Bombinakinin MPotent bradykinin receptor agonist CAS# 509151-65-9 |
- MK-5172 hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1763
CAS No.:1350462-55-3
- Telaprevir (VX-950)
Catalog No.:BCC2107
CAS No.:402957-28-2
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Danoprevir (RG7227)
Catalog No.:BCC2106
CAS No.:850876-88-9
- Narlaprevir
Catalog No.:BCC1785
CAS No.:865466-24-6
- Simeprevir
Catalog No.:BCC1949
CAS No.:923604-59-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 509151-65-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90473828 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C100H159N31O24 | M.Wt | 2179.55 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Maximakinin | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water | ||
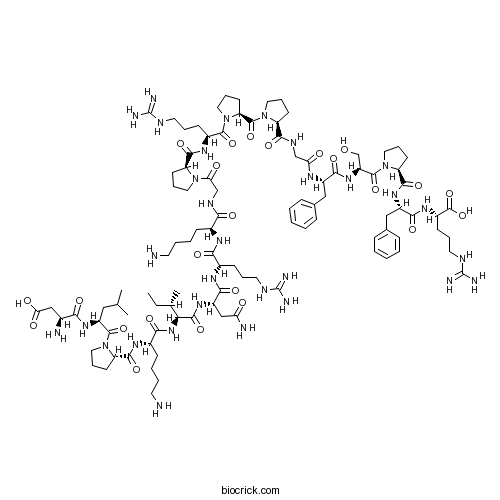
| Sequence | DLPKINRKGPRPPGFSPFR | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NCC(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)N3CCCC3C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CC4=CC=CC=C4)C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)N5CCCC5C(=O)NC(CC6=CC=CC=C6)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C7CCCN7C(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZEEWOWMYALYVCG-UOGIEMGNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C100H159N31O24/c1-5-57(4)80(126-84(141)62(29-13-15-39-102)119-90(147)73-35-21-44-128(73)94(151)69(48-56(2)3)124-81(138)60(103)51-79(136)137)92(149)123-68(52-76(104)133)87(144)118-63(30-16-40-111-98(105)106)83(140)117-61(28-12-14-38-101)82(139)115-54-78(135)127-43-19-34-72(127)89(146)120-64(31-17-41-112-99(107)108)93(150)131-47-23-37-75(131)96(153)130-46-20-33-71(130)88(145)114-53-77(134)116-66(49-58-24-8-6-9-25-58)85(142)125-70(55-132)95(152)129-45-22-36-74(129)91(148)122-67(50-59-26-10-7-11-27-59)86(143)121-65(97(154)155)32-18-42-113-100(109)110/h6-11,24-27,56-57,60-75,80,132H,5,12-23,28-55,101-103H2,1-4H3,(H2,104,133)(H,114,145)(H,115,139)(H,116,134)(H,117,140)(H,118,144)(H,119,147)(H,120,146)(H,121,143)(H,122,148)(H,123,149)(H,124,138)(H,125,142)(H,126,141)(H,136,137)(H,154,155)(H4,105,106,111)(H4,107,108,112)(H4,109,110,113)/t57-,60-,61-,62-,63-,64-,65-,66-,67-,68-,69-,70-,71-,72-,73-,74-,75-,80-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent bradykinin receptor agonist. Highly selective for mammalian arterial smooth muscle bradykinin receptors, displaying ~ 50-fold greater potency than bradykinin. Elicits dose-dependent contractile effects in smooth muscle of guinea pig ileum (EC50 = 4.0 nM). |

Bombinakinin M Dilution Calculator

Bombinakinin M Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Boc-D-Arg(NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2610
CAS No.:50913-12-7
- 2-Amino-3,5-dibromobenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC8523
CAS No.:50910-55-9
- IRAK-1-4 Inhibitor I
Catalog No.:BCC1659
CAS No.:509093-47-4
- 1beta-Hydroxytorilin
Catalog No.:BCN7095
CAS No.:509078-16-4
- Taiwanhomoflavone B
Catalog No.:BCN5624
CAS No.:509077-91-2
- Nemorensine
Catalog No.:BCN2099
CAS No.:50906-96-2
- Toxyloxanthone D
Catalog No.:BCN3070
CAS No.:50906-62-2
- Arteannuin B
Catalog No.:BCN5623
CAS No.:50906-56-4
- Mitraphylline
Catalog No.:BCC8213
CAS No.:509-80-8
- Strychnine phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC8257
CAS No.:509-42-2
- Napellonine
Catalog No.:BCN2536
CAS No.:509-24-0
- Aconine
Catalog No.:BCN2394
CAS No.:509-20-6
- Mizoribine
Catalog No.:BCC4454
CAS No.:50924-49-7
- Verminoside
