Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1BET bromodomain inhibitor CAS# 1268524-70-4 |
- GSK 525768A
Catalog No.:BCC1603
CAS No.:1260530-25-3
- (-)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC3603
CAS No.:1268524-71-5
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- PFI-1 (PF-6405761)
Catalog No.:BCC2225
CAS No.:1403764-72-6
- CPI-203
Catalog No.:BCC4099
CAS No.:1446144-04-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1268524-70-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 46907787 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H25ClN4O2S | M.Wt | 456.99 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | JQ1 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 45 mg/mL (98.47 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
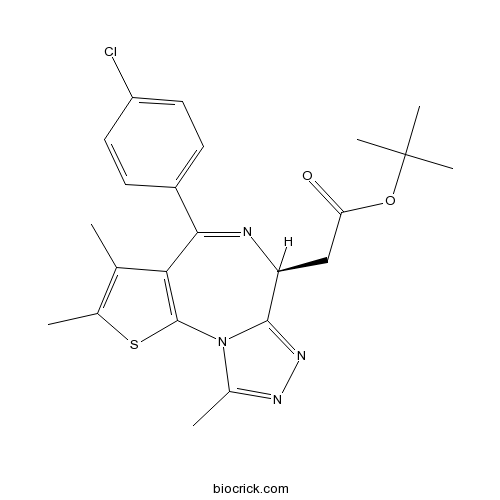
| SMILES | CC1=C(SC2=C1C(=NC(C3=NN=C(N32)C)CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)C4=CC=C(C=C4)Cl)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DNVXATUJJDPFDM-KRWDZBQOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H25ClN4O2S/c1-12-13(2)31-22-19(12)20(15-7-9-16(24)10-8-15)25-17(11-18(29)30-23(4,5)6)21-27-26-14(3)28(21)22/h7-10,17H,11H2,1-6H3/t17-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, high affinity, selective BET bromodomain inhibitor (IC50 values are 17.7, 32.6, 76.9 and 12942 nM for BRD2 (N-terminal (N)), BRD4 (C-terminal (C)), BRD4 (N) and CREBBP respectively; Kd values are 49, 59.5, 82, 90.1, 128 and 190 nM for BRD4 (N), BRD3 (N), BRD3 (C), BRD4 (C), BRD2 (N) and BRDT (N) respectively). Induces squamous differentiation in NUT midline carcinoma (NMC) cell lines; inhibits tumor growth in NMC xenograft models in vivo. Exhibits reversible contraceptive effects in germ cells from male mice. Inactive analog (-)-JQ1 available. |

Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1 Dilution Calculator

Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1882 mL | 10.9412 mL | 21.8823 mL | 43.7646 mL | 54.7058 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4376 mL | 2.1882 mL | 4.3765 mL | 8.7529 mL | 10.9412 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2188 mL | 1.0941 mL | 2.1882 mL | 4.3765 mL | 5.4706 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0438 mL | 0.2188 mL | 0.4376 mL | 0.8753 mL | 1.0941 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0219 mL | 0.1094 mL | 0.2188 mL | 0.4376 mL | 0.5471 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
JQ1 induces 3/7-mediated apoptosis and DNA damage response in p53-wild-type (OCI)-AML3 cell lines where it possibly sensitizes AML cells to p53-mediated cell death. A mechanism has been proposed that JQ1 is activated in OCI-AML3 cells preventing BRD4-mediated recruitment of p53 to chromatin targets and eventually leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a c-MYC-independent manner.
Abstract
The affinities of acetylated histone tails and JQ1 to ten different BRD4 BD1 mutants were analyzed by several complementary biochemical and biophysical methods, in which W81, Y97, N140 and M149 play similarly important roles in the recognition of both.
Abstract
JQ1, an inhibitor of MYC expression, exhibits different inhibition in tumor cells where it decreased ~90% MYC transcription in BL cells and exhibited lesser inhibition in several non-BL cells possibly due to requirements of Brd4, transcription factors (such as Gdown1 and MED26) and other unknown cell specific factors.
Abstract
The critical role of BET proteins in macrophage inflammatory responses has been demonstrated in studies using small interfering RNA knockdown and JQ1 where Brad2 and brd4 doesn’t physically associated with the promoters of inflammatory cytokine genes in macrophages following the inhibition of BET by JQ1. JQ1 reduces the production of cytokine in vitro and weakens the “cytokine storm” in endotoxemic mice through decreasing IL-6 and TNF-α levels while rescuing mice from LPS-induced death.
