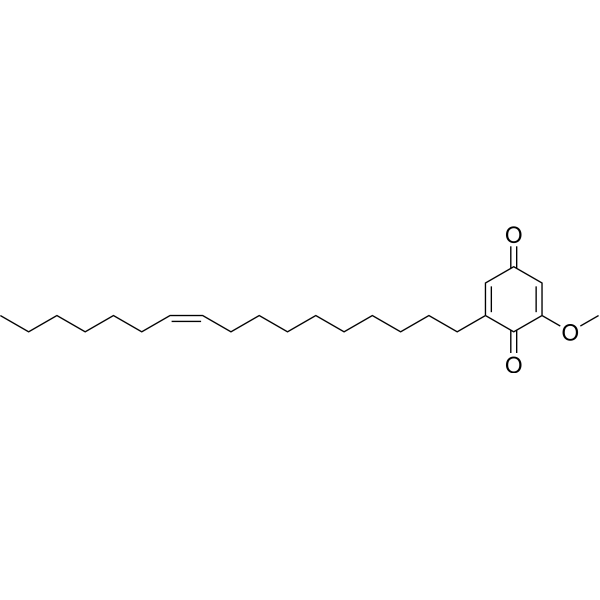
IrisquinoneCAS# 56495-82-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 56495-82-0 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H38O3 | M.Wt | 374.56 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Irisquinone A,2-(cis-10-Heptadecenyl)-6-methoxy-p-benzoquinone | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Irisquinone Dilution Calculator

Irisquinone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6698 mL | 13.349 mL | 26.698 mL | 53.396 mL | 66.745 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.534 mL | 2.6698 mL | 5.3396 mL | 10.6792 mL | 13.349 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.267 mL | 1.3349 mL | 2.6698 mL | 5.3396 mL | 6.6745 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0534 mL | 0.267 mL | 0.534 mL | 1.0679 mL | 1.3349 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0267 mL | 0.1335 mL | 0.267 mL | 0.534 mL | 0.6674 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Inflexuside B
Catalog No.:BCX1761
CAS No.:1395048-86-8
- Quercetin-3-O-(2''-O-galloyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1760
CAS No.:69624-79-9
- Salviandulin E
Catalog No.:BCX1759
CAS No.:158994-32-2
- Glaucocalyxin D
Catalog No.:BCX1758
CAS No.:140671-02-9
- Bulnesol
Catalog No.:BCX1757
CAS No.:22451-73-6
- Inflexuside A
Catalog No.:BCX1756
CAS No.:1395048-85-7
- Cnidioside B
Catalog No.:BCX1755
CAS No.:141896-54-0
- Pseudobatigenin-7-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosid
Catalog No.:BCX1754
CAS No.:224957-15-7
- Ladanetin
Catalog No.:BCX1753
CAS No.:23130-22-5
- Salvifaricin
Catalog No.:BCX1752
CAS No.:87321-87-7
- (5S,6R,7R,8S)-2-(2-phenylethyl)-5,6,7-trihydroxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-8-[2-(2-phenylethyl)chromonyl-6-...
Catalog No.:BCX1751
CAS No.:121795-56-0
- (-)-3,3'-Bisdemethylpinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCX1750
CAS No.:340167-81-9
- 2-Methoxy-6-pentadecyl-1,4-benzoquinone
Catalog No.:BCX1763
CAS No.:144078-11-5
- 2,4-Dihydroxy-allylbenzene-2-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1764
CAS No.:1416564-61-8
- Polyfuroside
Catalog No.:BCX1765
CAS No.:108886-03-9
- Donasine
Catalog No.:BCX1766
CAS No.:1017237-81-8
- Poricoic acid H
Catalog No.:BCX1767
CAS No.:415724-85-5
- Dugesin C
Catalog No.:BCX1768
CAS No.:1403505-97-4
- Salvileucantholide
Catalog No.:BCX1769
CAS No.:158994-33-3
- (7R,8S,8′R)-4,7-Dihydroxy-3,3′,4′-trimethoxyl-9-oxo dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan-4-O-β-D-glucopyrano...
