Glycoursodeoxycholic acidCAS# 64480-66-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 64480-66-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 126968461 | Appearance | Powder |
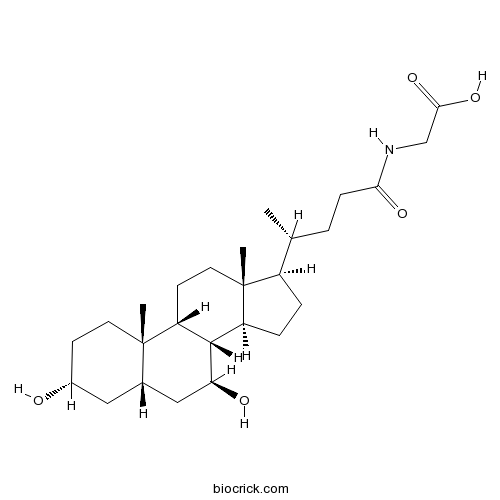
| Formula | C26H43NO5 | M.Wt | 449.63 |
| Type of Compound | Steroids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ursodeoxycholylglycine | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 125 mg/mL (278.01 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[[(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7S,8R,9R,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoyl]amino]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(CCC(=O)NCC(=O)O)C1CCC2C1(CCC3C2C(CC4C3(CCC(C4)O)C)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GHCZAUBVMUEKKP-JAADFPRLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H43NO5/c1-15(4-7-22(30)27-14-23(31)32)18-5-6-19-24-20(9-11-26(18,19)3)25(2)10-8-17(28)12-16(25)13-21(24)29/h15-21,24,28-29H,4-14H2,1-3H3,(H,27,30)(H,31,32)/t15-,16+,17-,18-,19+,20-,21+,24+,25+,26-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid shows protective effects in Barrett's esophagus cells by inhibiting oxidative stress. 2. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid and interleukin-10 modulate inflammation and cell survival, they may have potential benefits in reducing UCB-induced astrocyte immunostimulation and death. 3. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid reduces matrix metalloproteinase-9 and caspase-9 activation in a cellular model of superoxide dismutase-1 neurodegeneration. |
| Targets | TNF-α | IL Receptor | SOD | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | Caspase |

Glycoursodeoxycholic acid Dilution Calculator

Glycoursodeoxycholic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2241 mL | 11.1203 mL | 22.2405 mL | 44.481 mL | 55.6013 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4448 mL | 2.2241 mL | 4.4481 mL | 8.8962 mL | 11.1203 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2224 mL | 1.112 mL | 2.2241 mL | 4.4481 mL | 5.5601 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0445 mL | 0.2224 mL | 0.4448 mL | 0.8896 mL | 1.112 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0222 mL | 0.1112 mL | 0.2224 mL | 0.4448 mL | 0.556 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid, a acyl glycine and a bile acid-glycine conjugate, is a metabolite of ursodeoxycholic acid.
In Vitro:The antioxidant compound glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA) fully abrogates UCB-induced cytochrome c oxidase inhibition and significantly prevents oxidative stress, metabolic alterations, and cell demise[1].GUDCA has shown therapeutic efficacy in neurodegenerative models and diseases. Increased cytosolic SOD1 inclusions were observed in 4 DIV NSC-34/hSOD1(G93A) cells together with decreased mitochondria viability, caspase-9 activation, and apoptosis[2]. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid shows preventive and restorative effects against unconjugated bilirubin -induced blood-brain barrier disruption and damage to human brain microvascular endothelial cells[3].
References:
[1]. Vaz AR, et al. Bilirubin selectively inhibits cytochrome c oxidase activity and induces apoptosis in immature cortical neurons: assessment of the protective effects of glycoursodeoxycholic acid. J Neurochem. 2010 Jan;112(1):56-65.
[2]. Vaz AR, et al. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid reduces matrix metalloproteinase-9 and caspase-9 activation in a cellular model of superoxide dismutase-1 neurodegeneration.
[3]. Palmela I, et al. Hydrophilic bile acids protect human blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from disruption by unconjugated bilirubin: an in vitro study. Front Neurosci. 2015 Mar 13;9:80.
- Picroside III
Catalog No.:BCN6324
CAS No.:64461-95-6
- Tizanidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4357
CAS No.:64461-82-1
- 10-Hydroxycamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCN1226
CAS No.:64439-81-2
- Dulcoside A
Catalog No.:BCN3237
CAS No.:64432-06-0
- Grifolin monomethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN7568
CAS No.:64432-04-8
- Shanzhiside methylester
Catalog No.:BCN4187
CAS No.:64421-28-9
- Mussaenoside
Catalog No.:BCN4186
CAS No.:64421-27-8
- DL-2-Amino-n-octanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8949
CAS No.:644-90-6
- Precocene II
Catalog No.:BCN4605
CAS No.:644-06-4
- Alloalantolactone
Catalog No.:BCN8091
CAS No.:64340-41-6
- N6-Benzoyl-5'-O-(4,4'-dimethoxytrityl)-2'-deoxyadenosine
Catalog No.:BCC9074
CAS No.:64325-78-6
- Malvidin chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3017
CAS No.:643-84-5
- Cefotaxime sodium
Catalog No.:BCC8908
CAS No.:64485-93-4
- Rubianthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCN6880
CAS No.:644967-44-2
- Altretamine
Catalog No.:BCC1216
CAS No.:645-05-6
- Isovanillic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3376
CAS No.:645-08-9
- Scoulerine
Catalog No.:BCN6623
CAS No.:6451-73-6
- Oxprenolol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7630
CAS No.:6452-73-9
- Acantrifoside E
Catalog No.:BCN6646
CAS No.:645414-25-1
- Sinigrin monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN2595
CAS No.:64550-88-5
- H-D-Glu(OMe)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2940
CAS No.:6461-04-7
- VcMMAE
Catalog No.:BCC2033
CAS No.:646502-53-6
- Demethylluvangetin
Catalog No.:BCN7569
CAS No.:64652-10-4
- 1,9-Dideoxyforskolin
Catalog No.:BCC6352
CAS No.:64657-18-7
Protective effects of glycoursodeoxycholic acid in Barrett's esophagus cells.[Pubmed:19549210]
Dis Esophagus. 2010 Feb;23(2):83-93.