Abstract
JQ1 dissociates Brd4 from the HIV promoter, synergizes with another latency activator prostratin and activates viral latency without inducing global T cell activation, which allow it and other closely related compounds as well as their antagonization of Brd4 to be used as effective agents/strategies to eliminating latent HIV in further investigations.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1 is a potent and highly specific inhibitor for the BET (bromodomain and extra-terminal) family of bromodomains. (+)-JQ1 binds to BRD4 bromodomains 1 and 2 with Kd values of ~ 50 and 90 nM, respectively. The binding is competitive with acetyl lysine. (+)-JQ1 can be a useful chemical probe to investigate the role of BET bromodomains in the transcriptional regulation of oncogenesis.
JQ1 exhibited strong dose-and time- dependent inhibition of BRDT and could significantly diminish the activity of a close structural relative of BRDT. A close look at JQ1 bound BRDT confirmed that the acetyl-lysine recognition site of BRDT was blocked. [1]
JQ1 does not produce sedative or anxiolytic effects and is instead a potent and selective inhibitor of the bromodomain testis-specific protein BRDT [2], which is essential for chromatin remodeling during spermatogenesis. By blocking BRDT, JQ1 effectively blocks the production of sperm in the testes and consequently produces effective contraception, without the negative side effects associated with previously researched hormonal contraceptives for men.
References:
1. Matzuk, Martin M., et al. "Small-molecule inhibition of BRDT for male contraception." Cell 150.4 (2012): 673-684. 2. Filippakopoulos, P.; Qi, J.; Picaud, S.; Shen, Y.; Smith, W. B.; Fedorov, O.; Morse, E. M.; Keates, T. et al. (2010). "Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains". Nature 468 (7327): 1067–1073.
- 8alpha-Acetoxyarglabin
Catalog No.:BCN7315
CAS No.:126829-70-7
- 13-Acetoxy-3beta-hydroxygermacra-1(10)E,4E,7(11)-trien-12,6alpha-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7314
CAS No.:126829-66-1
- 5,7,3'-Trihydroxy-4'-methoxy-8-prenylflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN1590
CAS No.:1268140-15-3
- Ulipristal acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4068
CAS No.:126784-99-4
- Sventenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3923
CAS No.:126778-79-8
- GR 89696 fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC7083
CAS No.:126766-32-3
- Sarafotoxin S6a
Catalog No.:BCC5834
CAS No.:126738-34-9
- Acetylsventenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4849
CAS No.:126737-42-6
- Tilifodiolide
Catalog No.:BCN6145
CAS No.:126724-95-6
- Gancaonin I
Catalog No.:BCN7144
CAS No.:126716-36-7
- Gancaonin G
Catalog No.:BCN6837
CAS No.:126716-34-5
- Isoaltenuene
Catalog No.:BCN7313
CAS No.:126671-80-5
- (-)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC3603
CAS No.:1268524-71-5
- MC 1046
Catalog No.:BCC1733
CAS No.:126860-83-1
- Ssioriside
Catalog No.:BCN6146
CAS No.:126882-53-9
- 3-Methoxy-5-heneicosylphenol
Catalog No.:BCN6147
CAS No.:126882-76-6
- MK 1903
Catalog No.:BCC6242
CAS No.:1268882-43-4
- LGX818
Catalog No.:BCC4184
CAS No.:1269440-17-6
- Sar-[D-Phe8]-des-Arg9-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5996
CAS No.:126959-88-4
- Methylenedihydrotanshinquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3221
CAS No.:126979-81-5
- Tetrahydro tanshinone I
Catalog No.:BCN2602
CAS No.:126979-84-8
- CDK inhibitor II
Catalog No.:BCC1464
CAS No.:1269815-17-9
- 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptan-3-yl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6586
CAS No.:1269839-24-8
- 1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptane-3,5-diyl diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6572
CAS No.:1269839-26-0
PD-L1 Is a Therapeutic Target of the Bromodomain Inhibitor JQ1 and, Combined with HLA Class I, a Promising Prognostic Biomarker in Neuroblastoma.[Pubmed:28270499]
Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 1;23(15):4462-4472.
