C-VeratroylglycolCAS# 168293-10-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 168293-10-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15765124 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H12O5 | M.Wt | 212.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
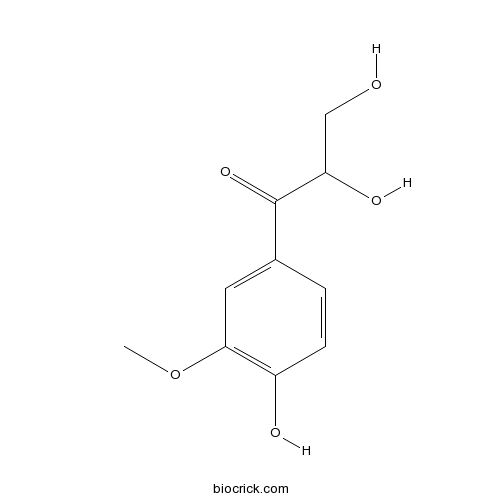
| Chemical Name | 2,3-dihydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propan-1-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C(=O)C(CO)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UTXNRISXYKZJTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H12O5/c1-15-9-4-6(2-3-7(9)12)10(14)8(13)5-11/h2-4,8,11-13H,5H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. C-Veratroylglycol shows antioxidant activity (IC50<100 uM). |

C-Veratroylglycol Dilution Calculator

C-Veratroylglycol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.7125 mL | 23.5627 mL | 47.1254 mL | 94.2507 mL | 117.8134 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9425 mL | 4.7125 mL | 9.4251 mL | 18.8501 mL | 23.5627 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4713 mL | 2.3563 mL | 4.7125 mL | 9.4251 mL | 11.7813 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0943 mL | 0.4713 mL | 0.9425 mL | 1.885 mL | 2.3563 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0471 mL | 0.2356 mL | 0.4713 mL | 0.9425 mL | 1.1781 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3,5-Dimethoxy-3'-hydroxybibenzyl
Catalog No.:BCN8112
CAS No.:168281-05-8
- Rimonabant
Catalog No.:BCC4414
CAS No.:168273-06-1
- Evofolin B
Catalog No.:BCN1101
CAS No.:168254-96-4
- Wilforol C
Catalog No.:BCN1100
CAS No.:168254-95-3
- Nortenuazonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1847
CAS No.:16820-44-3
- Agitoxin 2
Catalog No.:BCC8026
CAS No.:168147-41-9
- Taxin B
Catalog No.:BCN6945
CAS No.:168109-52-2
- Mearnsetin
Catalog No.:BCN6560
CAS No.:16805-10-0
- cis-Miyabenol C
Catalog No.:BCN3347
CAS No.:168037-22-7
- Boc-D-Threoninol(Bzl)
Catalog No.:BCC2703
CAS No.:168034-31-9
- NXY-059
Catalog No.:BCC4955
CAS No.:168021-79-2
- Triptonine B
Catalog No.:BCN3095
CAS No.:168009-85-6
- 3-O-Acetyl-16 alpha-hydroxytrametenolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1532
CAS No.:168293-13-8
- 3-O-Acetyl-16 alpha-hydroxydehydrotrametenolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1531
CAS No.:168293-14-9
- 3-Epidehydropachymic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3644
CAS No.:168293-15-0
- Asiaticoside
Catalog No.:BCN1011
CAS No.:16830-15-2
- Oxymatrine
Catalog No.:BCN1103
CAS No.:16837-52-8
- Tacrine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6869
CAS No.:1684-40-8
- Compound 401
Catalog No.:BCC7622
CAS No.:168425-64-7
- Rhodiocyanoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7852
CAS No.:168433-86-1
- Epifriedelanol
Catalog No.:BCN1104
CAS No.:16844-71-6
- SHU 9119
Catalog No.:BCC6019
CAS No.:168482-23-3
- Z-D-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2732
CAS No.:1685-33-2
- Dehydrogeijerin
Catalog No.:BCN7531
CAS No.:16850-91-2
Hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) Shells Extract: Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Effect and Cytotoxic Activity on Human Cancer Cell Lines.[Pubmed:28208804]
Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 13;18(2). pii: ijms18020392.
