IguratimodCOX-2 inhibitor,inhibits IL-1,IL-6,IL-8 and tumour necrosis factor. CAS# 123663-49-0 |
- FK 3311
Catalog No.:BCC1576
CAS No.:116686-15-8
- Ibuprofen
Catalog No.:BCC3791
CAS No.:15687-27-1
- Celecoxib
Catalog No.:BCC1099
CAS No.:169590-42-5
- Etoricoxib
Catalog No.:BCC1565
CAS No.:202409-33-4
- Ibuprofen Lysine
Catalog No.:BCC2547
CAS No.:57469-77-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 123663-49-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 124246 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H14N2O6S | M.Wt | 374.37 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | T614 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (89.03 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
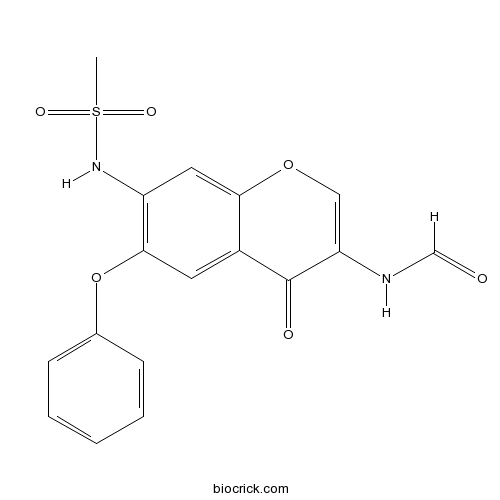
| Chemical Name | N-[7-(methanesulfonamido)-4-oxo-6-phenoxychromen-3-yl]formamide | ||
| SMILES | CS(=O)(=O)NC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)OC=C(C2=O)NC=O)OC3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ANMATWQYLIFGOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H14N2O6S/c1-26(22,23)19-13-8-15-12(17(21)14(9-24-15)18-10-20)7-16(13)25-11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-10,19H,1H3,(H,18,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Iguratimod(T-614) is a selective inhibitor of cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2), and inhibits the production of interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, IL-8 and tumour necrosis factor. | |||||
| Targets | COX-2 | |||||

Iguratimod Dilution Calculator

Iguratimod Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6712 mL | 13.3558 mL | 26.7115 mL | 53.4231 mL | 66.7789 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5342 mL | 2.6712 mL | 5.3423 mL | 10.6846 mL | 13.3558 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2671 mL | 1.3356 mL | 2.6712 mL | 5.3423 mL | 6.6779 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0534 mL | 0.2671 mL | 0.5342 mL | 1.0685 mL | 1.3356 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0267 mL | 0.1336 mL | 0.2671 mL | 0.5342 mL | 0.6678 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 2.0 (hepatocyte-stimulating activities) and 6.6 μg/ml (immunoreactivities) for IL-6 release.
Iguratimod is one of a series of 4H-1-benzopyran-4-ones which has potent anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic activity. Iguratimod also inhibits the production of tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, IL-8.
In vitro: Iguratimod inhibited the release of immunoreactive IL-1 beta from human monocytic cell line stimulated with lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in a dose-dependent manner (0.3-30 μg/ml). Northern blotting analysis using LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells indicated that the inhibitory effect of Iguratimod on IL-1 beta production is caused by the suppression of IL-1 beta mRNA expression [1].
In vivo: Administration of Iguratimod did not inhibit the tumor growth, but resulted in attenuation of cachexia symptoms. Furthermore, Iguratimod decreased the serum levels of IL-6, and also reduced its gene expression in the tumor tissues. In addition, exogenously administered IL-6 nullified the suppressive effect of Iguratimod [2].
Clinical trial: A 52-week clinical study of iguratimod in 394 Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis to evaluate the long-term safety of the drug was conducted. Iguratimod was administered orally at a daily dose of 25 mg for the first 4 weeks and 50 mg for the subsequent 48 weeks. The cumulative incidence of adverse events for 100 weeks was 97.6%. The cumulative incidence of adverse reactions was 65.3%; unfavorable symptoms and signs accounted for 33.2% of the reactions, and abnormal laboratory data changes accounted for 50.4% [3].
