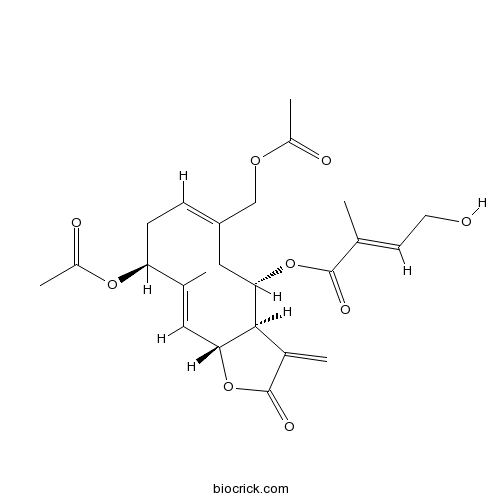
Eupalinolide BCAS# 877822-40-7 |
- Eupalinolide I
Catalog No.:BCN7367
CAS No.:1402067-84-8
- Eupalinolide A
Catalog No.:BCN2524
CAS No.:877822-41-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 877822-40-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 102004890 | Appearance | Cryst. |
| Formula | C24H30O9 | M.Wt | 462.49 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(3aR,4S,6E,9S,10E,11aR)-9-acetyloxy-6-(acetyloxymethyl)-10-methyl-3-methylidene-2-oxo-3a,4,5,8,9,11a-hexahydrocyclodeca[b]furan-4-yl] (E)-4-hydroxy-2-methylbut-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC2C(C(CC(=CCC1OC(=O)C)COC(=O)C)OC(=O)C(=CCO)C)C(=C)C(=O)O2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HPWMABTYJYZFLK-GOMZETCQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H30O9/c1-13(8-9-25)23(28)32-21-11-18(12-30-16(4)26)6-7-19(31-17(5)27)14(2)10-20-22(21)15(3)24(29)33-20/h6,8,10,19-22,25H,3,7,9,11-12H2,1-2,4-5H3/b13-8+,14-10+,18-6+/t19-,20+,21-,22-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Eupalinolide B demonstrates potent cytotoxicity against A-549, BGC-823, SMMC-7721, and HL-60 tumour cell lines.Eupalinolide B and Eupalinolide A induce the expression of HSP70 via the activation of HSF1 by inhibiting the interaction between HSF1 and HSP90, they could be beneficial for use in cosmetics and medicines as a consequence of their inhibitory action on UV-induced skin damage and melanin production. |
| Targets | HSP (e.g. HSP90) |
| In vitro | Pharmacokinetics of eupalinolide A, eupalinolide B and hyperoside from Eupatorium lindleyanum in rats by LC/MS/MS.[Pubmed: 26011510]J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Jul 15;995-996:1-7.A simple, selective, and sensitive LC/MS/MS method was developed and validated for simultaneous determination of eupalinolide A, Eupalinolide B, and hyperoside in rat plasma. Plasma samples were processed by protein precipitation with acetonitrile. |
| In vivo | Purification and characterization of HSP-inducers from Eupatorium lindleyanum.[Pubmed: 22245466]Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Apr 1;83(7):909-22.The expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs), particularly HSP70, provides resistance to stressors. We recently reported that ultraviolet (UV)-induced melanin production and skin damage were suppressed in transgenic mice expressing HSP70 and that an extract of Eupatorium lindleyanum induces the expression of HSP70 in cells. |
| Cell Research | Cytotoxic sesquiterpene lactones from Eupatorium lindleyanum.[Pubmed: 17613619 ]J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2007 Apr-Aug;9(3-5):339-45.
|

Eupalinolide B Dilution Calculator

Eupalinolide B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1622 mL | 10.811 mL | 21.6221 mL | 43.2442 mL | 54.0552 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4324 mL | 2.1622 mL | 4.3244 mL | 8.6488 mL | 10.811 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2162 mL | 1.0811 mL | 2.1622 mL | 4.3244 mL | 5.4055 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0432 mL | 0.2162 mL | 0.4324 mL | 0.8649 mL | 1.0811 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1081 mL | 0.2162 mL | 0.4324 mL | 0.5406 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- ML 221
Catalog No.:BCC6278
CAS No.:877636-42-5
- Tandospirone
Catalog No.:BCC4208
CAS No.:87760-53-0
- Bryostatin 2
Catalog No.:BCC5619
CAS No.:87745-28-6
- H-Tyrosinol
Catalog No.:BCC2697
CAS No.:87745-27-5
- (R)-Crizotinib
Catalog No.:BCC1284
CAS No.:877399-52-5
- GPBAR-A
Catalog No.:BCC6201
CAS No.:877052-79-4
- Alismoxide
Catalog No.:BCN1265
CAS No.:87701-68-6
- 3-(1-Piperazinyl)-1,2-benzisothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8585
CAS No.:87691-87-0
- Isomagnolol
Catalog No.:BCN8325
CAS No.:87688-90-2
- Pentoxyresorufin
Catalog No.:BCC6297
CAS No.:87687-03-4
- 6-Hydroxyrubiadin
Catalog No.:BCN4425
CAS No.:87686-86-0
- Trandolapril
Catalog No.:BCC5275
CAS No.:87679-37-6
- Eupalinolide A
Catalog No.:BCN2524
CAS No.:877822-41-8
- erythro-Guaiacylglycerol beta-sinapyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6605
CAS No.:877875-96-2
- TW-37
Catalog No.:BCC2257
CAS No.:877877-35-5
- 6beta-Hydroxyipolamiide
Catalog No.:BCN4426
CAS No.:87797-84-0
- Glucagon-like peptide 1 (1-37) (human, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5827
CAS No.:87805-34-3
- S1RA
Catalog No.:BCC4189
CAS No.:878141-96-9
- Alismol
Catalog No.:BCN4427
CAS No.:87827-55-2
- Walrycin B
Catalog No.:BCC5156
CAS No.:878419-78-4
- Isosalviamine A
Catalog No.:BCN3553
CAS No.:878475-29-7
- Isosalviamine B
Catalog No.:BCN3554
CAS No.:878475-30-0
- JNJ 303
Catalog No.:BCC7806
CAS No.:878489-28-2
- WRW4
Catalog No.:BCC5893
CAS No.:878557-55-2
Pharmacokinetics of eupalinolide A, eupalinolide B and hyperoside from Eupatorium lindleyanum in rats by LC/MS/MS.[Pubmed:26011510]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Jul 15;995-996:1-7.
