S1RAσ1R antagonist CAS# 878141-96-9 |
- Sodium Channel inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1959
CAS No.:1198117-23-5
- Nav1.7 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4191
CAS No.:1355631-24-1
- Riluzole
Catalog No.:BCC3849
CAS No.:1744-22-5
- Flecainide acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1578
CAS No.:54143-56-5
- Dibucaine (Cinchocaine) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3760
CAS No.:61-12-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 878141-96-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44247568 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H23N3O2 | M.Wt | 337.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | E-52862 | ||
| Solubility | >10.35mg/mL in DMSO | ||
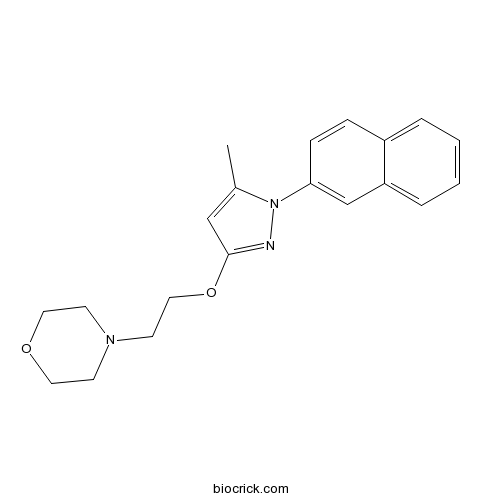
| Chemical Name | 4-[2-(5-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpyrazol-3-yl)oxyethyl]morpholine | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=NN1C2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C=C2)OCCN4CCOCC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DGPGXHRHNRYVDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H23N3O2/c1-16-14-20(25-13-10-22-8-11-24-12-9-22)21-23(16)19-7-6-17-4-2-3-5-18(17)15-19/h2-7,14-15H,8-13H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | S1RA(E-52862) is a potent and selective sigma-1 receptor(σ1R, Ki=17 nM) antagonist, showed good selectivity against σ2R (Ki > 1000 nM).
IC50 value: 17 nM (Ki) [1]
Target: σ1R
in vitro: S1RA behaved as a highly selective σ1 receptor antagonist. It showed high affinity for human (Ki= 17 nM) and guinea pig (Ki= 23.5 nM) σ1 receptors but no significant affinity for the σ2 receptors (Ki > 1000 nM for guinea pig and rat σ2 receptors). Moderate affinity (Ki= 328 nM) and antagonistic activity, with very low potency (IC50= 4700 nM) was found at the human 5-HT2B receptor. S1RA showed no significant affinity (Ki > 1 μM or % inhibition at 1 μM < 50%) for other additional 170 targets (receptors, transporters, ion channels and enzymes) [2].
in vivo: Control (non-operated) and nerve-injured mice received a single or repeated (twice daily for 12 days) i.p. administration of S1RA at 25 mg·kg?1, the same dose used for the assessment of behavioural hypersensitivity in the chronic treatment study. Acute treatment was given on day 12 post-surgery and repeated treatment with S1RA started the day of surgery, as in the behavioural studies [2]. Intrathecal pre-treatment with idazoxan prevented the systemic S1RA antinociceptive effect, suggesting that the S1RA antinociception depends on the activation of spinal α2 -adrenoceptors which, in turn, could induce an inhibition of formalin-evoked glutamate release. When administered locally, intrathecal S1RA inhibited only the flinching behavior, whereas intracerebroventricularly or intraplantarly injected also attenuated the lifting/licking behavior [3]. References: | |||||

S1RA Dilution Calculator

S1RA Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9637 mL | 14.8183 mL | 29.6367 mL | 59.2733 mL | 74.0916 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5927 mL | 2.9637 mL | 5.9273 mL | 11.8547 mL | 14.8183 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2964 mL | 1.4818 mL | 2.9637 mL | 5.9273 mL | 7.4092 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0593 mL | 0.2964 mL | 0.5927 mL | 1.1855 mL | 1.4818 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0296 mL | 0.1482 mL | 0.2964 mL | 0.5927 mL | 0.7409 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
S1RA is a potent and selective antagonist of σ1 receptor (σ1R) with Ki value of 17nM [1].
