ML 141Selective inhibitor of Cdc42 Rho family GTPase CAS# 71203-35-5 |
- BMN-673 8R,9S
Catalog No.:BCC1422
CAS No.:1207456-00-5
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- PJ34
Catalog No.:BCC1865
CAS No.:344458-19-1
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
- Veliparib dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2076
CAS No.:912445-05-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 71203-35-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2950007 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H21N3O3S | M.Wt | 407.49 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CID 2950007 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 55 mg/mL (134.97 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
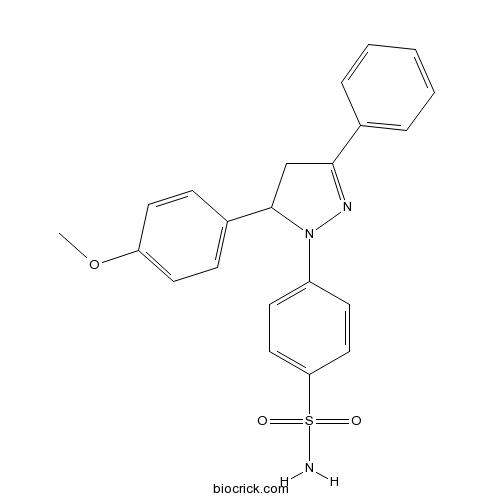
| Chemical Name | 4-[3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-phenyl-3,4-dihydropyrazol-2-yl]benzenesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2CC(=NN2C3=CC=C(C=C3)S(=O)(=O)N)C4=CC=CC=C4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QBNZBMVRFYREHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H21N3O3S/c1-28-19-11-7-17(8-12-19)22-15-21(16-5-3-2-4-6-16)24-25(22)18-9-13-20(14-10-18)29(23,26)27/h2-14,22H,15H2,1H3,(H2,23,26,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Allosteric inhibitor of Cdc42 GTPase (EC50 = 2.1 μM). Selective for Cdc42 over other members of the Rho GTPase family including Rac1, Rab2 and Rab7. Inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration in vitro. |

ML 141 Dilution Calculator

ML 141 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.454 mL | 12.2702 mL | 24.5405 mL | 49.081 mL | 61.3512 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4908 mL | 2.454 mL | 4.9081 mL | 9.8162 mL | 12.2702 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2454 mL | 1.227 mL | 2.454 mL | 4.9081 mL | 6.1351 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0491 mL | 0.2454 mL | 0.4908 mL | 0.9816 mL | 1.227 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0245 mL | 0.1227 mL | 0.2454 mL | 0.4908 mL | 0.6135 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
ML141(CID-2950007) is a potent, selective and reversible non-competitive inhibitor of Cdc42 GTPase(IC50=200 nM) with low micromolar potency and selectivity against other members of the Rho family of GTPases (Rac1, Rab2, Rab7). IC50 value: 200 nM [1] Target: Cdc42 inhibitor in vitro: In the primary HTS bead-based assay using 1 mM EDTA and 100 nM BODIPY-FL-GTP, potency for CID2950007 was IC50 = 2.6 and 5.4 μM for Cdc42 wild type and activated mutant, respectively [1]. ML141 exposure also enhanced the ability of TMX to suppress BLBC cell growth, through both induction of cell death and suppression of cell division [2]. in vivo: Treatment with ML141 + TMX caused a suppression of further tumour growth in vivo [2]. Parallel suppression of the conserved brain CDC42 activity by intracerebroventricular ML141 injection caused acute anxiety in mice [3]. using a pilocarpine-induced epileptic model, we found that pretreatment with ML141, a specific inhibitor of Cdc42, reduces seizure severity [4].
References:
[1]. Surviladze Z, et al. A Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Cdc42 GTPase. Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program
[2]. Chen HY, et al. Inhibition of redox/Fyn/c-Cbl pathway function by Cdc42 controls tumour initiation capacity and tamoxifen sensitivity in basal-like breast cancer cells. EMBO Mol Med. 2013 May;5(5):723-36.
[3]. Hanin G, et al. Competing targets of microRNA-608 affect anxiety and hypertension. Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Sep 1;23(17):4569-80.
[4]. Zhang Y, et al. Inhibition of the small GTPase Cdc42 in regulation of epileptic-seizure in rats. Neuroscience. 2015 Mar 19;289:381-91.
- Leukotriene B4
Catalog No.:BCC7322
CAS No.:71160-24-2
- (±)-Bay K 8644
Catalog No.:BCC3918
CAS No.:71145-03-4
- (E)-3-Acetoxy-5-methoxystilbene
Catalog No.:BCN4273
CAS No.:71144-78-0
- Meloxicam (Mobic)
Catalog No.:BCC3808
CAS No.:71125-38-7
- Bucindolol
Catalog No.:BCC7444
CAS No.:71119-11-4
- MRS 2578
Catalog No.:BCC4976
CAS No.:711019-86-2
- 5,8,4'-Trihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone 8-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1372
CAS No.:710952-13-9
- Griselinoside
Catalog No.:BCN4272
CAS No.:71035-06-8
- 1-Octacosanoyl glyceride
Catalog No.:BCN8190
CAS No.:71035-02-4
- Cathinone
Catalog No.:BCN1784
CAS No.:71031-15-7
- Digitoxin
Catalog No.:BCN5358
CAS No.:71-63-6
- Veratridine
Catalog No.:BCC7515
CAS No.:71-62-5
- Erythroxytriol P
Catalog No.:BCN4274
CAS No.:7121-99-5
- Schizandriside
Catalog No.:BCN6999
CAS No.:71222-06-5
- Obolactone
Catalog No.:BCN7190
CAS No.:712272-88-3
- Boc-Ala(2-pyridyl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3320
CAS No.:71239-85-5
- Salaspermic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7139
CAS No.:71247-78-4
- 2,5-Bis(5-tert-butyl-2-benzoxazolyl)thiophene
Catalog No.:BCC8503
CAS No.:7128-64-5
- Crotananine
Catalog No.:BCN2078
CAS No.:71295-28-8
- Cronaburmine
Catalog No.:BCN2072
CAS No.:71295-32-4
- (S)-3-Hydroxyphenylglycine
Catalog No.:BCC6605
CAS No.:71301-82-1
- 6(1H)-Azulenone, 2,3-dihydro-1,4-dimethyl
Catalog No.:BCN1371
CAS No.:71305-89-0
- Moclobemide (Ro 111163)
Catalog No.:BCC2322
CAS No.:71320-77-9
- Mcl1-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5405
CAS No.:713492-66-1
Assessment of potential factors associating with costs of hospitalizing cardiovascular diseases in 141 hospitals in Guangxi, China.[Pubmed:28301501]
PLoS One. 2017 Mar 16;12(3):e0173451.
