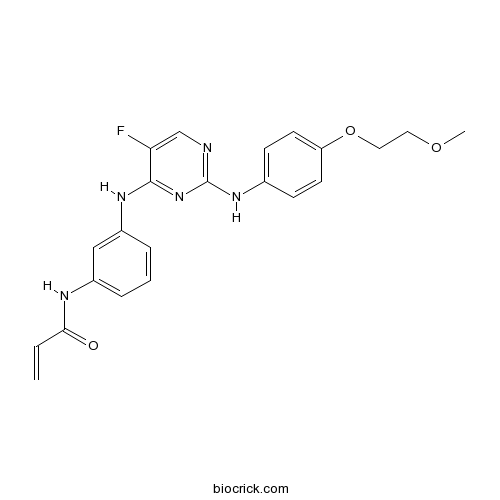
AVL-292Btk inhibitor CAS# 1202757-89-8 |
- RN486
Catalog No.:BCC3921
CAS No.:1242156-23-5
- QL47
Catalog No.:BCC3920
CAS No.:1469988-75-7
- PCI 29732
Catalog No.:BCC4100
CAS No.:330786-25-9
- CGI-1746
Catalog No.:BCC1473
CAS No.:910232-84-7
- PCI-32765 (Ibrutinib)
Catalog No.:BCC1266
CAS No.:936563-96-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1202757-89-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 59174488 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H22FN5O3 | M.Wt | 423.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Spebrutinib; CC-292 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 45 mg/mL (106.27 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | N-[3-[[5-fluoro-2-[4-(2-methoxyethoxy)anilino]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]phenyl]prop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | COCCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)NC2=NC=C(C(=N2)NC3=CC(=CC=C3)NC(=O)C=C)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KXBDTLQSDKGAEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H22FN5O3/c1-3-20(29)25-16-5-4-6-17(13-16)26-21-19(23)14-24-22(28-21)27-15-7-9-18(10-8-15)31-12-11-30-2/h3-10,13-14H,1,11-12H2,2H3,(H,25,29)(H2,24,26,27,28) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AVL-292 is a highly selective, orally active small-molecule inhibitor of Btk with IC50 value of 0.5 nM. | |||||
| Targets | Btk | |||||
| IC50 | 0.5 nM | |||||

AVL-292 Dilution Calculator

AVL-292 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3616 mL | 11.808 mL | 23.6161 mL | 47.2322 mL | 59.0402 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4723 mL | 2.3616 mL | 4.7232 mL | 9.4464 mL | 11.808 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2362 mL | 1.1808 mL | 2.3616 mL | 4.7232 mL | 5.904 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0472 mL | 0.2362 mL | 0.4723 mL | 0.9446 mL | 1.1808 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0236 mL | 0.1181 mL | 0.2362 mL | 0.4723 mL | 0.5904 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CC-292, formerly known as AVL-292, is an orally active, potent irreversible small molecule inhibitor of BTK with IC50 of 0.5 nM and EC50 of 8 nM. [1]
The B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway plays an important role in the fate and function of B cells by modulating cellular selection, maturation, proliferation, and production of antibody.
BTK, which is a tyrosine kinase member of the Tec kinase family, is a unique therapeutic target among kinases in the pathway BCR signaling. Studies showed that loss of gene function mutations of BTK in humans consequently leads to X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA), characterized by a complete lack of B cells, low concentrations of serum Ig, and recurring infections, which implies that BTK is required in the development and immunoglobulin production of B cells. CC-292 inhibits BTK by the formation of a covalent bond with Cys481 residue. [2]
The inhibitory activity of CC-292 has been examined in immunoblot analysis, which showed that CC-292 potently inhibits auto-phosphorylation in human naive primary B cells. Furthermore, CD69 upregulation tested by flow cytometry tracking also exhibited a dose-dependent reduction in CD69 expression with increasing levels of CC-292 in vitro. Covalent probe analysis of human B cells coupled with enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantification methods illustrated 42% BTK occupancy in a 1h incubation with CC-292 of 10 nM. [1, 2]
Studies in vivo for CC-292 has been conducted. CIA model in mice was orally treated with CC-292, which demonstrated a positive correlation between BTK occupancy and inhibition of the disease. In addition, CC-292 was assessed with clinical trials, which showed a T1/2 of 1.9h and suggested efficacy in B-NHL, WM, and CLL patients. [2]
References:
[1].Evans E K, Aslanian S, Karp R, et al. Inhibition of Btk with CC-292 provides early pharmacodynamic assessment of activity in mice and humans[J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 2013, 346(2): 219-228.
