FK866 (APO866)NAMPT inhibitor,non-competitive, highly specific CAS# 658084-64-1 |
- GNE-617
Catalog No.:BCC4280
CAS No.:1362154-70-8
- CB30865
Catalog No.:BCC1457
CAS No.:206275-15-2
- STF-118804
Catalog No.:BCC4850
CAS No.:894187-61-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 658084-64-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6914657 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H29N3O2 | M.Wt | 391.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Daporinad; APO866 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (127.71 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
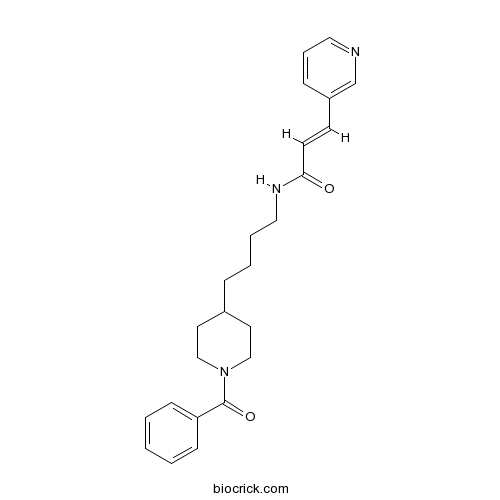
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-[4-(1-benzoylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CCC1CCCCNC(=O)C=CC2=CN=CC=C2)C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KPBNHDGDUADAGP-VAWYXSNFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H29N3O2/c28-23(12-11-21-8-6-15-25-19-21)26-16-5-4-7-20-13-17-27(18-14-20)24(29)22-9-2-1-3-10-22/h1-3,6,8-12,15,19-20H,4-5,7,13-14,16-18H2,(H,26,28)/b12-11+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | FK866 is a highly specific non-competitive inhibitor of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) with Ki value of 0.4 nM. | |||||
| Targets | NAMPT | |||||
| IC50 | 0.4 nM (Ki) | |||||

FK866 (APO866) Dilution Calculator

FK866 (APO866) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5542 mL | 12.7711 mL | 25.5421 mL | 51.0843 mL | 63.8553 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5108 mL | 2.5542 mL | 5.1084 mL | 10.2169 mL | 12.7711 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2554 mL | 1.2771 mL | 2.5542 mL | 5.1084 mL | 6.3855 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0511 mL | 0.2554 mL | 0.5108 mL | 1.0217 mL | 1.2771 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0255 mL | 0.1277 mL | 0.2554 mL | 0.5108 mL | 0.6386 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
FK866 is an inhibitor of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NMPRTase) with IC50 values ranging between 0.09nM and 27.2nM [1].
NAD plays a vital role in numerous biochemical and biologic processes. Targeting NAD synthesis is thought to be a selective manner to kill cancer cells since cancer cells have a higher rate of NAD turnover compared with normal cells. In the in vitro MTT assay using a panel of 41 human hematologic cancer
cell lines, most cancer cells are sensitive to low concentrations of FK866. Among these cancer cells, AML cells are most sensitive. FK866 is shown selective to human hematologic malignant cells and the normal human HPCs are resistant to FK866 treatment. It is found that FK866 induces cell death in a caspase-independent pathway but in a dose-dependent manner to induce mitochondrial membrane depolarization. Additionally, FK866 induces cell autophagy dependenting on de novo protein synthesis. FK866 also reduces ATP levels in ML-2 cells due to the inhibition of NAD synthesis. The antitumor efficacy of FK866 is also shown in the in vivo models. FK866 significantly prevents tumor growth both in mice xenografted subcutaneously with AML-M4 and Namalwa cells. Furthermore, FK866 clears tumor cells to below detectable levels and results in 80% survival for a long-term [1].
References:
[1] Nahimana A, Attinger A, Aubry D, Greaney P, Ireson C, Thougaard AV, Tjørnelund J, Dawson KM, Dupuis M, Duchosal MA. The NAD biosynthesis inhibitor APO866 has potent antitumor activity against hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2009 Apr 2;113(14):3276-86.