BACKGROUND: The rising cost of healthcare is of great concern in China, as evidenced by the media features negative reports almost daily. However there are only a few studies from well-developed cities, like Beijing or Shanghai, and little is known about healthcare costs in rest of the country. In this study, we use hospitalization summary reports (HSRs) from admitted cardiovascular diseases patients in Guangxi hospitals during 2013-2016, and we investigate temporal trends of healthcare costs and associated factors. METHODS: By generalized additive model, we compute temporal trends of cost per stay (CPS), cost per day (CPD) and others. We then use generalized linear models to assess which factors associate with CPS and CPD. FINDINGS: Using a total of 760,000 HSRs, we find that CPS appears to be stabilized around $1040 until the middle of year 2015, before exhibiting a downward trend. Similarly, CPD exhibits similar stable pattern. Meanwhile, surgery-specific CPS showed an increase in year 2013-2014, and then stabilized. Drug costs account for over 1/3 of CPS, but they are gradually declining. Costs associated with physicians' and nurses' services represent less than 5% of CPS. We found that age, sex, marital status, occupation and payment methods are significantly associated with CPS or CPD. Interestingly, we found no association between patient ethnicity and these costs. However, we did find that minority patients use more secondary hospitals than Han patients. INTERPRETATIONS: Healthcare costs in Guangxi are stable, contrary to the rise portrayed by Chinese mass media. Several factors can be associated with healthcare costs, and these may be useful for developing evidence-based policies. In particular, there is a need to encourage more Han patients to seek care in primary and secondary hospitals.
Glycated lysine-141 in haptoglobin improves the diagnostic accuracy for type 2 diabetes mellitus in combination with glycated hemoglobin HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose.[Pubmed:28360826]
Clin Proteomics. 2017 Mar 28;14:10.
BACKGROUND: Recent epidemiological studies indicate that only 30-50% of undiagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients are identified using glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and elevated fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels. Thus, novel biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis are urgently needed for providing early and personalized treatment. METHODS: Here, we studied the glycation degrees of 27 glycation sites representing nine plasma proteins in 48 newly diagnosed male T2DM patients and 48 non-diabetic men matched for age (range 35-65 years). Samples were digested with trypsin and enriched for glycated peptides using boronic acid affinity chromatography. Quantification relied on mass spectrometry (multiple reaction monitoring) using isotope-labelled peptides as internal standard. RESULTS: The combination of glycated lysine-141 of haptoglobin (HP K141) and HbA1c provided a sensitivity of 94%, a specificity of 98%, and an accuracy of 96% to identify T2DM. A set of 15 features considering three glycation sites in human serum albumin, HP K141, and 11 routine laboratory measures of T2DM, metabolic syndrome, obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance provided a sensitivity of 98%, a specificity of 100%, and an accuracy of 99% for newly diagnosed T2DM patients. CONCLUSIONS: Our studies demonstrated the great potential of glycation sites in plasma proteins providing an additional diagnostic tool for T2DM and elucidating that the combination of these sites with HbA1c and FPG could improve the diagnosis of T2DM.
Characterization of a Cdc42 protein inhibitor and its use as a molecular probe.[Pubmed:23382385]
J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8531-43.
Cdc42 plays important roles in cytoskeleton organization, cell cycle progression, signal transduction, and vesicle trafficking. Overactive Cdc42 has been implicated in the pathology of cancers, immune diseases, and neuronal disorders. Therefore, Cdc42 inhibitors would be useful in probing molecular pathways and could have therapeutic potential. Previous inhibitors have lacked selectivity and trended toward toxicity. We report here the characterization of a Cdc42-selective guanine nucleotide binding lead inhibitor that was identified by high throughput screening. A second active analog was identified via structure-activity relationship studies. The compounds demonstrated excellent selectivity with no inhibition toward Rho and Rac in the same GTPase family. Biochemical characterization showed that the compounds act as noncompetitive allosteric inhibitors. When tested in cellular assays, the lead compound inhibited Cdc42-related filopodia formation and cell migration. The lead compound was also used to clarify the involvement of Cdc42 in the Sin Nombre virus internalization and the signaling pathway of integrin VLA-4. Together, these data present the characterization of a novel Cdc42-selective allosteric inhibitor and a related analog, the use of which will facilitate drug development targeting Cdc42-related diseases and molecular pathway studies that involve GTPases.