Catalog No.:BCX1770
CAS No.:1807808-90-7
- Quercetin 3-O-β-D-xylofuranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-galactopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1771
CAS No.:1181635-91-5
- Dugesin B
Catalog No.:BCX1772
CAS No.:760973-66-8
- 6,7-Dihydrosalviandulin E
Catalog No.:BCX1773
CAS No.:1983982-37-1
- (±)-7-epi-Kadsurenone
Catalog No.:BCX1774
CAS No.:245648-20-8
Radiosensitizing effect of irisquinone on glioma through the downregulation of HIF-1alpha evaluated by 18F-FDG and 18F-FMISO PET/CT.[Pubmed:26963468]
Nucl Med Commun. 2016 Jul;37(7):705-14.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to elucidate the radiosensitizing mechanism of Irisquinone (IQ) and evaluate the utility of F-fluorodeoxyglucose (F-FDG) and F-fluoromisonidazole (F-FMISO) PET/computed tomography (CT) in assessing the radiosensitizing effect of IQ. MATERIALS AND METHODS: In an in-vitro experiment, C6 rat glioma cells were treated with IQ, radiation, or both. The viability and radiosensitivity of C6 cells were detected using the MTT assay and clonogenic survival assay. The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) was evaluated by real-time PCR and western blot. In an in-vivo experiment, C6 rat glioma cells were implanted into the right flank of rats and treated with IQ, radiation, both, or no treatment. F-FDG and F-FMISO PET/CT images were obtained before and after treatment. The expression of HIF-1alpha was detected by immunohistochemistry staining. RESULTS: In the in-vitro experiment, the results of the MTT assay showed that the half-inhibition concentration (IC50) of IQ for normoxic and hypoxic C6 tumor cells was 17.2 and 21.0 nmol/l, respectively. Clonogenic survival assay showed that IQ could improve the radiosensitivity of both normoxic and hypoxic C6 tumor cells. When the concentration of irradiation was 20% IC50 (4.2 nmol/l), the sensitive enhancement ratio of normoxic and hypoxic C6 tumor cells was 1.18 and 1.33, respectively. The mRNA and protein expression levels of HIF-1alpha decreased significantly when treated with IQ plus radiation compared with the other groups.In the in-vivo experiment, 24 or 48 h after different treatments, the maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) of F-FDG or F-FMISO uptake decreased in the radiation group and the IQ plus radiation group, whereas these values increased in the control and IQ groups. The SUVmax of F-FDG or F-FMISO uptake in IQ plus radiation group were lower than those of the radiation group (t=3.28, 2.62, P<0.05). However, there was no significant decrease in tumor volumes in the radiation group and the IQ plus radiation treatment group early after treatment.Immunohistochemistry staining showed that there were significant differences in the expression of HIF-1alpha in the four groups (F=87.1, P<0.01). The SUVmax of both F-FDG and F-FMISO uptake showed a significant correlation with the expression of HIF-1alpha. F-FMISO provided a higher correlation coefficient with HIF-1alpha than F-FDG (r=0.93, 0.82, P<0.01). CONCLUSION: The present experiments indicated that IQ enhanced the radiosensitivity of C6 rat glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. The primary mechanism of this radiosensitizing effect involves the downregulation of HIF-1alpha. F-FDG and F-FMISO PET/CT were sensitive and noninvasive for monitoring the early radiosensitizing effect of IQ. Meanwhile, F-FMISO PET/CT provided more information on the changes in tumor hypoxic status.
Dynamic observation of the radiosensitive effect of irisquinone on rabbit VX2 lung transplant tumors by using fluorine-18-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography.[Pubmed:23276827]
Nucl Med Commun. 2013 Mar;34(3):220-8.
OBJECTIVE: We studied the radiosensitizing effect of Irisquinone on a VX2 lung transplant tumor model during three-dimensional radiotherapy using fluorine-18-deoxyglucose ((18)F-FDG) PET/computed tomography (PET/CT). MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirty VX2 tumor-bearing rabbits were randomized into three groups: the radiotherapy group, the Irisquinone+radiotherapy group, and the control group, each comprising 10 rabbits. (18)F-FDG PET/CT images were obtained to monitor the tumor/muscle (T/M) ratio of F-FDG uptake and the retention index (RI) before treatment, when the radiation dose reached 6, 12, and 18 Gy, and 1 week after radiotherapy. Tumor volume changes were also assessed. The management of the control group followed the same procedure. RESULTS: At all treatment time points, the tumor volume was significantly smaller in the treatment groups than in the control group. The 1 and 2 h T/M ratios and RIs decreased gradually when the radiation dose reached 12 or 18 Gy in the treatment groups, whereas these values increased continuously in the control group. One week after treatment, the 1 and 2 h T/M ratios increased in the treatment groups, although these values remained lower than those in the control group. The RIs of the radiotherapy and Irisquinone+radiotherapy groups were 0.329+/-0.133 and 0.137+/-0.036, respectively. Histological evaluation revealed that tumor F-FDG uptake was strongly related to tumor cell density. CONCLUSION: F-FDG PET/CT was sensitive and noninvasive and could be used to monitor the radiosensitizing effects of Irisquinone and the therapeutic efficacy of radiotherapy.
