Plinabulin (NPI-2358)vascular disrupting agent CAS# 714272-27-2 |
- Reparixin
Catalog No.:BCC1885
CAS No.:266359-83-5
- Reparixin L-lysine salt
Catalog No.:BCC1886
CAS No.:266359-93-7
- SCH 527123
Catalog No.:BCC1932
CAS No.:473727-83-2
- AMD-070
Catalog No.:BCC1357
CAS No.:558447-26-0
- AMD-070 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1358
CAS No.:880549-30-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 714272-27-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9949641 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H20N4O2 | M.Wt | 336.39 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (148.64 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
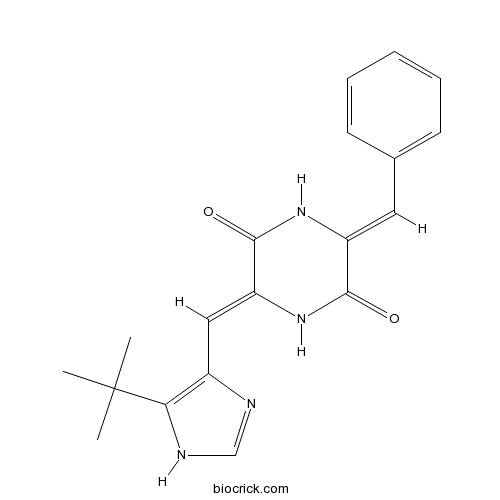
| Chemical Name | (3Z,6Z)-3-benzylidene-6-[(5-tert-butyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)methylidene]piperazine-2,5-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=C(N=CN1)C=C2C(=O)NC(=CC3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)N2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UNRCMCRRFYFGFX-TYPNBTCFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H20N4O2/c1-19(2,3)16-13(20-11-21-16)10-15-18(25)22-14(17(24)23-15)9-12-7-5-4-6-8-12/h4-11H,1-3H3,(H,20,21)(H,22,25)(H,23,24)/b14-9-,15-10- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Plinabulin (NPI-2358), a vascular disrupting agent (VDA), is an inhibitor of tubulin-depolymerizing with IC50 of 9.8~18 nM in tumor cells. | |||||
| Targets | Tubulin | |||||
| IC50 | 9.8 nM-18 nM | |||||

Plinabulin (NPI-2358) Dilution Calculator

Plinabulin (NPI-2358) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9727 mL | 14.8637 mL | 29.7274 mL | 59.4548 mL | 74.3185 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5945 mL | 2.9727 mL | 5.9455 mL | 11.891 mL | 14.8637 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2973 mL | 1.4864 mL | 2.9727 mL | 5.9455 mL | 7.4318 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0595 mL | 0.2973 mL | 0.5945 mL | 1.1891 mL | 1.4864 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0297 mL | 0.1486 mL | 0.2973 mL | 0.5945 mL | 0.7432 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
The IC50 values of NPI-2358 is 9.8 ± 2.4 nmol/l, 18 ± 5 nmol/l, 13 ± 1 nmol/l, 14 ± 2 nmol/l, 18 ± 1 nmol/l and 11 nmol/l for HT-29, DU 145, PC-3, MDA-MB-231, NCl-H292 and Jurkat cell lines, respectively[1].
Plinabulin (NPI-2358) is a vascular disrupting agent which binds to the colchicine-binding site of tubulin. NPI-2358 could destabilize tumor vascular endothelial architectural resulting in selective collapse of established tumor vasculature [1].
In vitro: NPI-2358 exhibited anti-tumor activity against various human tumor cell lines. In proliferating human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), administration of NPI-2358 at 10 nmol/l induced tubulin depolymerization within 30 min [1]. In an in-vitro model of tumor vascular collapse, NPI-2358 increased HUVEC monolayer permeability in a dose-dependent manner. Plinabulin had also shown the in-vitro cytotoxic activity with IC50 values of 11 ± 5 nmol/l and 4.3 ± 2.2 nmol/l for MES-SA and HL-60 tumor cell lines, respectively[1].
