(S)-3-HydroxyphenylglycineGroup I mGlu agonist, active isomer CAS# 71301-82-1 |
- I-BET-762
Catalog No.:BCC4474
CAS No.:1260907-17-2
- Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC1132
CAS No.:1268524-70-4
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- GSK1324726A
Catalog No.:BCC4038
CAS No.:1300031-52-0
- PFI-1 (PF-6405761)
Catalog No.:BCC2225
CAS No.:1403764-72-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 71301-82-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6604712 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H9NO3 | M.Wt | 167.16 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (<em>S</em>)-3H-PG | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in water | ||
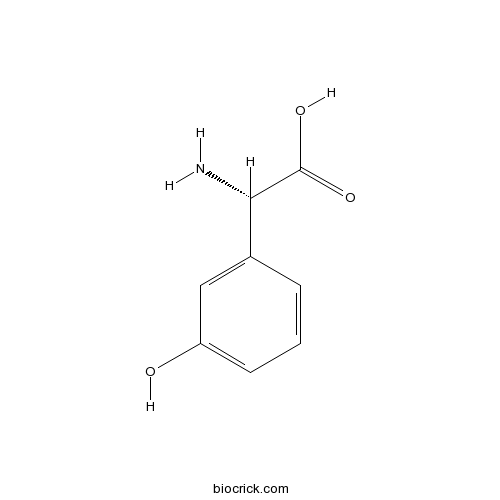
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-amino-2-(3-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC(=C1)O)C(C(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DQLYTFPAEVJTFM-ZETCQYMHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H9NO3/c9-7(8(11)12)5-2-1-3-6(10)4-5/h1-4,7,10H,9H2,(H,11,12)/t7-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Agonist at group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu1) having no effect at mGlu2 or mGlu4. (RS)-3-Hydroxyphenylglycine also available. |

(S)-3-Hydroxyphenylglycine Dilution Calculator

(S)-3-Hydroxyphenylglycine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.9823 mL | 29.9115 mL | 59.8229 mL | 119.6458 mL | 149.5573 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1965 mL | 5.9823 mL | 11.9646 mL | 23.9292 mL | 29.9115 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5982 mL | 2.9911 mL | 5.9823 mL | 11.9646 mL | 14.9557 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1196 mL | 0.5982 mL | 1.1965 mL | 2.3929 mL | 2.9911 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0598 mL | 0.2991 mL | 0.5982 mL | 1.1965 mL | 1.4956 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cronaburmine
Catalog No.:BCN2072
CAS No.:71295-32-4
- Crotananine
Catalog No.:BCN2078
CAS No.:71295-28-8
- 2,5-Bis(5-tert-butyl-2-benzoxazolyl)thiophene
Catalog No.:BCC8503
CAS No.:7128-64-5
- Salaspermic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7139
CAS No.:71247-78-4
- Boc-Ala(2-pyridyl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3320
CAS No.:71239-85-5
- Obolactone
Catalog No.:BCN7190
CAS No.:712272-88-3
- Schizandriside
Catalog No.:BCN6999
CAS No.:71222-06-5
- Erythroxytriol P
Catalog No.:BCN4274
CAS No.:7121-99-5
- ML 141
Catalog No.:BCC8092
CAS No.:71203-35-5
- Leukotriene B4
Catalog No.:BCC7322
CAS No.:71160-24-2
- (±)-Bay K 8644
Catalog No.:BCC3918
CAS No.:71145-03-4
- (E)-3-Acetoxy-5-methoxystilbene
Catalog No.:BCN4273
CAS No.:71144-78-0
- 6(1H)-Azulenone, 2,3-dihydro-1,4-dimethyl
Catalog No.:BCN1371
CAS No.:71305-89-0
- Moclobemide (Ro 111163)
Catalog No.:BCC2322
CAS No.:71320-77-9
- Mcl1-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5405
CAS No.:713492-66-1
- APETx2
Catalog No.:BCC6294
CAS No.:713544-47-9
- Jatropholone B
Catalog No.:BCC8192
CAS No.:71386-38-4
- 3-Methyl-GABA
Catalog No.:BCC6629
CAS No.:71424-95-8
- Plinabulin (NPI-2358)
Catalog No.:BCC5094
CAS No.:714272-27-2
- Methylecgonine
Catalog No.:BCN1908
CAS No.:7143-09-1
- Sylvestroside I
Catalog No.:BCN4163
CAS No.:71431-22-6
- TTNPB (Arotinoid Acid)
Catalog No.:BCC4874
CAS No.:71441-28-6
- Z-D-Asp(OtBu)-OH.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC2785
CAS No.:71449-08-6
- H-D-Val-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3147
CAS No.:7146-15-8
Metabotropic receptors in excitotoxicity: (S)-4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine ((S)-4C3HPG) protects against rat striatal quinolinic acid lesions.[Pubmed:8787843]
Neurosci Lett. 1995 Dec 29;202(1-2):109-12.