S1RA is the first σ1 receptor antagonist with potent antinociceptive activities in various pain models. In the binding assay, S1RA shows good affinity to human σ1 receptor transfected in HEK293 membranes with Ki value of 17nM. The Ki value for guinea pig brain membrane σ1 receptor is higher than 1μM. S1RA also shows no significant affinity to another 170 molecular targets including receptors, ion channels and enzymes [1, 2].
In the mouse tests, S1RA exhibits potent analgesic effects on capsaicin-induced mechanical hypersensitivity and formalin-induced pain. Besides that, S1RA inhibits both mechanical allodynia and thermal hypersensitivity with ED50 values of 23.4mg/kg and 18.8mg/kg in the partial sciatic nerve ligation model in mice [1].
References:
[1] Díaz J L, Cuberes R, Berrocal J, et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of the 1-Arylpyrazole Class of σ1 Receptor Antagonists: Identification of 4-{2-[5-Methyl-1-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1 H-pyrazol-3-yloxy] ethyl} morpholine (S1RA, E-52862). Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2012, 55(19): 8211-8224.
[2] Wunsch B. The σ1 Receptor Antagonist S1RA Is a Promising Candidate for the Treatment of Neurogenic PainJ. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2012, 55(19): 8209-8210.
- Glucagon-like peptide 1 (1-37) (human, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5827
CAS No.:87805-34-3
- 6beta-Hydroxyipolamiide
Catalog No.:BCN4426
CAS No.:87797-84-0
- TW-37
Catalog No.:BCC2257
CAS No.:877877-35-5
- erythro-Guaiacylglycerol beta-sinapyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6605
CAS No.:877875-96-2
- Eupalinolide A
Catalog No.:BCN2524
CAS No.:877822-41-8
- Eupalinolide B
Catalog No.:BCN2525
CAS No.:877822-40-7
- ML 221
Catalog No.:BCC6278
CAS No.:877636-42-5
- Tandospirone
Catalog No.:BCC4208
CAS No.:87760-53-0
- Bryostatin 2
Catalog No.:BCC5619
CAS No.:87745-28-6
- H-Tyrosinol
Catalog No.:BCC2697
CAS No.:87745-27-5
- (R)-Crizotinib
Catalog No.:BCC1284
CAS No.:877399-52-5
- GPBAR-A
Catalog No.:BCC6201
CAS No.:877052-79-4
- Alismol
Catalog No.:BCN4427
CAS No.:87827-55-2
- Walrycin B
Catalog No.:BCC5156
CAS No.:878419-78-4
- Isosalviamine A
Catalog No.:BCN3553
CAS No.:878475-29-7
- Isosalviamine B
Catalog No.:BCN3554
CAS No.:878475-30-0
- JNJ 303
Catalog No.:BCC7806
CAS No.:878489-28-2
- WRW4
Catalog No.:BCC5893
CAS No.:878557-55-2
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
- Lesinurad
Catalog No.:BCC1699
CAS No.:878672-00-5
- AZ 628
Catalog No.:BCC3730
CAS No.:878739-06-1
- 15-deoxy-Δ-12,14-Prostaglandin J2
Catalog No.:BCC7321
CAS No.:87893-55-8
- GDC-0449 (Vismodegib)
Catalog No.:BCC1285
CAS No.:879085-55-9
- CP 93129 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6899
CAS No.:879089-64-2
Effects of the selective sigma-1 receptor antagonist S1RA on formalin-induced pain behavior and neurotransmitter release in the spinal cord in rats.[Pubmed:24384038]
J Neurochem. 2014 May;129(3):484-94.