- SU11274
Catalog No.:BCC1243
CAS No.:658084-23-2
- Goserelin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC5352
CAS No.:65807-02-5
- 10(14)-Cadinene-4,11-diol
Catalog No.:BCN7099
CAS No.:658062-23-8
- 3-Eudesmene-1beta,11-diol
Catalog No.:BCN7096
CAS No.:658062-22-7
- Z-D-Ser(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2739
CAS No.:65806-90-8
- Boc-Dap(Z)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2667
CAS No.:65710-58-9
- Apramycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4628
CAS No.:65710-07-8
- Z-D-Glu-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC2774
CAS No.:65706-99-2
- H-Lys-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2978
CAS No.:657-27-2
- H-Lys-OH.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2979
CAS No.:657-26-1
- Metformin
Catalog No.:BCC9026
CAS No.:657-24-9
- Reversine
Catalog No.:BCC1892
CAS No.:656820-32-5
- Peucedanol 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7689
CAS No.:65853-04-5
- Z(2-Cl)-Osu
Catalog No.:BCC2691
CAS No.:65853-65-8
- 1-Benzyl-5-ethoxyhydantoin
Catalog No.:BCC8460
CAS No.:65855-02-9
- 3-Epiglochidiol diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN4202
CAS No.:6587-37-7
- 2-(2-Aminothiazole-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8478
CAS No.:65872-41-5
- Peucedanol 3'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7688
CAS No.:65891-61-4
- Daturabietatriene
Catalog No.:BCN4203
CAS No.:65894-41-9
- Tioconazole
Catalog No.:BCC4867
CAS No.:65899-73-2
- Betaxolol
Catalog No.:BCC4342
CAS No.:659-18-7
- Danshenxinkun A
Catalog No.:BCN2469
CAS No.:65907-75-7
- Danshenxinkun B
Catalog No.:BCN2470
CAS No.:65907-76-8
- Danshenxinkun C
Catalog No.:BCN2471
CAS No.:65907-77-9
NAMPT protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells through modulating SIRT1 activity.[Pubmed:27035562]
Mol Med Rep. 2016 May;13(5):4058-64.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common progressive neurodegenerative movement disorder. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) catalyzes the first ratelimiting step in the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) biosynthetic pathway in mammals, is a substrate for NAD+dependent enzymes, such as sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), and contributes to cell fate decisions. However, the role of NAMPT in PD has remained to be fully elucidated. In the present study, PC12 cells were treated with the neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine (6OHDA) to establish an in vitro model of PD, following which an obvious inhibitory effect on the levels of NAMPT and NAD+ as well as the NAD+/NADH ratio was detected. In addition, preincubation with FK866, a highly specific NAMPT inhibitor, enhanced the inhibitory effects of 6OHDA on the viability of PC12, while preincubation with nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), am enzymatic product of NAMPT, had the opposite effect. Furthermore, it was revealed that NMN markedly attenuated 6OHDAinduced decreases in superoxide dismutase activity and glutathione levels, as well as 6OHDAinduced increases in malondialdehyde and lactate dehydrogenase in PC12 cells. Furthermore, 6OHDA significantly reduced SIRT1 activity in PC12 cells, which was inhibited by NMN. The pharmacological activator resveratrol also significantly inhibited 6OHDAmediated decreases in PC12 cell viability while reversing 6OHDAinduced decreases in SIRT1 levels. The results of the present study suggested that NMT protected against 6OHDAinduced decreases in PC12 cell viability, and that SIRT1 activation had a role in this process. Treatment with NMN to activate SIRT1 may represent a novel therapeutic strategy for treating PD.
Nampt Expression Decreases Age-Related Senescence in Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Targeting Sirt1.[Pubmed:28125705]
PLoS One. 2017 Jan 26;12(1):e0170930.