A new belamcandaquinone from the seeds of Iris bungei Maxim.[Pubmed:21820495]
Fitoterapia. 2011 Oct;82(7):1137-9.
A novel dimeric 1,4-benzoquinone and resorcinol derivative, Belamcandaquinone N (1), and two known compounds, 3-hydroxyIrisquinone (2) and 5-[(Z)-10-heptadecenyl] resorcinol (3), were isolated from the seeds of Iris bungei Maxim. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and comparing with literature data of known compounds. These compounds showed remarkable cytotoxic activity against RM-1 cell lines.
[Preparation, identification and inclusion actions of irisquinone hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex].[Pubmed:16011270]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2005 Apr;40(4):369-72.
AIM: To perpare and identify Irisquinone hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex (Irisquinone-HP-beta-CD), as well as to study the inclusion mechanism and molecule stoichiometry between Irisquinone and hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. METHODS: Irisquinone-HP-beta-CD was prepared by freeze-drying technique. The ratio of host and guest was also studied in inclusion process by mol gradient and continuing variational methods. At the same time, the inclusion complex was identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). RESULTS: It was demonstrated that the solubility of Irisquinone was enhanced markedly by inclusion with HP-beta-CD when stoichiometry was 2:1 of host and guest at 25 degrees C, 35 degrees C and 45 degrees C. CONCLUSION: The solubility and stability of Irisquinone could be increased by preparing the inclusion complex with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin.
[Determination of irisquinone by single sweep oscillopolarography].[Pubmed:12579764]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2002 Mar;37(3):207-9.
AIM: To propose a polarographic method for the determination of Irisquinone. METHODS: A reduction wave of Irisquinone was recorded by single sweep oscillopolarography. RESULTS: In 8.0 x 10(-3) mol.L-1 Na2B4O7-1.6 x 10(-2) mol.L-1 KH2PO4 (pH 7.7) supporting electrolyte, a redution wave of Irisquinone with peak potential -1.23 V (vs SCE) achieved high sensitivity. The 2nd-order derivative peak current of the reduction wave was proportional to Irisquinone concentration in the range of 1.5 x 10(-7)-5.2 x 10(-6) mol.L-1 (gamma = 0.9992, n = 9). The detection limit was 6.0 x 10(-8) mol.L-1. Relative standard deviation (RSD) was 0.87% by performing 13 independent measurements on 2.0 x 10(-6) mol.L-1 Irisquinone. CONCLUSION: The proposed method was sensitive, simple, rapid, and can be applied to the determination of Irisquinone in raw medicine and capsule.
Analytical approaches for traditional chinese medicines exhibiting antineoplastic activity.[Pubmed:11817032]
J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2001 Nov 25;764(1-2):27-48.
Traditional Chinese medicines have attracted great interest in recent researchers as alternative antineoplastic therapies. This review focuses on analytical approaches to various aspects of the antineoplastic ingredients of traditional Chinese medicines. Emphasis will be put on the processes of biological sample extraction, separation, clean-up steps and the detection. The problems of the extraction solvent selection and different types of column chromatography are also discussed. The instruments considered are gas chromatography, capillary electrophoresis (CE) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) connected with various detectors (ultraviolet, fluorescence, electrochemistry, mass, etc.). In addition, determinations of antineoplastic herbal ingredients, including camptothecin, taxol (paclitaxel), vinblastine. vincristine, podophyllotoxin, colchicine, and their related compounds, such as irinotecan, SN-38, topotecan, 9-aminocamptothecin, docetaxel (taxotere) and etoposide, are briefly summarized. These drugs are structurally based on the herbal ingredients, and some of them are in trials for clinical use. Evaluation of potential antineoplastic herbal ingredients, such as harringtonine, berberine, emodin, genistein, berbamine, daphnoretin, and Irisquinone, are currently investigated in laboratories. Other folk medicines are excluded from this paper because their antineoplastic ingredients are unknown.
