H-Glu(OBzl)-OHCAS# 1676-73-9 |
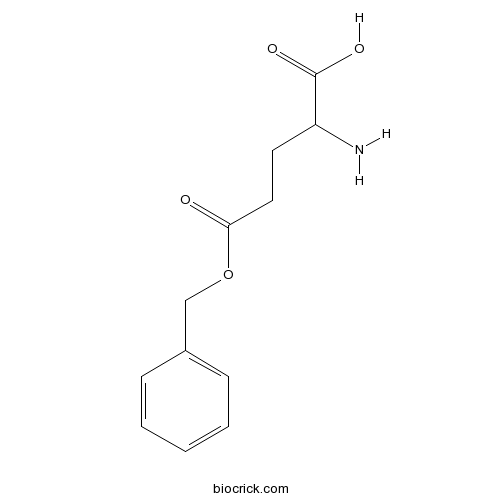
- H-D-Glu(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2939
CAS No.:2578-33-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1676-73-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 95441 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H15NO4 | M.Wt | 237.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-5-oxo-5-phenylmethoxypentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)COC(=O)CCC(C(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BGGHCRNCRWQABU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H15NO4/c13-10(12(15)16)6-7-11(14)17-8-9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-5,10H,6-8,13H2,(H,15,16) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

H-Glu(OBzl)-OH Dilution Calculator

H-Glu(OBzl)-OH Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.2141 mL | 21.0704 mL | 42.1408 mL | 84.2815 mL | 105.3519 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8428 mL | 4.2141 mL | 8.4282 mL | 16.8563 mL | 21.0704 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4214 mL | 2.107 mL | 4.2141 mL | 8.4282 mL | 10.5352 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0843 mL | 0.4214 mL | 0.8428 mL | 1.6856 mL | 2.107 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0421 mL | 0.2107 mL | 0.4214 mL | 0.8428 mL | 1.0535 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
H-Glu(OBzl)-OH
- Benoxafos
Catalog No.:BCC5470
CAS No.:16759-59-4
- 11-Hydroxy-12-methoxyabietatriene
Catalog No.:BCN3253
CAS No.:16755-54-7
- PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC6520
CAS No.:1675203-84-5
- BADGE
Catalog No.:BCC7022
CAS No.:1675-54-3
- LY335979 (Zosuquidar 3HCL)
Catalog No.:BCC3878
CAS No.:167465-36-3
- Sophoracarpan B
Catalog No.:BCN6979
CAS No.:1674359-84-2
- Sophoracarpan A
Catalog No.:BCN6980
CAS No.:1674359-82-0
- H-Cys(Bzl)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2907
CAS No.:16741-80-3
- Fmoc-Lys(Mtt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3523
CAS No.:167393-62-6
- Zosuquidar
Catalog No.:BCC2074
CAS No.:167354-41-8
- 9-Hydroxyeriobofuran
Catalog No.:BCN7444
CAS No.:167278-41-3
- Malvidin 3,5-Diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCC8206
CAS No.:16727-30-3
- Z-Ser(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2740
CAS No.:1676-75-1
- Boc-Asp(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3368
CAS No.:1676-90-0
- RS 39604 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5694
CAS No.:167710-87-4
- Ornidazole
Catalog No.:BCC4815
CAS No.:16773-42-5
- 3-Epidehydrotumulosic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3649
CAS No.:167775-54-4
- PD98059
Catalog No.:BCC1098
CAS No.:167869-21-8
- Rubelloside B
Catalog No.:BCN1099
CAS No.:167875-39-0
- Wilforol A
Catalog No.:BCN3064
CAS No.:167882-66-8
- ent-Kaurane-16beta,19,20-triol
Catalog No.:BCN7654
CAS No.:167898-32-0
- 2,5-Bis(4-diethylaminophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8502
CAS No.:1679-98-7
- Crassanine
Catalog No.:BCN4073
CAS No.:16790-92-4
- 19(S)-Hydroxyconopharyngine
Catalog No.:BCN3976
CAS No.:16790-93-5
Enhancement of peptide coupling reactions by 4-dimethylaminopyridine.[Pubmed:7341528]
Int J Pept Protein Res. 1981 Nov;18(5):459-67.
4-Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) was found to be useful in the enhancement of peptide coupling reactions mediated by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide or symmetrical anhydrides. In an automated synthesis of the model heptapeptide Boc-Ala-Cle-Ile-Val-Pro-Arg(Tos)-Gly-OCH2-Resin (Cle, cycloleucine), the efficiencies of various coupling methods such as dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide plus 1-hydroxybenzotriazole, and symmetrical anhydride were compared with that of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide plus 4-dimethylaminopyridine. Based on the amino acid composition of the peptide-resin samples and high pressure liquid chromatographic analyses of the protected heptapeptide amide obtained from the ammonolytic cleavage of the peptide-resin samples, it was concluded that only dicyclohexylcarbodiimide plus 4-dimethylaminopyridine gave the desired near quantitative couplings in those cycles involving the sterically hindered amino acid residues. Observations were also made that 4-dimethylaminopyridine was a useful additive in a modified symmetrical anhydride method of coupling. In the synthesis of the model tetrapeptide Leu-Ala-Gly-Val on a Pam resin, the anhydride couplings were accelerated by DMAP and the product was equivalent in homogeneity to that obtained by the best previous methods. In addition, no racemization was detectable by a sensitive chromatographic method. There also was no detectable racemization found in a DCC-DMAP coupling of Boc-Ile-OH with H-Val-OCH2-resin. However, significant racemization was observed during the coupling of Boc-Phe-OH with H-Glu(OBzl)-OCH2-resin. DMAP is recommended as an additive for coupling hindered amino acids, particularly C alpha-substituted residues, where little or no racemization is expected.