References:
[1] Tanaka K, Aikawa Y, Kawasaki H, Asaoka K, Inaba T, Yoshida C. Pharmacological studies on 3-formylamino-7-methylsulfonylamino-6-phenoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (T-614), a novel antiinflammatory agent. 4th communication: inhibitory effect on the production of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1992;15(11):649-55.
[2] Tanaka K, Urata N, Mikami M, Ogasawara M, Matsunaga T, Terashima N, Suzuki H. Effect of iguratimod and other anti-rheumatic drugs on adenocarcinoma colon 26-induced cachexia in mice. Inflamm Res. 2007;56(1):17-23.
[3] Hara M, Abe T, Sugawara S, Mizushima Y, Hoshi K, Irimajiri S, Hashimoto H, Yoshino S, Matsui N, Nobunaga M. Long-term safety study of iguratimod in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2007;17(1):10-6.
- NS 398
Catalog No.:BCC6857
CAS No.:123653-11-2
- Fmoc-Glu(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3493
CAS No.:123639-61-2
- Tenofovir maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4262
CAS No.:1236287-04-9
- Diosbulbin L
Catalog No.:BCN7305
CAS No.:1236285-87-2
- Salviaplebeiaside
Catalog No.:BCN7304
CAS No.:1236273-88-3
- Clerosterol glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6123
CAS No.:123621-00-1
- 740 Y-P
Catalog No.:BCC5861
CAS No.:1236188-16-1
- PHP 501 trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC6193
CAS No.:1236105-75-1
- Curcumadionol
Catalog No.:BCN3561
CAS No.:1235984-45-8
- Peptide YY(3-36), PYY, human
Catalog No.:BCC1041
CAS No.:123583-37-9
- rac BHFF
Catalog No.:BCC7644
CAS No.:123557-91-5
- AQ-RA 741
Catalog No.:BCC7314
CAS No.:123548-16-3
- Pimasertib (AS-703026)
Catalog No.:BCC2529
CAS No.:1236699-92-5
- Trigoxyphin A
Catalog No.:BCN6875
CAS No.:1236874-00-2
- Bongardol
Catalog No.:BCN6124
CAS No.:123690-76-6
- CGP 35348
Catalog No.:BCC6988
CAS No.:123690-79-9
- CGP 46381
Catalog No.:BCC6990
CAS No.:123691-14-5
- CGP 36216 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7605
CAS No.:123691-29-2
- Kuwanol C
Catalog No.:BCN3941
CAS No.:123702-94-3
- Moracin O
Catalog No.:BCN4004
CAS No.:123702-97-6
- Acetyl-Calpastatin (184-210) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC2350
CAS No.:123714-50-1
- Aucherine
Catalog No.:BCN2058
CAS No.:123715-12-8
- Escin IA
Catalog No.:BCN3862
CAS No.:123748-68-5
- ML 786 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7997
CAS No.:1237536-18-3
Effect of iguratimod and methotrexate on RANKL and OPG expression in serum and IL-1beta-induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.[Pubmed:27894399]
Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016 Oct 31;62(12):44-50.
The receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL)/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB (RANK)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) system plays a key role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA)-associated bone erosion. The upregulation of the RANKL/OPG ratio promotes bone erosion. The objective of this study is to explore the effects of Iguratimod, a small-molecule disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), alone or in combination with methotrexate (MTX), on RANKL and OPG expression in RA. We performed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to investigate the modulatory effects of Iguratimod, MTX, or their combination on serum RANKL and OPG levels of patients with RA before and after treatment for 12 and 24 weeks. Furthermore, fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) from patients with RA were interleukin (IL)-1beta-stimulated and then treated with different concentrations of Iguratimod, MTX, or both, and RANKL and OPG expressions were investigated by using ELISA, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and western blot analysis. We found that RANKL levels and the RANKL/OPG ratio significantly decreased in both serum and IL-1beta-induced RA FLS after treatment. Moreover, combination therapy with Iguratimod and MTX showed an even stronger inhibition than each drug alone did. Our results suggest that Iguratimod and MTX, especially in combination, efficaciously protected against bone erosion by suppressing the production of RANKL.