Highlight on the studies of anticancer drugs derived from plants in China.[Pubmed:8142920]
Stem Cells. 1994 Jan;12(1):53-63.
Recent progress on the study of anticancer drugs originating from plants in China is reviewed in this paper. Guided by the experience of traditional Chinese medicine, several new drugs have been found. Indirubin from Indigofera tinctoria is useful for the treatment of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Irisquinone from Iris latea pallasii and 10-hydroxy camptothecin from Camptotheca accuminata have exhibited definite activity on rodent tumors. Recent studies indicate that ginsenoside Rh2 is an inducer of cell differentiation in melanoma B-16 cells in vitro. Pharmacological studies have demonstrated that curcumin from Curcuma longa is an antimutagen as well as an antipromotor for cancer. Daidzein and acetyl boswellic acid have been shown to be effective inducers of cell differentiation in HL-60 cells. Guided by the chemotaxonomic principle of plants, harringtonine and homoharringtonine isolated from Cephalotaxus hainanesis have exhibited significant antileukemia activity and are widely used in clinics in China. Taxol from Taxus chinensis has been shown to be an important new anticancer drug with unique chemical structure and mechanism of action. The continuous search for new anticancer drugs from plants will be a fruitful frontier in cancer treatment and chemoprevention.
Recent advances in pharmacologic study of natural anticancer agents in China.[Pubmed:1842013]
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1991;86 Suppl 2:51-4.
In this paper a number of anticancer agents of natural origin will be presented. Hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT) was found to produce a strong inhibitory action on a variety of animal tumors. It is also effective for treatment of patients with gastric carcinoma, liver carcinoma, tumor of head and neck or leukemia. Pharmacologic studies showed that it could depress S phase of tumor cells significantly and cause formation of cellular chromatid breaks. By means of alkaline elution and nick translation methods it has been proved that HCPT induced DNA single strand breaks remarkably. Homoharringtonine (HHRT) was shown to be effective against acute leukemia. Recent experiments in tumor-bearing mice indicated that (HHRT) could diminish tumor metastasis. Using molecular hybridization technique it was demonstrated that (HHRT) decreased the content of c-myc RNA in the cytoplasm but not in the nuclei. Lycobetaine (LBT) possessed strong inhibitory effects on a number of ascites tumors. In clinical trials it was effective against ovarian and gastric carcinomas. It is able to intercalate into DNA. Oxalysine (OXL) is a new antibiotic and shown to be effective against tumor metastatis. When used in combination with 5-FU, its anticancer action could be enhanced. Other natural compounds such as indirubin, beta-elemene, Irisquinone, oridonine, norcantharidin and PSP have been also found to possess antitumor action.
Traditional Chinese medicine and the search for new antineoplastic drugs.[Pubmed:3059066]
J Ethnopharmacol. 1988 Sep;24(1):1-17.
The experience of traditional Chinese medicine affords a valuable approach in the search for new antineoplastic drugs as illustrated by indirubin from Dang Gui Lu Hui Wan, Irisquinone from Iris lactea pallasii and Zhuling polysaccharide from Polyporus umbellata. The application of chemotaxonomic principles to related species of those plants used in folk medicine has also provided an approach which can be used successfully for the development of new drugs. The studies of Cephalotaxus hainanesis and Camptotheca accuminata provide two typical examples in this regard. One must be aware that the experience of traditional Chinese medicine cannot be used without elaborate efforts in many cases. For example, the ancient Chinese ideograph for spleen does not mean spleen in the modern sense, instead it refers to the entire gastrointestinal system. Similarly, the ancient ideograph for kidney does not mean kidney in the modern sense, and can mean the entire endocrine system. Therefore, for the reasonable utilization of traditional Chinese medicine, one must be familiar with its basic concepts and terminology. In addition, one must bear in mind that the term "tumor" in folk medicine is applied to a very wide range of pathological manifestations which sometimes have no relation to the various forms of neoplasia. It is important for drugs and treatments to be analyzed carefully in modern terms to eliminate the false and to utilize the true information. Only in such a way can the experience of traditional medicine be integrated into modern medicine and make its contribution in the advancement of health care in the world.