Senescence restricts the development of applications involving mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in research fields, such as tissue engineering, and stem cell therapeutic strategies. Understanding the mechanisms underlying natural aging processes may contribute to the development of novel approaches to preventing age-related diseases or slowing individual aging processes. Nampt is a rate-limiting NAD biosynthetic enzyme that plays critical roles in energy metabolism, cell senescence and maintaining life spans. However, it remains unknown whether Nampt influences stem cell senescence. In this study, the function of Nampt was investigated using a rat model of natural aging. Our data show that Nampt expression was significantly lower in MSCs obtained from aged rats than in those obtained from young rats during physiological aging. Reducing the level of Nampt in aged MSCs resulted in lower intracellular concentrations of NAD+ and downregulated Sirt1 expression and activity. After the Nampt inhibitor FK866 was added, young MSCs were induced to become aged cells. The enhanced senescence was correlated with NAD+ depletion and Sirt1 activity attenuation. In addition, Nampt overexpression attenuated cell senescence in aged MSCs. Our findings provide a new explanation for the mechanisms underlying stem cell senescence and a novel target for delaying stem cell senescence and preventing and treating age-related diseases.
Inhibitor of Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase Sensitizes Glioblastoma Cells to Temozolomide via Activating ROS/JNK Signaling Pathway.[Pubmed:28097126]
Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1450843.
Overcoming temozolomide (TMZ) resistance is a great challenge in glioblastoma (GBM) treatment. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) is a rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and has a crucial role in cancer cell metabolism. In this study, we investigated whether FK866 and CHS828, two specific NAMPT inhibitors, could sensitize GBM cells to TMZ. Low doses of FK866 and CHS828 (5 nM and 10 nM, resp.) alone did not significantly decrease cell viability in U251-MG and T98 GBM cells. However, they significantly increased the antitumor action of TMZ in these cells. In U251-MG cells, administration of NAMPT inhibitors increased the TMZ (100 muM)-induced apoptosis and LDH release from GBM cells. NAMPT inhibitors remarkably enhanced the activities of caspase-1, caspase-3, and caspase-9. Moreover, NAMPT inhibitors increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and superoxide anion level but reduced the SOD activity and total antioxidative capacity in GBM cells. Treatment of NAMPT inhibitors increased phosphorylation of c-Jun and JNK. Administration of JNK inhibitor SP600125 or ROS scavenger tocopherol with TMZ and NAMPT inhibitors substantially attenuated the sensitization of NAMPT inhibitor on TMZ antitumor action. Our data indicate a potential value of NAMPT inhibitors in combined use with TMZ for GBM treatment.
Regulation of the Nampt-mediated NAD salvage pathway and its therapeutic implications in pancreatic cancer.[Pubmed:27233476]
Cancer Lett. 2016 Aug 28;379(1):1-11.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a crucial cofactor for the redox reactions in the metabolic pathways of cancer cells that have elevated aerobic glycolysis (Warburg effect). Cancer cells are reported to rely on NAD recycling and inhibition of the NAD salvage pathway causes metabolic collapse and cell death. However, the underlying regulatory mechanisms and clinical implications for the NAD salvage pathway in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remain unclear. This study showed that the expression of Nampt, the rate-limiting enzyme of the NAD salvage pathway, was significantly increased in PDAC cells and PDAC tissues. Additionally, inhibition of Nampt impaired tumor growth in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo, which was accompanied by a decreased cellular NAD level and glycolytic activity. Mechanistically, the Nampt expression was independent of Kras and p16 status, but it was directly regulated by miR-206, which was inversely correlated with the expression of Nampt in PDAC tissues. Importantly, pharmacological inhibition of Nampt by its inhibitor, FK866, significantly enhanced the antitumor activity of gemcitabine in PDAC cells and in orthotopic xenograft mouse models. In conclusion, the present study revealed a novel regulatory mechanism for Nampt in PDAC and suggested that Nampt inhibition may override gemcitabine resistance by decreasing the NAD level and suppressing glycolytic activity, warranting further clinical investigation for pancreatic cancer treatment.