[2].Aalipour A, Advani R H. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a promising novel targeted treatment for B cell lymphomas[J]. British journal of haematology, 2013, 163(4): 436-443.
- CGS 21680
Catalog No.:BCC1475
CAS No.:120225-54-9
- 1beta-Hydroxyeuscaphic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3517
CAS No.:120211-98-5
- Tenidap
Catalog No.:BCC7419
CAS No.:120210-48-2
- NMS-P715
Catalog No.:BCC6373
CAS No.:1202055-34-2
- Clopidogrel Related Compound C
Catalog No.:BCN2689
CAS No.:120202-71-3
- Clopidogrel
Catalog No.:BCC2497
CAS No.:120202-66-6
- 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamamide
Catalog No.:BCN6090
CAS No.:1202-41-1
- Cynoglossamine
Catalog No.:BCN1970
CAS No.:120193-39-7
- TCS 2210
Catalog No.:BCC7798
CAS No.:1201916-31-5
- MLN9708
Catalog No.:BCC2091
CAS No.:1201902-80-8
- Vinflunine Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4602
CAS No.:1201898-17-0
- Crotaleschenine
Catalog No.:BCN2077
CAS No.:120154-95-2
- CNX-774
Catalog No.:BCC4394
CAS No.:1202759-32-7
- Salvinolone
Catalog No.:BCN3215
CAS No.:120278-22-0
- 4-Hydroxysapriparaquinone
Catalog No.:BCN4806
CAS No.:120278-25-3
- Dorzolamide
Catalog No.:BCC4287
CAS No.:120279-96-1
- CX-6258
Catalog No.:BCC1504
CAS No.:1202916-90-2
- Citroside A
Catalog No.:BCN7294
CAS No.:120330-44-1
- DASA-58
Catalog No.:BCC6522
CAS No.:1203494-49-8
- Cyclotraxin B
Catalog No.:BCC6357
CAS No.:1203586-72-4
- AS 1949490
Catalog No.:BCC7762
CAS No.:1203680-76-5
- Jionoside B1
Catalog No.:BCN2858
CAS No.:120406-37-3
- Biapenem
Catalog No.:BCC1071
CAS No.:120410-24-4
- AZD1208
Catalog No.:BCC2079
CAS No.:1204144-28-4
Bruton's tyrosine kinase is a potential therapeutic target in prostate cancer.[Pubmed:26383180]
Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(11):1604-15.
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that has mainly been studied in haematopoietic cells. We have investigated whether BTK is a potential therapeutic target in prostate cancer. We find that BTK is expressed in prostate cells, with the alternate BTK-C isoform predominantly expressed in prostate cancer cells and tumors. This isoform is transcribed from an alternative promoter and results in a protein with an amino-terminal extension. Prostate cancer cell lines and prostate tumors express more BTK-C transcript than the malignant NAMALWA B-cell line or human lymphomas. BTK protein expression is also observed in tumor tissue from prostate cancer patients. Down regulation of this protein with RNAi or inhibition with BTK-specific inhibitors, Ibrutinib, AVL-292 or CGI-1746 decrease cell survival and induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Microarray results show that inhibiting BTK under these conditions increases expression of apoptosis related genes, while overexpression of BTK-C is associated with elevated expression of genes with functions related to cell adhesion, cytoskeletal structure and the extracellular matrix. These results are consistent with studies that show that BTK signaling is important for adhesion and migration of B cells and suggest that BTK-C may confer similar properties to prostate cancer cells. Since BTK-C is a survival factor for these cells, it represents both a potential biomarker and novel therapeutic target for prostate cancer.
