS No.:86639-63-6
- Magnoshinin
Catalog No.:BCC8205
CAS No.:86702-02-5
- Tropanyl 3-hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN1325
CAS No.:86702-58-1
- Colivelin
Catalog No.:BCC7821
CAS No.:867021-83-8
- Linsitinib
Catalog No.:BCC3697
CAS No.:867160-71-2
- TRC 051384
Catalog No.:BCC7968
CAS No.:867164-40-7
- TG 100572 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1995
CAS No.:867331-64-4
- TG 100801
Catalog No.:BCC1996
CAS No.:867331-82-6
- TG 100572
Catalog No.:BCC1994
CAS No.:867334-05-2
- Astrasieversianin VII
Catalog No.:BCN2788
CAS No.:86764-11-6
- CRF (human, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5710
CAS No.:86784-80-7
- H-Cys-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2904
CAS No.:868-59-7
- Carasiphenol C
Catalog No.:BCN8251
CAS No.:868168-04-1
The ROCK Inhibitor Fasudil Prevents Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Depressive-Like Behaviors and Dendritic Spine Loss in Rat Hippocampus.[Pubmed:27927737]
Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 Apr 1;20(4):336-345.
Background: Dendritic arbor simplification and dendritic spine loss in the hippocampus, a limbic structure implicated in mood disorders, are assumed to contribute to symptoms of depression. These morphological changes imply modifications in dendritic cytoskeleton. Rho GTPases are regulators of actin dynamics through their effector Rho kinase. We have reported that chronic stress promotes depressive-like behaviors in rats along with dendritic spine loss in apical dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons, changes associated with Rho kinase activation. The present study proposes that the Rho kinase inhibitor Fasudil may prevent the stress-induced behavior and dendritic spine loss. Methods: Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected with saline or Fasudil (i.p., 10 mg/kg) starting 4 days prior to and maintained during the restraint stress procedure (2.5 h/d for 14 days). Nonstressed control animals were injected with saline or Fasudil for 18 days. At 24 hours after treatment, forced swimming test, Golgi-staining, and immuno-western blot were performed. Results: Fasudil prevented stress-induced immobility observed in the forced swimming test. On the other hand, Fasudil-treated control animals showed behavioral patterns similar to those of saline-treated controls. Furthermore, we observed that stress induced an increase in the phosphorylation of MYPT1 in the hippocampus, an exclusive target of Rho kinase. This change was accompanied by dendritic spine loss of apical dendrites of pyramidal hippocampal neurons. Interestingly, increased pMYPT1 levels and spine loss were both prevented by Fasudil administration. Conclusion: Our findings suggest that Fasudil may prevent the development of abnormal behavior and spine loss induced by chronic stress by blocking Rho kinase activity.
L-F001, a novel multifunctional ROCK inhibitor, suppresses neuroinflammation in vitro and in vivo: Involvement of NF-kappaB inhibition and Nrf2 pathway activation.[Pubmed:28320516]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Jul 5;806:1-9.
Microglia and astrocytes are largely responsible for inflammatory injury in the brain of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Increasing evidence has indicated that Rho kinase (ROCK) plays an important role in the regulation of neuroinflammation. Previously, we synthesized a new chemical entity L-F001 and proved its potential inhibitory effects on ROCK and oxidative stress. Here, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects and the molecular mechanisms of L-F001 in vitro and in vivo. L-F001 remarkably suppressed lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-elevated expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) as well as LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO), reactive oxygen species, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necreactive oxygen speciesis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in microglial BV-2 cells and in cultured astrocytes. Furthermore, L-F001 inhibited the degradation of IkappaB and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) p65 subunit. Moreover, L-F001 induced the upregulation of heme-oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and glutamate cysteine ligase modifier subunit (GCLM) expression, two downstream effectors of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2). It was interesting that L-F001 also activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway and induced M1 (CD16/32, M1 marker)/ M2 (CD206, M2 maker) transition in BV-2 cells which was significantly blocked by a PI3K inhibitor, wortmannin. Finally, L-F001 markedly attenuated the level of pro-inflammatory mediators in a murine model of systemic acute brain inflammation induced by LPS. Taken together, these results indicate that the novel multifunctional ROCK inhibitor L-F001 suppresses neuroinflammation in vitro and in vivo via NF-kappaB inhibition and Nrf2 activation, suggesting that L-F001 may be a promising drug candidate for treating neuroinflammation-associated CNS diseases, including AD.
Human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells maintain phenotype but alter their metabolism after exposure to ROCK inhibitor.[Pubmed:28165055]
Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 6;7:42138.
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are adhesion-dependent cells that require cultivation in colonies to maintain growth and pluripotency. Robust differentiation protocols necessitate single cell cultures that are achieved by use of ROCK (Rho kinase) inhibitors. ROCK inhibition enables maintenance of stem cell phenotype; its effects on metabolism are unknown. hPSCs were exposed to 10 muM ROCK inhibitor for varying exposure times. Pluripotency (TRA-1-81, SSEA3, OCT4, NANOG, SOX2) remained unaffected, until after prolonged exposure (96 hrs). Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry metabolomics analysis identified differences between ROCK-treated and untreated cells as early as 12 hrs. Exposure for 48 hours resulted in reduction in glycolysis, glutaminolysis, the citric acid (TCA) cycle as well as the amino acids pools, suggesting the adaptation of the cells to the new culture conditions, which was also reflected by the expression of the metabolic regulators, mTORC1 and tp53 and correlated with cellular proliferation status. While gene expression and protein levels did not reveal any changes in the physiology of the cells, metabolomics revealed the fluctuating state of the metabolism. The above highlight the usefulness of metabolomics in providing accurate and sensitive information on cellular physiological status, which could lead to the development of robust and optimal stem cell bioprocesses.