We have previously shown that the selective sigma-1 receptor (sigma1 R) antagonist S1RA (E-52862) inhibits neuropathic pain and activity-induced spinal sensitization in various pre-clinical pain models. In this study we characterized both the behavioral and the spinal neurochemical effects of S1RA in the rat formalin test. Systemic administration of S1RA produced a dose-related attenuation of flinching and lifting/licking behaviors in the formalin test. Neurochemical studies using concentric microdialysis in the ipsilateral dorsal horn of awake, freely moving rats revealed that the systemic S1RA-induced antinociceptive effect occurs concomitantly with an enhancement of noradrenaline levels and an attenuation of formalin-evoked glutamate release in the spinal dorsal horn. Intrathecal pre-treatment with idazoxan prevented the systemic S1RA antinociceptive effect, suggesting that the S1RA antinociception depends on the activation of spinal alpha2 -adrenoceptors which, in turn, could induce an inhibition of formalin-evoked glutamate release. When administered locally, intrathecal S1RA inhibited only the flinching behavior, whereas intracerebroventricularly or intraplantarly injected also attenuated the lifting/licking behavior. These results suggest that S1RA supraspinally activates the descending noradrenergic pain inhibitory system, which may explain part of its antinociceptive properties in the formalin test; however, effects at other central and peripheral sites also account for the overall effect. Formalin-induced nociceptive effect occurs concomitantly with an enhancement of glutamate (Glu) level in the dorsal horn spinal cord. The selective sigma1 receptor antagonist S1RA results in inhibition of formalin-evoked Glu release, no modification of GABA levels, and enhancement of noradrenaline (NA) levels. This increased spinal NA activates spinal alpha2-adrenoceptors producing the attenuation of the formalin-induced pain behaviour.
Analysis of the molecular interactions of the potent analgesic S1RA with the sigma1 receptor.[Pubmed:23582276]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 May 15;23(10):2868-71.
The highly selective sigma1 receptor antagonist S1RA is endowed with a surprisingly high affinity for its target protein given a missing fundamental hydrophobic pharmacophoric requirement. Here we show that, with respect to other potent sigma1 ligands, S1RA is able to compensate this loss by fulfilling all other pharmacophoric requirements and by gaining in solvation energy.
S1RA, a selective sigma-1 receptor antagonist, inhibits inflammatory pain in the carrageenan and complete Freund's adjuvant models in mice.[Pubmed:24776490]
Behav Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;25(3):226-35.
The therapeutic potential of S1RA (E-52862), a selective sigma-1 receptor (sigma1R) antagonist, has been explored in experimental neuropathic pain, but not in inflammatory pain models. The present study investigated the effect of the intraperitoneal administration of S1RA on the hind paw withdrawal response to thermal and mechanical stimulation following an intraplantar injection of carrageenan (CARR) and complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA), which are two well-characterized models of acute and chronic inflammatory pain, respectively. S1RA fully reversed both mechanical [dose of drug that produced half of its maximal response (ED50)=35.9 and 42.1 mg/kg for CARR-induced and CFA-induced pain, respectively] and thermal (ED50=27.9 mg/kg, CARR) hypersensitivity, whereas ibuprofen (CARR, mechanical allodynia) and celecoxib (CARR, thermal hyperalgesia; CFA, mechanical allodynia) failed to reach maximum efficacy. Morphine also showed maximum efficacy in all tests. Unlike celecoxib and ibuprofen, which decreased paw volume significantly, CARR-induced paw oedema was not reduced by S1RA and morphine, thus suggesting that the antinociceptive effect of S1RA does not involve a major anti-inflammatory (antioedema) action. S1RA was devoid of efficacy when administered to sigma1R knockout mice, thus suggesting the involvement of sigma1R in the antinociceptive effects exerted by S1RA. We conclude that S1RA represents a promising novel analgesic therapy for inflammatory pain.


