Leukotriene B4CAS# 71160-24-2 |
- Levomefolate calcium
Catalog No.:BCC1702
CAS No.:151533-22-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 71160-24-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5312972 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H32O4 | M.Wt | 336.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (supplied pre-dissolved in anhydrous ethanol, 50µg/ml) | ||
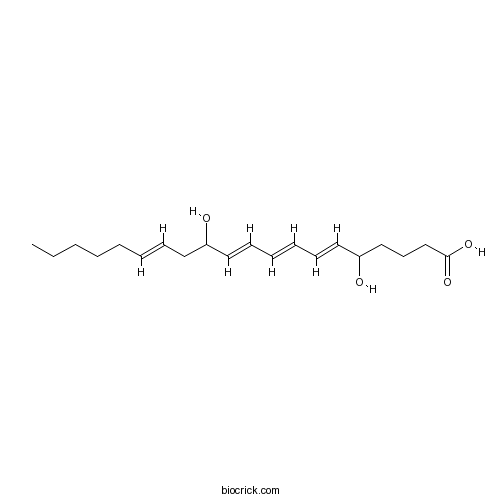
| Chemical Name | (6E,8E,10E,14E)-5,12-dihydroxyicosa-6,8,10,14-tetraenoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCC=CCC(C=CC=CC=CC(CCCC(=O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VNYSSYRCGWBHLG-XUOUMLBJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H32O4/c1-2-3-4-5-6-9-13-18(21)14-10-7-8-11-15-19(22)16-12-17-20(23)24/h6-11,14-15,18-19,21-22H,2-5,12-13,16-17H2,1H3,(H,23,24)/b8-7+,9-6+,14-10+,15-11+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent lipid inflammatory mediator derived from the 5-lipoxygenase pathway of arachidonic acid metabolism. Binds to BLT1 and BLT2 receptors and acts as a potent chemotactic agent and activator of leukocytes. Also displays antiviral activity towards DNA viruses and retroviruses. |

Leukotriene B4 Dilution Calculator

Leukotriene B4 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.972 mL | 14.8602 mL | 29.7203 mL | 59.4407 mL | 74.3008 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5944 mL | 2.972 mL | 5.9441 mL | 11.8881 mL | 14.8602 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2972 mL | 1.486 mL | 2.972 mL | 5.9441 mL | 7.4301 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0594 mL | 0.2972 mL | 0.5944 mL | 1.1888 mL | 1.486 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0297 mL | 0.1486 mL | 0.2972 mL | 0.5944 mL | 0.743 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (±)-Bay K 8644
Catalog No.:BCC3918
CAS No.:71145-03-4
- (E)-3-Acetoxy-5-methoxystilbene
Catalog No.:BCN4273
CAS No.:71144-78-0
- Meloxicam (Mobic)
Catalog No.:BCC3808
CAS No.:71125-38-7
- Bucindolol
Catalog No.:BCC7444
CAS No.:71119-11-4
- MRS 2578
Catalog No.:BCC4976
CAS No.:711019-86-2
- 5,8,4'-Trihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone 8-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1372
CAS No.:710952-13-9
- Griselinoside
Catalog No.:BCN4272
CAS No.:71035-06-8
- 1-Octacosanoyl glyceride
Catalog No.:BCN8190
CAS No.:71035-02-4
- Cathinone
Catalog No.:BCN1784
CAS No.:71031-15-7
- Digitoxin
Catalog No.:BCN5358
CAS No.:71-63-6
- Veratridine
Catalog No.:BCC7515
CAS No.:71-62-5
- Medroxyprogesterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4485
CAS No.:71-58-9
- ML 141
Catalog No.:BCC8092
CAS No.:71203-35-5
- Erythroxytriol P
Catalog No.:BCN4274
CAS No.:7121-99-5
- Schizandriside
Catalog No.:BCN6999
CAS No.:71222-06-5
- Obolactone
Catalog No.:BCN7190
CAS No.:712272-88-3
- Boc-Ala(2-pyridyl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3320
CAS No.:71239-85-5
- Salaspermic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7139
CAS No.:71247-78-4
- 2,5-Bis(5-tert-butyl-2-benzoxazolyl)thiophene
Catalog No.:BCC8503
CAS No.:7128-64-5
- Crotananine
Catalog No.:BCN2078
CAS No.:71295-28-8
- Cronaburmine
Catalog No.:BCN2072
CAS No.:71295-32-4
- (S)-3-Hydroxyphenylglycine
Catalog No.:BCC6605
CAS No.:71301-82-1
- 6(1H)-Azulenone, 2,3-dihydro-1,4-dimethyl
Catalog No.:BCN1371
CAS No.:71305-89-0
- Moclobemide (Ro 111163)
Catalog No.:BCC2322
CAS No.:71320-77-9
Inhibition of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction: role of AMPK-regulated mitochondrial function.[Pubmed:28290498]
Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 14;7:44352.