A simple, selective, and sensitive LC/MS/MS method was developed and validated for simultaneous determination of eupalinolide A, Eupalinolide B, and hyperoside in rat plasma. Plasma samples were processed by protein precipitation with acetonitrile. The three analytes, together with internal standard (IS, lysionotin), were separated on a Venusil MP-C18 column (50mmx2.1mm, 3mum) using a mobile phase of methanol and 10mM ammonium acetate (45:55, v/v) with isocratic elution. Mass spectrometric detection was performed by multiple-reaction monitoring mode via electrospray ionization source. Linear calibration curves were obtained for the following concentration range: 1.28-640ng/mL for EA; 1.98-990ng/mL for EB; and 2.00-1000ng/mL for HYP. The intra- and inter-day precision was less than 10.25%, and the accuracy was between 89.16% and 110.63%. The extraction recovery of the analytes and IS from rat plasma was above 88.75%. The validated method has been successfully applied to pharmacokinetic studies of the three analytes following intragastric administration of Eupatorium lindleyanum extract at a single dose of 100, 250, and 625mg/kg to Sprague-Dawley rats, respectively. The pharmacokinetic results may help to better understand the pharmacological actions of the herb E. lindleyanum.
Cytotoxic sesquiterpene lactones from Eupatorium lindleyanum.[Pubmed:17613619]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2007 Apr-Aug;9(3-5):339-45.
Three new germacrane sesquiterpenes, eupalinolides C-E (1-3), along with three known germacrane sesquiterpenes, eupalinolide A (4), Eupalinolide B (5), and 3beta-acetoxy-8beta-(4'-hydroxytigloyloxy)-14-hydroxycostunolide (6), were isolated from Eupatorium lindleyanum. They were tested for cytotoxicity against A-549, BGC-823, SMMC-7721, and HL-60 tumour cell lines. The results showed that these compounds demonstrated potent cytotoxicity. The structures of the compounds were elucidated by means of (1)H and (13)C NMR spectroscopic analysis, including 2D NMR experiments.
Purification and characterization of HSP-inducers from Eupatorium lindleyanum.[Pubmed:22245466]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Apr 1;83(7):909-22.
The expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs), particularly HSP70, provides resistance to stressors. We recently reported that ultraviolet (UV)-induced melanin production and skin damage were suppressed in transgenic mice expressing HSP70 and that an extract of Eupatorium lindleyanum induces the expression of HSP70 in cells. Here we report the purification of eupalinolide A and B (EA and EB) from E. lindleyanum, and describe their actions as HSP-inducers. EA and EB both induced the expression of HSP70 in cells at concentrations that did not significantly affect cell viability. Treatment of cells with EA or EB activated heat shock factor 1 (HSF1), while the artificial suppression of HSF1 expression diminished the EA- or EB-mediated induction of HSP70 expression. Furthermore, EB inhibited the interaction between HSF1 and HSP90, which is known to inhibit the activity of HSF1. These findings suggest that EA and EB induce the expression of HSP70 via the activation of HSF1 by inhibiting the interaction between HSF1 and HSP90. EA and EB both induced the expression of HSP70 synergistically with other stressors. Furthermore, pre-treatment of cells with EA or EB suppressed melanin production and stressor-induced apoptosis. These effects were suppressed by the artificial suppression of HSP70 expression. In vivo, the percutaneous administration of EB induced the expression of HSP70 and suppressed UVB radiation-induced damage, inflammatory responses and melanin production in the skin. These results suggest that EA and EB could be beneficial for use in cosmetics and medicines as a consequence of their inhibitory action on UV-induced skin damage and melanin production.