L-F001, a Multifunction ROCK Inhibitor Prevents 6-OHDA Induced Cell Death Through Activating Akt/GSK-3beta and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in PC12 Cells and Attenuates MPTP-Induced Dopamine Neuron Toxicity in Mice.[Pubmed:28078613]
Neurochem Res. 2017 Feb;42(2):615-624.
Amounting evidences demonstrated that Rho/Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) might be a novel target for the therapy of Parkinson's disease (PD). Recently, we synthesized L-F001 and revealed it was a potent ROCK inhibitor with multifunctional effects. Here we investigated the effects of L-F001 in PD models. We found that L-F001 potently attenuated 6-OHDA-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells and significantly decreased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), prevented the 6-OHDA-induced decline of mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular GSH levels. In addition, L-F001 increased Akt and GSK-3beta phosphorylation and induced the nuclear Nrf2 and HO-1 expression in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Moreover, L-F001 restored the levels of p-Akt and p-GSK-3beta (Ser9) as well as HO-1 expression reduced by 6-OHDA. Those effects were blocked by the specific PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, indicating the involvement of Akt/GSK-3beta pathway in the neuroprotective effect of L-F001. In addition, L-F001 significantly attenuated the tyrosinehydroxylase immunoreactive cell loss in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6 tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced mice PD model. Together, our findings suggest that L-F001 prevents 6-OHDA-induced cell death through activating Akt/GSK-3beta and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and attenuates MPTP-induced dopaminergic neuron toxicity in mice. L-F001 might be a promising drug candidate for PD.
Therapeutic efficacy of azaindole-1 in experimental pulmonary hypertension.[Pubmed:20530035]
Eur Respir J. 2010 Oct;36(4):808-18.
An accumulating body of evidence incriminates Rho kinase (ROCK) in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension (PH). The therapeutic efficacy of azaindole-1, a novel highly selective and orally active ROCK inhibitor, has not yet been investigated in PH. This study aimed to investigate the effects of azaindole-1 on 1) acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV), 2) proliferation of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) and 3) animal models of PH. Azaindole-1 significantly inhibited HPV in isolated, ventilated and buffer-perfused murine lungs and proliferation of primary rat PASMCs in vitro. Azaindole-1 was administered orally from 21 to 35 days after monocrotaline (MCT) injection in rats and hypoxic exposure in mice. Azaindole-1 (10 and 30 mg per kg body weight per day in rats and mice, respectively) significantly improved haemodynamics and right ventricular hypertrophy. Moreover, the medial wall thickness and muscularisation of peripheral pulmonary arteries were ameliorated. Azaindole-1 treatment resulted in a decreased immunoreactivity for phospho-myosin phosphatase target subunit 1 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in pulmonary vessels of MCT-injected rats, suggesting an impaired ROCK activity and reduced proliferating cells. Azaindole-1 provided therapeutic benefit in experimental PH, and this may be attributable to its potent vasorelaxant and antiproliferative effects. Azaindole-1 may offer a useful approach for treatment of PH.
Cardiovascular effects of a novel potent and highly selective azaindole-based inhibitor of Rho-kinase.[Pubmed:17934515]
Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;152(7):1070-80.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Rho-kinase (ROCK) has been implicated in the pathophysiology of altered vasoregulation leading to hypertension. Here we describe the pharmacological characterization of a potent, highly selective and orally active ROCK inhibitor, the derivative of a class of azaindoles, azaindole 1 (6-chloro-N4-{3,5-difluoro-4-[(3-methyl-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-yl)oxy]-phenyl }pyrimidine-2,4-diamine). EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: Pharmacological characterization of azaindole 1 was performed with human recombinant ROCK in vitro. Vasodilator activity was determined using isolated vessels in vitro and different animal models in vivo. KEY RESULTS: This compound inhibited the ROCK-1 and ROCK-2 isoenzymes with IC50 s of 0.6 and 1.1 nM in an ATP-competitive manner. Although ATP-competitive, azaindole 1 was inactive against 89 kinases (IC50>10 microM) and showed only weak activity against an additional 21 different kinases (IC50=1-10 microM). Only the kinases TRK und FLT3 were inhibited by azaindole 1 in the sub-micromolar range, albeit with IC50 values of 252 and 303 nM, respectively. In vivo, azaindole 1 lowered blood pressure dose-dependently after i.v. administration in anaesthetized normotensive rats. In conscious normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats azaindole 1 induced a dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure after oral administration without inducing a significant reflex increase in heart rate. In anaesthetized dogs, azaindole 1 induced vasodilatation with a moderately elevated heart rate. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: Azaindole 1 is representative of a new class of selective and potent ROCK inhibitors and is a valuable tool for the elucidation of the role of ROCK in the cardiovascular system.