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Prevent Therapeutic Escape in Breast Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:27256378]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Sep;15(9):2198-208.
We have reported that a novel isoform of BTK (BTK-C) expressed in breast cancer protects these cells from apoptosis. In this study, we show that recently developed inhibitors of BTK, such as ibrutinib (PCI-32765), AVL-292, and CGI-1746, reduce breast cancer cell survival and prevent drug-resistant clones from arising. Ibrutinib treatment impacts HER2(+) breast cancer cell viability at lower concentrations than the established breast cancer therapeutic lapatinib. In addition to inhibiting BTK, ibrutinib, but not AVL-292 and CGI-1746, efficiently blocks the activation of EGFR, HER2, ErbB3, and ErbB4. Consequently, the activation of AKT and ERK signaling pathways are also blocked leading to a G1-S cell-cycle delay and increased apoptosis. Importantly, inhibition of BTK prevents activation of the AKT signaling pathway by NRG or EGF that has been shown to promote growth factor-driven lapatinib resistance in HER2(+) breast cancer cells. HER2(+) breast cancer cell proliferation is blocked by ibrutinib even in the presence of these factors. AVL-292, which has no effect on EGFR family activation, prevents NRG- and EGF-dependent growth factor-driven resistance to lapatinib in HER2(+) breast cancer cells. In vivo, ibrutinib inhibits HER2(+) xenograft tumor growth. Consistent with this, immunofluorescence analysis of xenograft tumors shows that ibrutinib reduces the phosphorylation of HER2, BTK, Akt, and Erk and histone H3 and increases cleaved caspase-3 signals. As BTK-C and HER2 are often coexpressed in human breast cancers, these observations indicate that BTK-C is a potential therapeutic target and that ibrutinib could be an effective drug especially for HER2(+) breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther; 15(9); 2198-208. (c)2016 AACR.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors as potential drugs for B-cell lymphoid malignancies and autoimmune disorders.[Pubmed:22612424]
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012 Jul;21(7):921-47.
INTRODUCTION: In the last few years, several tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been synthesized and become available for preclinical studies and clinical trials. This article summarizes recent achievements in the mechanism of action, pharmacological properties, and clinical activity and toxicity, as well as the emerging role of TKIs in lymphoid malignancies, allergic diseases, and autoimmune disorders. AREAS COVERED: A literature review was conducted of the MEDLINE database PubMed for articles in English. Publications from 2000 through January 2012 were scrutinized. The search terms used were Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitors, PCI-32765, GDC-0834, LFM-A13, AVL-101, AVL-292, spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitors, R343, R406, R112, R788, fostamatinib, BAY-61-3606, C-61, piceatannol, Lyn, imatinib, nilotinib, bafetinib, dasatinib, GDC-0834, PP2, SU6656 in conjunction with lymphoid malignancy, NHL, CLL, autoimmune disease, allergic disease, asthma, and rheumatoid arthritis. Conference proceedings from the previous 5 years of the American Society of Hematology, European Hematology Association, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and ACR/ARHP Annual Scientific Meetings were searched manually. Additional relevant publications were obtained by reviewing the references from the chosen articles. EXPERT OPINION: The use of TKIs, especially inhibitors of Btk, Syk, and Lyn, is a promising new strategy for targeted treatment of B-cell lymphoid malignancies, autoimmune disorders and allergic diseases. However, definitive data from ongoing and future clinical trials will aid in better defining the status of TKIs in the treatment of these disorders.
Discovery of Novel Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitors Bearing a N,9-Diphenyl-9H-purin-2-amine Scaffold.[Pubmed:27994736]
ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016 Sep 21;7(12):1050-1055.
