Glucagon-like peptide 1 (1-37) (human, rat)Endogenous pancreatic peptide CAS# 87805-34-3 |
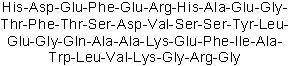
- Repaglinide
Catalog No.:BCC2504
CAS No.:135062-02-1
- Dronedarone
Catalog No.:BCN2176
CAS No.:141626-36-0
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
- TRAM-34
Catalog No.:BCC1122
CAS No.:289905-88-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 87805-34-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16131070 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C186H275N51O59 | M.Wt | 4169.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | GLP-1 (1-37) amide | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 5 mg/ml in water | ||
| Sequence | HDEFERHAEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAKEFIA | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CC6=CN=CN6)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC7=CC=CC=C7)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC8=CN=CN8)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UKVFVQPAANCXIL-FJVFSOETSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C186H275N51O59/c1-17-94(10)149(182(294)209-98(14)155(267)220-128(73-105-78-199-111-42-28-27-41-109(105)111)171(283)223-123(68-91(4)5)173(285)234-147(92(6)7)180(292)219-113(43-29-31-63-187)158(270)200-81-136(245)210-112(45-33-65-197-185(191)192)157(269)203-84-146(262)263)236-174(286)126(70-102-37-23-19-24-38-102)225-165(277)120(55-61-142(254)255)216-162(274)114(44-30-32-64-188)212-153(265)96(12)206-152(264)95(11)207-161(273)118(51-57-135(190)244)211-137(246)82-201-160(272)117(53-59-140(250)251)215-168(280)122(67-90(2)3)222-170(282)125(72-104-47-49-108(243)50-48-104)226-177(289)132(85-238)230-179(291)134(87-240)231-181(293)148(93(8)9)235-176(288)131(77-145(260)261)228-178(290)133(86-239)232-184(296)151(100(16)242)237-175(287)127(71-103-39-25-20-26-40-103)229-183(295)150(99(15)241)233-138(247)83-202-159(271)116(52-58-139(248)249)213-154(266)97(13)208-167(279)129(75-107-80-196-89-205-107)227-163(275)115(46-34-66-198-186(193)194)214-164(276)119(54-60-141(252)253)217-169(281)124(69-101-35-21-18-22-36-101)224-166(278)121(56-62-143(256)257)218-172(284)130(76-144(258)259)221-156(268)110(189)74-106-79-195-88-204-106/h18-28,35-42,47-50,78-80,88-100,110,112-134,147-151,199,238-243H,17,29-34,43-46,51-77,81-87,187-189H2,1-16H3,(H2,190,244)(H,195,204)(H,196,205)(H,200,270)(H,201,272)(H,202,271)(H,203,269)(H,206,264)(H,207,273)(H,208,279)(H,209,294)(H,210,245)(H,211,246)(H,212,265)(H,213,266)(H,214,276)(H,215,280)(H,216,274)(H,217,281)(H,218,284)(H,219,292)(H,220,267)(H,221,268)(H,222,282)(H,223,283)(H,224,278)(H,225,277)(H,226,289)(H,227,275)(H,228,290)(H,229,295)(H,230,291)(H,231,293)(H,232,296)(H,233,247)(H,234,285)(H,235,288)(H,236,286)(H,237,287)(H,248,249)(H,250,251)(H,252,253)(H,254,255)(H,256,257)(H,258,259)(H,260,261)(H,262,263)(H4,191,192,197)(H4,193,194,198)/t94-,95-,96-,97-,98-,99+,100+,110-,112-,113-,114-,115-,116-,117-,118-,119-,120-,121-,122-,123-,124-,125-,126-,127-,128-,129-,130-,131-,132-,133-,134-,147-,148-,149-,150-,151-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Pancreatic hormone synthesized by post-translational processing of proglucagon. Unlike truncated forms of GLP-1, it has no effect on food intake in rats and does not enhance pancreatic insulin secretion. However it induces insulin expression in intestinal epithelial cells, which can restore glucose homeostasis when implanted into diabetic mice. |

Glucagon-like peptide 1 (1-37) (human, rat) Dilution Calculator

Glucagon-like peptide 1 (1-37) (human, rat) Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 6beta-Hydroxyipolamiide
Catalog No.:BCN4426
CAS No.:87797-84-0
- TW-37
Catalog No.:BCC2257
CAS No.:877877-35-5
- erythro-Guaiacylglycerol beta-sinapyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6605