Identification of Iguratimod as an Inhibitor of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) with Steroid-sparing Potential.[Pubmed:27793992]
J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 16;291(51):26502-26514.
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine that has been implicated in a broad range of inflammatory and oncologic diseases. MIF is unique among cytokines in terms of its release profile and inflammatory role, notably as an endogenous counter-regulator of the anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. In addition, it exhibits a catalytic tautomerase activity amenable to the design of high affinity small molecule inhibitors. Although several classes of these compounds have been identified, biologic characterization of these molecules remains a topic of active investigation. In this study, we used in vitro LPS-driven assays to characterize representative molecules from several classes of MIF inhibitors. We determined that MIF inhibitors exhibit distinct profiles of anti-inflammatory activity, especially with regard to TNFalpha. We further investigated a molecule with relatively low anti-inflammatory activity, compound T-614 (also known as the anti-rheumatic drug Iguratimod), and found that, in addition to exhibiting selective MIF inhibition in vitro and in vivo, Iguratimod also has additive effects with glucocorticoids. Furthermore, we found that Iguratimod synergizes with glucocorticoids in attenuating experimental autoimmune encephalitis, a model of multiple sclerosis. Our work identifies Iguratimod as a valuable new candidate for drug repurposing to MIF-relevant diseases, including multiple sclerosis.
Safety and effectiveness of 24-week treatment with iguratimod, a new oral disease-modifying antirheumatic drug, for patients with rheumatoid arthritis: interim analysis of a post-marketing surveillance study of 2679 patients in Japan.[Pubmed:27919207]
Mod Rheumatol. 2017 Sep;27(5):755-765.
OBJECTIVE: To determine the real-world safety and effectiveness of Iguratimod (IGU) for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a 52-week, Japanese, post-marketing surveillance study was conducted. An interim analysis at week 24 was performed. METHODS: This study included all RA patients who received IGU following its introduction to the market. All adverse events (AEs) and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were collected. Effectiveness was evaluated by the change in Disease Activity Score 28-C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) from baseline to week 24. RESULTS: Safety was analyzed in 2679 patients. The overall incidences of AEs, ADRs, and serious ADRs were 38.41, 31.65, and 3.21%, respectively; the most commonly reported serious ADRs were pneumonia/bacterial pneumonia, interstitial lung disease, and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. Concomitant glucocorticoid use and comorbid conditions associated with respiratory disease were identified as risk factors for serious infections. Pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage and increased international normalized ratio of prothrombin time were observed with concomitant use of IGU and warfarin. The DAS28-CRP decreased from baseline to week 24. CONCLUSION: Although a safety concern was identified with concomitant use of IGU and warfarin, this real-world study showed no other new safety concerns and similar effectiveness to clinical trials. IGU is a new therapeutic option for RA patients.
Anti-rheumatic drug iguratimod (T-614) alleviates cancer-induced bone destruction via down-regulating interleukin-6 production in a nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent manner.[Pubmed:27752889]
J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Oct;36(5):691-699.
Cytokines are believed to be involved in a "vicious circle" of progressive interactions in bone metastasis. Iguratimod is a novel anti-rheumatic drug which is reported to have the capability of anti-cytokines. In this study, a rat model was constructed to investigate the effect of Iguratimod on bone metastasis and it was found that Iguratimod alleviated cancer-induced bone destruction. To further explore whether an anti-tumor activity of Iguratimod contributes to the effect of bone resorption suppression, two human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 were studied. The effect of Iguratimod on tumor proliferation was detected by CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry. The effects of Iguratimod on migration and invasion of cancer cells were determined by wound-healing and Transwell assays. Results showed that high dose (30 mug/mL) Iguratimod slightly suppressed the proliferation of cancer cells but failed to inhibit their migration and invasion capacity. Interestingly, Iguratimod decreased the transcription level of IL-6 in MDA-MB-231 cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Moreover, Iguratimod partially impaired NF-kappaB signaling by suppressing the phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 subunit. Our findings indicated that Iguratimod may alleviate bone destruction by partially decreasing the expression of IL-6 in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner, while it has little effect on the tumor proliferation and invasion.