Based on the pyrimidine skeleton of EGFR(T790M) inhibitors, a series of N,9-diphenyl-9H-purin-2-amine derivatives were identified as effective BTK inhibitors. Among these compounds, inhibitors 10d, 10i, and 10j, possessing IC50 values of 0.5, 0.5, and 0.4 nM, displayed anti-BTK kinase activity that was as potent as the reference compounds. In particular, compound 10j suppressed the proliferation of two typical B-cell leukemia cell lines expressing high levels of BTK with concentrations of 7.75 and 12.6 muM. The activity of the subject compound as determined by the CCK-8 method and apoptosis analysis validated that inhibitor 10j is slightly more potent than AVL-292 and ibrutinib. The results of these experimental explorations suggested that 10j could serve as a valuable molecule for control of leukemia pending further developments.
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors in clinical trials.[Pubmed:24357428]
Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2014 Mar;9(1):44-9.
BTK is a cytoplasmic, non-receptor tyrosine kinase that transmits signals from a variety of cell-surface molecules, including the B-cell receptor (BCR) and tissue homing receptors. Genetic BTK deletion causes B-cell immunodeficiency in humans and mice, making this kinase an attractive therapeutic target for B-cell disorders. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765, brand name: Imbruvica) demonstrated high clinical activity in B-cell malignancies, especially in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia (WM). Therefore, ibrutinib was granted a 'breakthrough therapy' designation for these indications and was recently approved for the treatment of relapsed MCL by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Other BTK inhibitors in earlier clinical development include CC-292 (AVL-292), and ONO-4059. In CLL and MCL, ibrutinib characteristically induces redistribution of malignant B cells from tissue sites into the peripheral blood, along with rapid resolution of enlarged lymph nodes and a surge in lymphocytosis. With continuous ibrutinib therapy, growth- and survival-inhibitory activities of ibrutinib result in the normalization of lymphocyte counts and remissions in a majority of patients. This review discusses the clinical advances with BTK inhibitor therapy, as well as its pathophysiological basis, and outlines perspectives for future use of BTK inhibitors.
BTK inhibition is a potent approach to block IgE-mediated histamine release in human basophils.[Pubmed:28328081]
Allergy. 2017 Nov;72(11):1666-1676.
BACKGROUND: Recent data suggest that Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is an emerging therapeutic target in IgE receptor (IgER)-cross-linked basophils. METHODS: We examined the effects of four BTK inhibitors (ibrutinib, dasatinib, AVL-292, and CNX-774) on IgE-dependent activation and histamine release in blood basophils obtained from allergic patients (n=11) and nonallergic donors (n=5). In addition, we examined the effects of these drugs on the growth of the human basophil cell line KU812 and the human mast cell line HMC-1. RESULTS: All four BTK blockers were found to inhibit anti-IgE-induced histamine release from basophils in nonallergic subjects and allergen-induced histamine liberation from basophils in allergic donors. Drug effects on allergen-induced histamine release were dose dependent, with IC50 values ranging between 0.001 and 0.5 mumol/L, and the following rank order of potency: ibrutinib>AVL-292>dasatinib>CNX-774. The basophil-targeting effect of ibrutinib was confirmed by demonstrating that IgE-dependent histamine release in ex vivo blood basophils is largely suppressed in a leukemia patient treated with ibrutinib. Dasatinib and ibrutinib were also found to counteract anti-IgE-induced and allergen-induced upregulation of CD13, CD63, CD164, and CD203c on basophils, whereas AVL-292 and CNX-774 showed no significant effects. Whereas dasatinib and CNX-774 were found to inhibit the growth of HMC-1 cells and KU812 cells, no substantial effects were seen with ibrutinib or AVL-292. CONCLUSIONS: BTK-targeting drugs are potent inhibitors of IgE-dependent histamine release in human basophils. The clinical value of BTK inhibition in the context of allergic diseases remains to be determined.