Catalog No.:BCN5625
CAS No.:50932-19-9
- Carminomycin
Catalog No.:BCC6379
CAS No.:50935-04-1, 39472-31-6
- Anacrotine
Catalog No.:BCN2057
CAS No.:5096-49-1
- Crotanecine
Catalog No.:BCN1963
CAS No.:5096-50-4
- Canadine
Catalog No.:BCN5626
CAS No.:5096-57-1
- N-Methylcoclaurine
Catalog No.:BCN7079
CAS No.:5096-70-8
- 16-Methoxystrychnidin-10-One
Catalog No.:BCN8472
CAS No.:5096-72-0
- 7ACC1
Catalog No.:BCC5553
CAS No.:50995-74-9
- Pronethalol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5678
CAS No.:51-02-5
- Procaine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5072
CAS No.:51-05-8
- Benzimidazole
Catalog No.:BCC8847
CAS No.:51-17-2
Bombinakinin M gene associated peptide, a novel bioactive peptide from skin secretions of the toad Bombina maxima.[Pubmed:12668203]
Peptides. 2003 Feb;24(2):199-204.
A novel 28-amino acid peptide, termed bombinakinin-GAP, was purified and characterized from skin secretions of the toad Bombina maxima. Its primary structure was established as DMYEIKQYKTAHGRPPICAPGEQCPIWV-NH(2), in which two cysteines form a disulfide bond. A FASTA search of SWISS-PROT databank detected a 32% sequence identity between the sequences of the peptide and a segment of rat cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART). Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of the peptide induced a significant decrease in food intake in rats, suggesting that it played a role in the control of feeding by brain. Analysis of its cDNA structure revealed that this peptide is coexpressed with Bombinakinin M, a bradykinin-related peptide from the same toad. Bombinakinin-GAP appears to be the first example of a novel class of bioactive peptides from amphibian skin, which may be implicated in feeding behavior.
Cloning of bradykinin precursor cDNAs from skin of Bombina maxima reveals novel bombinakinin M antagonists and a bradykinin potential peptide.[Pubmed:15680489]
Regul Pept. 2005 Apr 15;127(1-3):207-15.
Bombinakinin M (DLPKINRKGP-bradykinin) is a bradykinin-related peptide purified from skin secretions of the frog Bombina maxima. As previously reported, its biosynthesis is characterized by a tandem repeats with various copy numbers of the peptide and sometimes co-expressed with other structure-function distinguishable peptides. At present study, two novel cDNAs encoding Bombinakinin M and its variants were cloned from a cDNA library from the skin of the frog. The encoded two precursor proteins are common in that each contains three repeats of a novel 16-amino acid peptide unit and one copy of kinestatin at their N- and C-terminal parts, respectively. They differ in that the first precursor contains two copies of Bombinakinin M and the second one contains one copy of a novel Bombinakinin M variant. Bombinakinin M was found to elicit concentration-dependent contractile effects on guinea pig ileum, with an EC50 value of 4 nM that is four times higher than that of bradykinin (1 nM). Interestingly, the synthetic peptide (DYTIRTRLH-amide), as deduced from the 16-amino acid peptide repeats in the newly cloned cDNAs, possessed weak inhibitory activity on the contractile effects of Bombinakinin M, but not on that of bradykinin. Furthermore, the newly identified Bombinakinin M variant (DLSKMSFLHG-Ile1-bradykinin), did not show contractile activity on guinea pig ileum, but showed potentiation effect on the myotropic activity of bradykinin. In a molar ratio of 1:58, it augmented the activity of bradykinin up to two-fold.