Barrett's esophagus (BE) is a premalignant condition associated with the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). Previous studies have implicated hydrophobic bile acids and gastric acid in BE and EAC pathogenesis. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that DNA damage, cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by bile acids and gastric acid can be attenuated by the cytoprotective, hydrophilic bile acid Glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA). Non-dysplastic BE cells were exposed for 10 min to pH 4 and/or bile acid cocktail or to pH 4 and a modified cocktail consisting of a mixture of bile acids and GUDCA. DNA damage was evaluated by the comet assay; cell viability and proliferation were measured by trypan blue staining and the MTS assay; reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured using hydroethidium staining; oxidative DNA/RNA damage was detected by immunostaining with antibody against 8-OH-dG; thiol levels were measured by 5-chloromethylfluorescein diacetate (CMFDA) staining; and the expression of antioxidant proteins was evaluated by western blotting. DNA damage and oxidative stress were significantly increased, while thiol levels were decreased in BE cells treated with pH 4 and bile acid cocktail compared with cells treated with pH 4 alone or untreated cells. Bile acids and low pH also significantly decreased cell proliferation. Expression of the antioxidant enzymes, MnSOD and CuZnSOD, was elevated in the cells treated with bile acids and low pH. When GUDCA was included in the medium, all these effects of pH 4 and bile acids were markedly reduced. In conclusion, treatment of BE cells with acidified medium and a bile acid cocktail at physiologically relevant concentrations induces DNA damage, cytotoxicity, and ROS. The cytoprotective bile acid, GUDCA, inhibits these deleterious effects by inhibiting oxidative stress.
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid and interleukin-10 modulate the reactivity of rat cortical astrocytes to unconjugated bilirubin.[Pubmed:17805009]
J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007 Sep;66(9):789-98.
The pathogenesis of bilirubin encephalopathy seems to result from accumulation of unconjugated bilirubin (UCB) within the brain. We have recently demonstrated that UCB causes astroglial release of proinflammatory cytokines and glutamate, as well as cell death. The bile acid Glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA) and the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-10 have been reported to modulate inflammation and cell survival. In this study we investigated the effect of these therapeutic agents on the astroglial response to UCB. Only GUDCA prevented UCB-induced astroglial death. The secretion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and IL-1beta elicited by UCB in astrocytes was reduced in the presence of GUDCA and IL-10, whereas the suppression of IL-6 was only counteracted by GUDCA. Neither GUDCA nor IL-10 modulated the accumulation of extracellular glutamate. Additionally, IL-10 markedly inhibited UCB-induced nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear translocation and cytokine mRNA expression, whereas GUDCA only prevented TNF-alpha mRNA expression. Moreover, GUDCA inhibited TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-converting enzymes, preventing the maturation of these cytokines and their consequent release. Collectively, this study shows that IL-10 action is restricted to UCB-induced release of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta from the astrocytes, whereas GUDCA presents a more ubiquitous action on the astroglial reactivity to UCB. Hence, GUDCA may have potential benefits over an IL-10 therapeutic approach in reducing UCB-induced astrocyte immunostimulation and death.
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid reduces matrix metalloproteinase-9 and caspase-9 activation in a cellular model of superoxide dismutase-1 neurodegeneration.[Pubmed:24848512]
Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(3):864-77.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease that affects mainly motor neurons (MNs). NSC-34 MN-like cells carrying the G93A mutation in human superoxide dismutase-1 (hSOD1(G93A)) are a common model to study the molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration in ALS. Although the underlying pathways of MN failure still remain elusive, increased apoptosis and oxidative stress seem to be implicated. Riluzole, the only approved drug, only slightly delays ALS progression. Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), as well as its glycine (Glycoursodeoxycholic acid, GUDCA) and taurine (TUDCA) conjugated species, have shown therapeutic efficacy in neurodegenerative models and diseases. Pilot studies in ALS patients indicate safety and tolerability for UDCA oral administration. We explored the mechanisms associated with superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD1) accumulation and MN degeneration in NSC-34/hSOD1(G93A) cells differentiated for 4 days in vitro (DIV). We examined GUDCA efficacy in preventing such pathological events and in restoring MN functionality by incubating cells with 50 muM GUDCA at 0 DIV and at 2 DIV, respectively. Increased cytosolic SOD1 inclusions were observed in 4 DIV NSC-34/hSOD1(G93A) cells together with decreased mitochondria viability (1.2-fold, p < 0.01), caspase-9 activation (1.8-fold, p < 0.05), and apoptosis (2.1-fold, p < 0.01). GUDCA exerted preventive effects (p < 0.05) while also reduced caspase-9 levels when added at 2 DIV (p < 0.05). ATP depletion (2-fold, p < 0.05), increased nitrites (1.6-fold, p < 0.05) and metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activation (1.8-fold, p < 0.05), but no changes in MMP-2, were observed in the extracellular media of 4 DIV NSC-34/hSOD1(G93A) cells. GUDCA inhibited nitrite production (p < 0.05) while simultaneously prevented and reverted MMP-9 activation (p < 0.05), but not ATP depletion. Data highlight caspase-9 and MMP-9 activation as key pathomechanisms in ALS and GUDCA as a promising therapeutic strategy for slowing disease onset and progression.


