H-Lys-OEt .2HClCAS# 3844-53-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3844-53-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16667420 | Appearance | Powder |
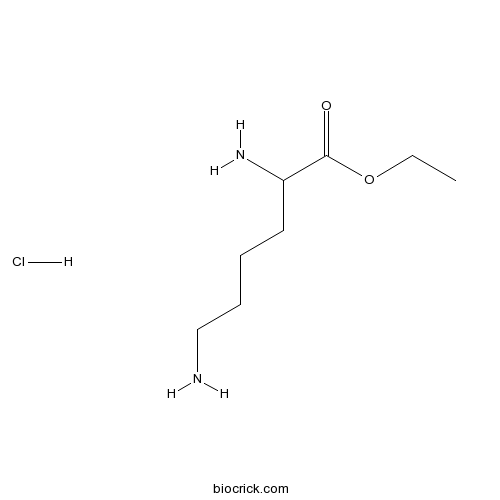
| Formula | C8H19ClN2O2 | M.Wt | 210.7 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | ethyl 2,6-diaminohexanoate;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C(CCCCN)N.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SGEJVUZMEHMANQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H18N2O2.ClH/c1-2-12-8(11)7(10)5-3-4-6-9;/h7H,2-6,9-10H2,1H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

H-Lys-OEt .2HCl Dilution Calculator

H-Lys-OEt .2HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.7461 mL | 23.7304 mL | 47.4608 mL | 94.9217 mL | 118.6521 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9492 mL | 4.7461 mL | 9.4922 mL | 18.9843 mL | 23.7304 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4746 mL | 2.373 mL | 4.7461 mL | 9.4922 mL | 11.8652 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0949 mL | 0.4746 mL | 0.9492 mL | 1.8984 mL | 2.373 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0475 mL | 0.2373 mL | 0.4746 mL | 0.9492 mL | 1.1865 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
H-Lys-OEt ·2HCl
- Sclareol glycol
Catalog No.:BCN7007
CAS No.:38419-75-9
- 3,4,4',7-Tetrahydroxyflavan
Catalog No.:BCN5438
CAS No.:38412-82-7
- Altechromone A
Catalog No.:BCN7422
CAS No.:38412-47-4
- Aloenin
Catalog No.:BCN8438
CAS No.:38412-46-3
- Ganaxolone
Catalog No.:BCC7397
CAS No.:38398-32-2
- Caudatin
Catalog No.:BCN5810
CAS No.:38395-02-7
- NSC 663284
Catalog No.:BCC7199
CAS No.:383907-43-5
- 3',4'-Anhydrovinblastine
Catalog No.:BCN2392
CAS No.:38390-45-3
- Taxinine
Catalog No.:BCN6944
CAS No.:3835-52-7
- Neuropeptide W-23 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5961
CAS No.:383415-79-0
- UC 112
Catalog No.:BCC8042
CAS No.:383392-66-3
- Homovanillic Acid Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2226
CAS No.:38339-06-9
- Asatone
Catalog No.:BCN7761
CAS No.:38451-63-7
- Deacetyleupaserrin
Catalog No.:BCN7228
CAS No.:38456-39-2
- Eucannabinolide
Catalog No.:BCN7221
CAS No.:38458-58-1
- Crotafoline
Catalog No.:BCN2075
CAS No.:38494-87-0
- Tarafenacin
Catalog No.:BCC4147
CAS No.:385367-47-5
- Daphnicyclidin D
Catalog No.:BCN7081
CAS No.:385384-24-7
- Daphnicyclidin F
Catalog No.:BCN6400
CAS No.:385384-26-9
- Daphnicyclidin H
Catalog No.:BCN7080
CAS No.:385384-29-2
- Oxotremorine M
Catalog No.:BCC6920
CAS No.:3854-04-4
- Prostaglandin F2α
Catalog No.:BCC7889
CAS No.:38562-01-5
- Chloroprocaine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5556
CAS No.:3858-89-7
- Lasiodonin
Catalog No.:BCN7156
CAS No.:38602-52-7
The Smac mimetic RMT5265.2HCL induces apoptosis in EBV and HTLV-I associated lymphoma cells by inhibiting XIAP and promoting the mitochondrial release of cytochrome C and Smac.[Pubmed:22325366]
Leuk Res. 2012 Jun;36(6):784-90.
The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP) are important regulators of apoptosis. However, little is known about the capacity of Smac mimetics (IAP inhibitor) to overcome virally associated-lymphoma's (VAL) resistance to apoptosis. Here, we explored the pro-apoptotic effect of a novel Smac mimetic, RMT5265.2HCL (RMT) in VAL cells. RMT improved the sensitivity to apoptosis in EBV- and to some extend in HTLV-1- but not in HHV-8-VAL. Furthermore, we identified that RMT promotes caspase 3 and 9 cleavage by inhibiting XIAP and inducing the mitochondrial efflux of Smac and cytochrome C. This investigation further support exploring the use of Smac inhibitors in VAL.
Probing the micellar properties of Quinacrine 2HCl and its binding with surfactants and human serum albumin.[Pubmed:23727671]
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2013 Sep;113:182-90.
This manuscript reports physicochemical behavior of an antimalarial drug Quinacrine 2HCl (QUN) drug as well as its interaction with surfactant and Human Serum Albumin (HSA). Surface tension and specific conductivity were employed to detect the critical micelle concentration (CMC) and thus its surface and thermodynamic parameters were calculated. Solublization of this drug within micelles of anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) has also been studied. UV/Visible spectroscopy was used to calculate partition coefficient (Kx), free energy of partition and number of drug molecules per micelle. The complexation of drug with HSA at physiological conditions (pH 7.4) has been analyzed by using UV/Visible and fluorescence spectroscopy. In this way the values of drug-protein binding constant, number of binding sites and free energy of binding were calculated.
Reduction of oxidative stress in adjuvant arthritis. Comparison of efficacy of two pyridoindoles: stobadine dipalmitate and SMe1.2HCl.[Pubmed:20548970]
Acta Biochim Pol. 2010;57(2):223-8. Epub 2010 Jun 14.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic potential of oxidative stress (OS) reduction by using pyridoindole (PI) antioxidants in adjuvant arthritis (AA). The substances tested were stobadine dipalmitate (STB) and SMe1. AA was used as animal model. The experiments included healthy animals, control arthritic animals and arthritic animals with administration of PI in the oral daily dose of 15 mg/kg b.m during 28 experimental days. The rats were sacrificed on day 28. Clinical and biochemical parameters were determined. The effect of PI administration was evaluated on the basis of the following parameters: (a) arthritis (volume of hind paws - HPW, change of animal body mass - CBM), (b) OS (chemiluminescence of whole blood - CWB, levels of thiobarbituric acid reacting substance - TBARS and of HNE- and MDA-protein adducts in plasma and activity of gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) in hind paw joint homogenates). The PI studied significantly increased the CBM of animals and corrected the HPW. STB also significantly decreased the activity of GGT in joint homogenates. SMe1 was more effective in decreasing plasmatic TBARS levels, but STB was more effective in reducing plasmatic HNE- and MDA-protein adducts. The assay for HNE- and MDA-adducts in plasma as a function of time was applied for the first time in AA. STB markedly decreased spontaneous and PMA-stimulated CWB and reduced neutrophil count. In summary, STB was more effective than SMe1 in reducing OS in AA. Our results showed that the reduction of OS in arthritis also corrected the clinical manifestations of the disease.