Leukotriene B4 (LTB4)-mediated leukocyte recruitment and inflammatory cytokine production make crucial contributions to chronic inflammation and sepsis; however, the role of LTB4 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cardiac dysfunction remains unclear. Therefore, the present study addressed this issue using an LTB4 receptor 1 (BLT1) inhibitor. Administration of LPS to mice resulted in decreased cardiovascular function. Inhibition of LTB4/BLT1 with the BLT1 inhibitor U75302 significantly improved survival and attenuated the LPS-induced acute cardiac dysfunction. During LPS challenge, the phosphorylated AMPK/ACC signaling pathway was slightly activated, and this effect was enhanced by U75302. Additionally, pNF-kappaB, Bax and cleaved caspase-3 were upregulated by LPS, and Bcl-2, IkappaB-alpha, mitochondrial complex I, complex II, and OPA1 were downregulated; however, these effects were reversed by U75302. The results indicated that the BLT1 antagonist suppressed cardiac apoptosis, inflammation, and mitochondrial impairment. Furthermore, the protection provided by the BLT1 inhibitor against LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction was significantly reversed by the AMPK inhibitor Compound C. In conclusion, inhibiting the LTB4/BLT1 signaling pathway via AMPK activation is a potential treatment strategy for septic cardiac dysfunction because it efficiently attenuates cardiac apoptosis, which may occur via the inhibition of inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction.
The leukotriene B4-leukotriene B4 receptor axis promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by modulating neutrophil recruitment.[Pubmed:28318626]
Kidney Int. 2017 Jul;92(1):89-100.
Cisplatin is an effective chemotherapeutic agent and widely used in treatment of various solid organ malignancies, including head and neck, ovarian, and testicular cancers. However, the induction of acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of its main side effects. Leukotriene B4 receptor 1 (BLT1) mediates the majority of physiological effects of Leukotriene B4 (LTB4), a potent lipid chemoattractant generated at inflammation sites, but the role of the LTB4-BLT1 axis in cisplatin-induced AKI remains unknown. Here we found upregulated LTB4 synthesis and BLT1 expression in the kidney after cisplatin administration. Cisplatin was found to directly upregulate gene expression of leukotriene A4 hydrolase and stimulate LTB4 production in renal tubular epithelial cells. Reduced kidney structural/functional damage, inflammation, and apoptosis were observed in BLT1(-/-) mice, as well as in wild-type mice treated with the LTA4H inhibitor SC-57461A and the BLT1 antagonist U-75302. Neutrophils were likely the target of this pathway, as BLT1 absence induced a significant decrease in infiltrating neutrophils in the kidney. Adoptive transfer of neutrophils from wild-type mice restored kidney injury in BLT1(-/-) mice following cisplatin challenge. Thus, the LTB4-BLT1 axis contributes to cisplatin-induced AKI by mediating kidney recruitment of neutrophils, which induce inflammation and apoptosis in the kidney. Hence, the LTB4-BLT1 axis could be a potential therapeutic target in cisplatin-induced AKI.
Low salivary resolvin D1 to leukotriene B4 ratio predicts carotid intima media thickness: A novel biomarker of non-resolving vascular inflammation.[Pubmed:28195518]
Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017 Jun;24(9):903-906.
Background Different lipid mediators may have opposing effects on vascular inflammation. For example, whereas Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) transduces inflammation, resolvin D1 (RvD1), which is synthesized from the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid, facilitates the resolution of inflammation. The aim of this study was to determine the association of the RvD1/LTB4 ratio with subclinical atherosclerosis. Methods Saliva samples and ultrasound measurements of the intima media thickness of the carotid artery was obtained for 254 participants. The lipid mediators RvD1 and LTB4 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results Participants with a salivary RvD1/LTB4 ratio >1 had a significantly lower intima media thickness than those in whom LTB4 prevailed. The salivary RvD1/LTB4 ratio independently predicted carotid intima media thickness. Conclusions The ratio between the proresolving and proinflammatory salivary lipid mediators RvD1 and LTB4 may serve as a biomarker of non-resolving inflammation and its relation to intima media thickness in cardiovascular disease.
The leukotriene B4 receptors BLT1 and BLT2 form an antagonistic sensitizing system in peripheral sensory neurons.[Pubmed:28242764]
J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 14;292(15):6123-6134.
Sensitization of the heat-activated ion channel transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) through lipids is a fundamental mechanism during inflammation-induced peripheral sensitization. Leukotriene B4 is a proinflammatory lipid mediator whose role in peripheral nociceptive sensitization is not well understood to date. Two major G-protein-coupled receptors for Leukotriene B4 have been identified: the high-affinity receptor BLT1 and the low-affinity receptor BLT2. Transcriptional screening for the expression G-protein-coupled receptors in murine dorsal root ganglia showed that both receptors were among the highest expressed in dorsal root ganglia. Calcium imaging revealed a sensitization of TRPV1-mediated calcium increases in a relative narrow concentration range for Leukotriene B4 (100-200 nm). Selective antagonists and neurons from knock-out mice demonstrated a BLT1-dependent sensitization of TRPV1-mediated calcium increases. Accordingly, Leukotriene B4-induced thermal hyperalgesia was mediated through BLT1 and TRPV1 as shown using the respective knock-out mice. Importantly, higher Leukotriene B4 concentrations (>0.5 mum) and BLT2 agonists abolished sensitization of the TRPV1-mediated calcium increases. Also, BLT2 activation inhibited protein kinase C- and protein kinase A-mediated sensitization processes through the phosphatase calcineurin. Consequently, a selective BLT2-receptor agonist increased thermal and mechanical withdrawal thresholds during zymosan-induced inflammation. In accordance with these data, immunohistochemical analysis showed that both Leukotriene B4 receptors were expressed in peripheral sensory neurons. Thus, the data show that the two Leukotriene B4 receptors have opposing roles in the sensitization of peripheral sensory neurons forming a self-restricting system.