CAS No.:877875-96-2
- Eupalinolide A
Catalog No.:BCN2524
CAS No.:877822-41-8
- Eupalinolide B
Catalog No.:BCN2525
CAS No.:877822-40-7
- ML 221
Catalog No.:BCC6278
CAS No.:877636-42-5
- Tandospirone
Catalog No.:BCC4208
CAS No.:87760-53-0
- Bryostatin 2
Catalog No.:BCC5619
CAS No.:87745-28-6
- H-Tyrosinol
Catalog No.:BCC2697
CAS No.:87745-27-5
- (R)-Crizotinib
Catalog No.:BCC1284
CAS No.:877399-52-5
- GPBAR-A
Catalog No.:BCC6201
CAS No.:877052-79-4
- Alismoxide
Catalog No.:BCN1265
CAS No.:87701-68-6
- S1RA
Catalog No.:BCC4189
CAS No.:878141-96-9
- Alismol
Catalog No.:BCN4427
CAS No.:87827-55-2
- Walrycin B
Catalog No.:BCC5156
CAS No.:878419-78-4
- Isosalviamine A
Catalog No.:BCN3553
CAS No.:878475-29-7
- Isosalviamine B
Catalog No.:BCN3554
CAS No.:878475-30-0
- JNJ 303
Catalog No.:BCC7806
CAS No.:878489-28-2
- WRW4
Catalog No.:BCC5893
CAS No.:878557-55-2
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
- Lesinurad
Catalog No.:BCC1699
CAS No.:878672-00-5
- AZ 628
Catalog No.:BCC3730
CAS No.:878739-06-1
- 15-deoxy-Δ-12,14-Prostaglandin J2
Catalog No.:BCC7321
CAS No.:87893-55-8
- GDC-0449 (Vismodegib)
Catalog No.:BCC1285
CAS No.:879085-55-9
Colocalization of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors, glucose transporter GLUT-2, and glucokinase mRNAs in rat hypothalamic cells: evidence for a role of GLP-1 receptor agonists as an inhibitory signal for food and water intake.[Pubmed:8863504]
J Neurochem. 1996 Nov;67(5):1982-91.
This study was designed to determine the possible role of brain glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors in feeding behavior. In situ hybridization showed colocalization of the mRNAs for GLP-1 receptors, glucokinase, and GLUT-2 in the third ventricle wall and adjacent arcuate nucleus, median eminence, and supraoptic nucleus. These brain areas are considered to contain glucose-sensitive neurons mediating feeding behavior. Because GLP-1 receptors, GLUT-2, and glucokinase are proteins involved in the multistep process of glucose sensing in pancreatic beta cells, the colocalization of specific GLP-1 receptors and glucose sensing-related proteins in hypothalamic neurons supports a role of this peptide in the hypothalamic regulation of macronutrient and water intake. This hypothesis was confirmed by analyzing the effects of both systemic and central administration of GLP-1 receptor ligands. Acute or subchronic intraperitoneal administration of GLP-1 (7-36) amide did not modify food and water intake, although a dose-dependent loss of body weight gain was observed 24 h after acute administration of the higher dose of the peptide. By contrast, the intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of GLP-1 (7-36) amide produced a biphasic effect on food intake characterized by an increase in the amount of food intake after acute i.c.v. delivery of 100 ng of the peptide. There was a marked reduction of food ingestion with the 1,000 and 2,000 ng doses of the peptide, which also produced a significant decrease of water intake. These effects seemed to be specific because i.c.v. administration of GLP-1 (1-37), a peptide with lower biological activity than GLP-1 (7-36) amide, did not change feeding behavior in food-deprived animals. Exendin-4, when given by i.c.v. administration in a broad range of doses (0.2, 1, 5, 25, 100, and 500 ng), proved to be a potent agonist of GLP-1 (7-36) amide. It decreased, in a dose-dependent manner, both food and water intake, starting at the dose of 25 ng per injection. Pretreatment with an i.c.v. dose of a GLP-1 receptor antagonist [exendin (9-39); 2,500 ng] reversed the inhibitory effects of GLP-1 (7-36) amide (1,000 ng dose) and exendin-4 (25 ng dose) on food and water ingestion. These findings suggest that GLP-1 (7-36) amide may modulate both food and drink intake in the rat through a central mechanism.