In vivo: In the foot implanted C3H mammary carcinomas or leg implanted KHT sarcomas mice model, 7.5 mg/kg plinabulin (intraperitoneally injected) significantly reduced the transfer constant (K(trans)) and the initial area under curve (IAUC) within 1 hour after injection, reaching a lowest point at 3 h, but returning to normal within 24 h. A dose-dependent decrease in IAUC and K(trans) was seen at 3 h. 12.5 mg/kg and 1.5 mg/kg NPI-2358 showed significant anti-tumour effects in the C3H tumours and the KHT sarcoma, respectively .
Clinical trials: In patients evaluated at a dose of 30 mg/m?, tumor blood flow (Ktrans) showed a 16% to 82% decrease. The half-life of NPI-2358 was 6.06 ± 3.03 hours, clearance was 30.50 ± 22.88 L/h, and distributive volume was 211 ± 67.9 L.
References:
Nicholson B1, Lloyd GK, Miller BR, Palladino MA, Kiso Y, Hayashi Y, Neuteboom ST. NPI-2358 is a tubulin-depolymerizing agent: in-vitro evidence for activity as a tumor vascular-disrupting agent.Anticancer Drugs. 2006 Jan; 17(1):25-31.
Bertelsen L B, Shen Y Y, Nielsen T, et al. Vascular effects of plinabulin (NPI-2358) and the influence on tumour response when given alone or combined with radiation[J]. International journal of radiation biology, 2011, 87(11): 1126-1134.
Millward M, Mainwaring P, Mita A, et al. Phase 1 study of the novel vascular disrupting agent plinabulin (NPI-2358) and docetaxel[J]. Investigational new drugs, 2012, 30(3): 1065-1073.
- 3-Methyl-GABA
Catalog No.:BCC6629
CAS No.:71424-95-8
- Jatropholone B
Catalog No.:BCC8192
CAS No.:71386-38-4
- APETx2
Catalog No.:BCC6294
CAS No.:713544-47-9
- Mcl1-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5405
CAS No.:713492-66-1
- Moclobemide (Ro 111163)
Catalog No.:BCC2322
CAS No.:71320-77-9
- 6(1H)-Azulenone, 2,3-dihydro-1,4-dimethyl
Catalog No.:BCN1371
CAS No.:71305-89-0
- (S)-3-Hydroxyphenylglycine
Catalog No.:BCC6605
CAS No.:71301-82-1
- Cronaburmine
Catalog No.:BCN2072
CAS No.:71295-32-4
- Crotananine
Catalog No.:BCN2078
CAS No.:71295-28-8
- 2,5-Bis(5-tert-butyl-2-benzoxazolyl)thiophene
Catalog No.:BCC8503
CAS No.:7128-64-5
- Salaspermic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7139
CAS No.:71247-78-4
- Boc-Ala(2-pyridyl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3320
CAS No.:71239-85-5
- Methylecgonine
Catalog No.:BCN1908
CAS No.:7143-09-1
- Sylvestroside I
Catalog No.:BCN4163
CAS No.:71431-22-6
- TTNPB (Arotinoid Acid)
Catalog No.:BCC4874
CAS No.:71441-28-6
- Z-D-Asp(OtBu)-OH.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC2785
CAS No.:71449-08-6
- H-D-Val-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3147
CAS No.:7146-15-8
- Vinorelbine
Catalog No.:BCN2543
CAS No.:71486-22-1
- AC480 (BMS-599626)
Catalog No.:BCC1252
CAS No.:714971-09-2
- Safrolglycol
Catalog No.:BCN4596
CAS No.:7154-01-0
- NSC 319726
Catalog No.:BCC2242
CAS No.:71555-25-4
- 3alpha,6beta-Ditigloyloxytropan-7beta-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1370
CAS No.:7159-86-6
- D-(-)-threo-2-Amino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-propanediol
Catalog No.:BCC8924
CAS No.:716-61-0
- Biphenyl-3-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8878
CAS No.:716-76-7
Vascular effects of plinabulin (NPI-2358) and the influence on tumour response when given alone or combined with radiation.[Pubmed:21815749]
Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Nov;87(11):1126-34.