Striatal quinolinate lesions mimic many of the neuropathological characteristics of Huntington's disease. This excitotoxicity is mediated by combined activity of N-methyl-D-aspartate and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). Using recently developed phenylglycine derivatives, (S)-4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine ((S)-4C3HPG) and (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine ((+)-MCPG), we investigated the role of the different sub-classes of mGluRs in the in vivo excitotoxic process. (S)-4C3HPG (500 and 1000 nmol), co-injected with quinolinic acid, significantly reduced lesion volumes by 52 and 89%, respectively, whereas the same doses of (+)-MCPG had no effect on lesion size. The differential actions of these two drugs at Group 1 and Group 2 metabotropic receptors may explain their differential effects. These observations confirm the important role of mGluRs in excitotoxicity and identify them as promising targets for intervention.
(S)-4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine, an antagonist of metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) 1a and an agonist of mGluR2, protects against audiogenic seizures in DBA/2 mice.[Pubmed:8189254]
J Neurochem. 1994 Jun;62(6):2492-5.
The in vivo anticonvulsant effects and in vitro metabotropic glutamate receptor selectivity of (S)-4-carboxy-3-hydroxy-phenylglycine [(S)-4C3HPG] were examined. Intracerebroventricular injection of (S)-4C3HPG dose-dependently antagonized audiogenic-induced clonic and tonic convulsions in DBA/2 mice with ED50 values of 76 and 110-nmol per mouse, respectively. (S)-4C3HPG dose-dependently inhibited the spontaneously evoked epileptic spikes in a cingulate cortex-corpus callosum slice preparation. (S)-4C3HPG displaced the binding of [3H]glutamate in membranes prepared from baby hamster kidney (BHK) cells expressing the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR1a with an EC50 of 5 +/- 1 microM. (S)-4C3HPG dose-dependently antagonized glutamate-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in BHK cells expressing mGluR1a with an IC50 of 15 +/- 3 microM. (S)-4C3HPG was, however, an agonist at mGluR2 with an EC50 of 21 +/- 4 microM for inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP formation in BHK cells expressing the mGluR2. (S)-4C3HPG had no effects at mGluR4a. These data suggest that the anticonvulsant action of (S)-4C3HPG is mediated by combined antagonism of mGluR1a and agonism of mGluR2. These results suggest the importance of mGluR1a and/or mGluR2 in the control of epileptic activity.
(S)-4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine activates phosphatidyl inositol linked metabotropic glutamate receptors in different brain regions of the neonatal rat.[Pubmed:9460705]
Neurochem Int. 1998 Jan;32(1):77-85.
In the present investigation, effects of several agonists and antagonists of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) which are coupled to phosphatidyl inositol (PI) hydrolysis were evaluated in slices of neonatal rat hippocampus, striatum, cortex and cerebellum. The rank order of potency of agonists in the PI hydrolysis assay was identical in all brain regions: quisqualic acid (Quis) > (RS)-3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine (3,5-DHPG) > 1S, 3R-aminocyclopentane dicarboxylic acid (1S,3R-ACPD) >> L-glutamate (Glu). All agonists were equiefficacious in the four brain regions tested. The responses to 3,5-DHPG, a highly selective Class I mGluR agonist, were attenuated by (S)-4-carboxyphenylglycine ((S)-4CPG), (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine ((+)-MCPG) and 1-aminoindan-1,5-dicarboxylic acid (UPF-523) with a rank order of potency of (+)-MCPG > or = (S)-4CPG > or = UPF-523 in the different brain regions. These results suggest little selectivity among these putative mGluR antagonists in the different brain regions studied. Interestingly, (S)-4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine ((S)-4C3HPG), a compound reported to act as antagonist at Class I mGluRs, produced concentration-dependent increases in PI hydrolysis in all four brain regions suggesting that (S)-4C3HPG acts as an agonist. In striatum, hippocampus and cortex, (S)-4C3HPG was equiefficacious to Quis, 3,5-DHPG, 1S,3R-ACPD and Glu. However, in the cerebellum, (S)-4C3HPG displayed weak agonist activity (37% of that of a maximally effective concentration of Quis). The effects of (S)-4C3HPG in the PI hydrolysis assay appeared to be mediated by the activation of an mGluR subtype since it was significantly blocked by (S)-4CPG, an mGluR antagonist. In addition, the agonistic effects of (S)-4C3HPG appear to be unrelated to inhibition of [3H]-Glu uptake into rat hippocampal or cerebellar synaptosomes. These results demonstrate a unique pharmacological profile of (S)-4C3HPG which can be interpreted as (S)-4C3HPG being a highly selective mGluR5 agonist or alternatively, that the effects of (S)-4C3HPG may be mediated through a novel Class I mGluR subtype(s), yet to be identified.