Hazelnut shells, a by-product of the kernel industry processing, are reported to contain high amount of polyphenols. However, studies on the chemical composition and potential effects on human health are lacking. A methanol hazelnut shells extract was prepared and dried. Our investigation allowed the isolation and characterization of different classes of phenolic compounds, including neolignans, and a diarylheptanoid, which contribute to a high total polyphenol content (193.8 +/- 3.6 mg of gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g of extract). Neolignans, lawsonicin and cedrusin, a cyclic diarylheptanoid, carpinontriol B, and two phenol derivatives, C-Veratroylglycol, and beta-hydroxypropiovanillone, were the main components of the extract (0.71%-2.93%, w/w). The biological assays suggested that the extract could be useful as a functional ingredient in food technology and pharmaceutical industry showing an in vitro scavenging activity against the radical 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH) (EC50 = 31.7 mug/mL with respect to alpha-tocopherol EC50 = 10.1 mug/mL), and an inhibitory effect on the growth of human cancer cell lines A375, SK-Mel-28 and HeLa (IC50 = 584, 459, and 526 mug/mL, respectively). The expression of cleaved forms of caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) suggested that the extract induced apoptosis through caspase-3 activation in both human malignant melanoma (SK-Mel-28) and human cervical cancer (HeLa) cell lines. The cytotoxic activity relies on the presence of the neolignans (balanophonin), and phenol derivatives (gallic acid), showing a pro-apoptotic effect on the tested cell lines, and the neolignan, cedrusin, with a cytotoxic effect on A375 and HeLa cells.
Maple syrup phytochemicals include lignans, coumarins, a stilbene, and other previously unreported antioxidant phenolic compounds.[Pubmed:21033720]
J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Nov 24;58(22):11673-9.
Twenty-three phenolic compounds were isolated from a butanol extract of Canadian maple syrup (MS-BuOH) using chromatographic methods. The compounds were identified from their nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectral data as 7 lignans [lyoniresinol (1), secoisolariciresinol (2), dehydroconiferyl alcohol (3), 5'-methoxy-dehydroconiferyl alcohol (4), erythro-guaiacylglycerol-beta-O-4'-coniferyl alcohol (5), erythro-guaiacylglycerol-beta-O-4'-dihydroconiferyl alcohol (6), and [3-[4-[(6-deoxy-alpha-l-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-3-methoxyphenyl]methyl]-5-(3,4-dimeth oxyphenyl)dihydro-3-hydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)-2(3H)-furanone (7)], 2 coumarins [scopoletin (8) and fraxetin (9)], a stilbene [(E)-3,3'-dimethoxy-4,4'-dihydroxystilbene (10)], and 13 phenolic derivatives [2-hydroxy-3',4'-dihydroxyacetophenone (11), 1-(2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-methylphenyl)ethanone (12), 2,4,5-trihydroxyacetophenone (13), catechaldehyde (14), vanillin (15), syringaldehyde (16), gallic acid (17), trimethyl gallic acid methyl ester (18), syringic acid (19), syringenin (20), (E)-coniferol (21), C-Veratroylglycol (22), and catechol (23)]. The antioxidant activities of MS-BuOH (IC50>1000 mug/mL), pure compounds, vitamin C (IC50=58 muM), and a synthetic commercial antioxidant, butylated hydroxytoluene (IC50=2651 muM), were evaluated in the diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay. Among the isolates, the phenolic derivatives and coumarins showed superior antioxidant activity (IC50<100 muM) compared to the lignans and stilbene (IC50>100 muM). Also, this is the first report of 16 of these 23 phenolics, that is, compounds 1, 2, 4-14, 18, 20, and 22, in maple syrup.
[Chemical constituents of Osmanthus fragrans fruits].[Pubmed:24791540]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Dec;38(24):4329-34.
By Silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 and other materials for isolation and purification and by physicochemical methods and spectral analysis for structural identification, 23 compounds were isolated and identified from ethyl acetate portion of alcohol extract solution of Osmanthus fragrans fruits. Their structures were identified as nicotinamide (1), D-allitol (2), 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furancarboxaldehyde (3), acetyloleanolic acid (4), benzoic acid (5), ergosta-7,22-dien-3-one (6), beta-sitosterol (7), borreriagenin (8), cerevistero (9), C-Veratroylglycol (10), methyl-2-O-beta-glucopyranosylbenzoate (11), 3', 7-dihydroxy-4'-methoxyisoflavon (12), umbelliferone (13), caffeic acid methyl ester (14), oleanolic acid (15), (-) -chicanine (16), dillapiol (17), 3beta,5alpha, 9alpha-trihydroxyergosta-7-22-dien-6-one (18), 2alpha-hydroxy-oleanolic acid (19), betulinic acid (20), betulin (21), 3, 3'-bisdemethylpinoresinol (22), and lupeol (23). All compounds were isolated from the osmanthus fruit for the first time. Except for compounds 4, 7, 15, 19, 23, the rest ones were isolated from the this plant for the first time.