PURPOSE: This study investigated the anti-tumour effects of the novel vascular disrupting agent Plinabulin (NPI-2358) when given alone or combined with radiation. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Foot implanted C3H mammary carcinomas or leg implanted KHT sarcomas were used, with plinabulin injected intraperitoneally. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) measurements were made with gadolinium-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA) on a 7-tesla magnet. Treatment response was assessed using regrowth delay (C3H tumours), clonogenic survival (KHT sarcomas) or histological estimates of necrosis for both models. RESULTS: Plinabulin (7.5 mg/kg) significantly reduced the initial area under curve (IAUC) and the transfer constant (K(trans)) within 1 hour after injection, reaching a nadir at 3 h, but returning to normal within 24 h. A dose-dependent decrease in IAUC and K(trans), was seen at 3 h. No significant anti-tumour effects were observed in the C3H tumours until doses of 12.5 mg/kg were achieved, but started at 1.5 mg/kg in the KHT sarcoma. Irradiating tumours 1 h after injecting plinabulin enhanced response in both models. CONCLUSIONS: Plinabulin induced a time- and dose-dependent decrease in tumour perfusion. The KHT sarcoma was more sensitive than the C3H tumour to the anti-tumour effects of plinabulin, while radiation response was enhanced in both models.
Phase 1 first-in-human trial of the vascular disrupting agent plinabulin(NPI-2358) in patients with solid tumors or lymphomas.[Pubmed:21138873]
Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 1;16(23):5892-9.
PURPOSE: Plinabulin (NPI-2358) is a vascular disrupting agent that elicits tumor vascular endothelial architectural destabilization leading to selective collapse of established tumor vasculature. Preclinical data indicated plinabulin has favorable safety and antitumor activity profiles, leading to initiation of this clinical trial to determine the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) and assess the safety, pharmacokinetics, and biologic activity of plinabulin in patients with advanced malignancies. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Patients received a weekly infusion of plinabulin for 3 of every 4 weeks. A dynamic accelerated dose titration method was used to escalate the dose from 2 mg/m(2) to the RP2D, followed by enrollment of an RP2D cohort. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and cardiovascular assessments were conducted, and Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) scans were performed to estimate changes in tumor blood flow. RESULTS: Thirty-eight patients were enrolled. A dose of 30 mg/m(2) was selected as the RP2D based on the adverse events of nausea, vomiting, fatigue, fever, tumor pain, and transient blood pressure elevations, with DCE-MRI indicating decreases in tumor blood flow (Ktrans) from 13.5 mg/m(2) (defining a biologically effective dose) with a 16% to 82% decrease in patients evaluated at 30 mg/m(2). Half-life was 6.06 +/- 3.03 hours, clearance was 30.50 +/- 22.88 L/h, and distributive volume was 211 +/- 67.9 L. CONCLUSIONS: At the RP2D of 30 mg/m(2), plinabulin showed a favorable safety profile, while eliciting biological effects as evidenced by decreases in tumor blood flow, tumor pain, and other mechanistically relevant adverse events. On the basis of these results additional clinical trials were initiated with plinabulin in combination with standard chemotherapy agents.
Phase 1 study of the novel vascular disrupting agent plinabulin (NPI-2358) and docetaxel.[Pubmed:21327495]
Invest New Drugs. 2012 Jun;30(3):1065-73.
BACKGROUND: Plinabulin (NPI-2358) is a vascular disrupting agent (VDA) that destabilizes tumor vascular endothelial cell architecture resulting in selective collapse of established tumor vasculature producing anti-tumor activity alone or in combination with cytotoxic agents. The objective of this study was to assess the recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D) of plinabulin combined with docetaxel. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Patients received 75 mg/m(2) docetaxel on day 1 and plinabulin on days 1 and 8 intravenously in 21 day cycles. Plinabulin was escalated from the biologically effective dose (BED) of 13.5 mg/m(2) to the standard single agent dose of 30 mg/m(2) using a "3+3" design. RESULTS: Thirteen patients were enrolled. Adverse events were consistent with those of both agents alone. Fatigue, pain, nausea, diarrhea and vomiting were the most common events. One dose limiting toxicity of nausea, vomiting, dehydration and neutropenia occurred. The RP2D was 30 mg/m(2) of plinabulin with 75 mg/m(2) docetaxel. Pharmacokinetics did not indicate drug-drug interactions. Of the 8 patients with NSCLC evaluable for response, 2 achieved a partial response and 4 demonstrated lesser decreases in tumor measurements. CONCLUSIONS: The combination of full doses of plinabulin and docetaxel is tolerable. With encouraging antitumor activity, this supported further development of this combination.