Analysis of agonist and antagonist activities of phenylglycine derivatives for different cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes.[Pubmed:8182479]
J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3370-7.
The metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) consist of at least seven different subtypes and are coupled to intracellular signal transduction via G proteins. However, the lack of specific antagonists for the mGluRs limited the precise characterization of the role of the individual mGluRs. In this study, we investigated the agonist and antagonist activities of a series of phenylglycine derivatives for the mGluRs by examining their effects on the signal transduction of representative mGluR1, mGluR2, and mGluR4 subtypes expressed individually in Chinese hamster ovary cells. The phenylglycine derivatives examined included (S)- and (R)-forms of 3-hydroxyphenylglycine (3HPG), 4-carboxy-phenylglycine (4CPG), 4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine (4C3HPG), 3-carboxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycine (3C4HPG), and (+)- and (-)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (alpha M4CPG). Among these 10 compounds, (S)-3HPG acted as an agonist for mGluR1, while (S)-4C3HPG, (S)-3C4HPG, and (S)-4CPG served as effective agonists for mGluR2. The rank order of agonist potencies for mGluR2 was L-glutamate > (S)-4C3HPG > (S)-3C4HPG > (S)-4CPG. No other phenylglycine derivatives showed any definite agonist activity on either mGluR1 or mGluR2. Among the phenylglycine derivatives with no mGluR1 agonist activity, (S)-4C3HPG, (S)-3C4HPG, (S)-4CPG, and (+)-alpha M4CPG effectively antagonized the action of L-glutamate on mGluR1. The rank order of antagonist potencies was (S)-4C3HPG > or = (S)-4CPG > or = (+)-alpha M4CPG > (S)-3C4HPG. The Schild plot analysis indicated that (RS)-4C3HPG, (S)-4CPG, and (+)-alpha M4CPG all act as competitive antagonists for mGluR1 with pA2 values of 4.38, 4.46, and 4.38, respectively.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Phenylglycine derivatives as new pharmacological tools for investigating the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the central nervous system.[Pubmed:7680790]
Neuroscience. 1993 Feb;52(3):481-8.
The possible roles of G-protein coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors in central nervous function are currently the focus of intensive investigation. The complexity of effects produced by agonists at these receptors probably reflects the activity of a range of sub-types. The metabotropic glutamate receptors first described are linked to phospholipase C, mediating phosphoinositide hydrolysis and release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. A substance generally considered to be a selective agonist for these receptors is (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (ACPD). This substance not only stimulates phosphoinositide hydrolysis, but also inhibits cyclic AMP formation. A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors, incorporating both phospholipase C- and adenylcyclase-linked sub-types has been cloned. Various effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists on membrane ion fluxes and synaptic events have been reported, including neuronal depolarization and/or excitation, hyperpolarization, inhibition of Ca(2+)-dependent and voltage-gated K+ currents, potentiation of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced responses, depression of synaptic excitation and either induction or augmentation of long-term potentiation. To clarify the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in central nervous activity and to aid the characterization of the various receptor types that may be involved, a range of highly selective agonists and antagonists is required. To date, currently available antagonists such as L-2-amino-3-phosphonopropionate and L-aspartic acid-beta-hydroxamate appear to be unselective and insufficiently potent. We report here the actions of three phenylglycine derivatives, the particular agonist and/or antagonist properties of which may help to elucidate the roles of metabotropic glutamate receptors in central nervous activity.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)