Purpose: This study sought to evaluate the expression of programmed cell death-ligand-1 (PD-L1) and HLA class I on neuroblastoma cells and programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG3) on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes to better define patient risk stratification and understand whether this tumor may benefit from therapies targeting immune checkpoint molecules.Experimental Design:In situ IHC staining for PD-L1, HLA class I, PD-1, and LAG3 was assessed in 77 neuroblastoma specimens, previously characterized for tumor-infiltrating T-cell density and correlated with clinical outcome. Surface expression of PD-L1 was evaluated by flow cytometry and IHC in neuroblastoma cell lines and tumors genetically and/or pharmacologically inhibited for MYC and MYCN. A dataset of 477 human primary neuroblastomas from GEO and ArrayExpress databases was explored for PD-L1, MYC, and MYCN correlation.Results: Multivariate Cox regression analysis demonstrated that the combination of PD-L1 and HLA class I tumor cell density is a prognostic biomarker for predicting overall survival in neuroblastoma patients (P = 0.0448). MYC and MYCN control the expression of PD-L1 in neuroblastoma cells both in vitro and in vivo Consistently, abundance of PD-L1 transcript correlates with MYC expression in primary neuroblastoma.Conclusions: The combination of PD-L1 and HLA class I represents a novel prognostic biomarker for neuroblastoma. Pharmacologic inhibition of MYCN and MYC may be exploited to target PD-L1 and restore an efficient antitumor immunity in high-risk neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res; 23(15); 4462-72. (c)2017 AACR.
The BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells by upregulating p21.[Pubmed:28143717]
Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 10;391:141-151.
Radiotherapy is an important treatment modality in the management of locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, radioresistance markedly impairs its efficacy in clinic. Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) bromodomain inhibitors have demonstrated dramatic antitumor activity in several preclinical human cancer models. In this study, we investigated for the first time the effect of JQ1, a novel BET bromodomain inhibitor, on tumor cell radiosensitivity of NSCLC in vitro and in vivo. Our results demonstrated that JQ1 significantly enhanced the effect of irradiation in NSCLC cell lines through a c-myc-independent mechanism. The notable findings in response to this combined treatment were prolonged delay in IR-induced DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair, induced robust G2/M checkpoint arrest and increased cell apoptosis. Additional investigations revealed that induction of p21 played an important role in its radiosensitizing effects. In conclusion, these results suggested that BET bromodomain inhibition might offer a potential strategy for enhancing the effects of radiotherapy and reducing radioresistance.
Gene expression profiling of patient-derived pancreatic cancer xenografts predicts sensitivity to the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1: implications for individualized medicine efforts.[Pubmed:28275007]
EMBO Mol Med. 2017 Apr;9(4):482-497.
c-MYC controls more than 15% of genes responsible for proliferation, differentiation, and cellular metabolism in pancreatic as well as other cancers making this transcription factor a prime target for treating patients. The transcriptome of 55 patient-derived xenografts show that 30% of them share an exacerbated expression profile of MYC transcriptional targets (MYC-high). This cohort is characterized by a high level of Ki67 staining, a lower differentiation state, and a shorter survival time compared to the MYC-low subgroup. To define classifier expression signature, we selected a group of 10 MYC target transcripts which expression is increased in the MYC-high group and six transcripts increased in the MYC-low group. We validated the ability of these markers panel to identify MYC-high patient-derived xenografts from both: discovery and validation cohorts as well as primary cell cultures from the same patients. We then showed that cells from MYC-high patients are more sensitive to JQ1 treatment compared to MYC-low cells, in monolayer, 3D cultured spheroids and in vivo xenografted tumors, due to cell cycle arrest followed by apoptosis. Therefore, these results provide new markers and potentially novel therapeutic modalities for distinct subgroups of pancreatic tumors and may find application to the future management of these patients within the setting of individualized medicine clinics.
Small-molecule inhibition of BRD4 as a new potent approach to eliminate leukemic stem- and progenitor cells in acute myeloid leukemia AML.[Pubmed:23249862]
Oncotarget. 2012 Dec;3(12):1588-99.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a life-threatening stem cell disease characterized by uncontrolled proliferation and accumulation of myeloblasts. Using an advanced RNAi screen-approach in an AML mouse model we have recently identified the epigenetic 'reader' BRD4 as a promising target in AML. In the current study, we asked whether inhibition of BRD4 by a small-molecule inhibitor, JQ1, leads to growth-inhibition and apoptosis in primary human AML stem- and progenitor cells. Primary cell samples were obtained from 37 patients with freshly diagnosed AML (n=23) or refractory AML (n=14). BRD4 was found to be expressed at the mRNA and protein level in unfractionated AML cells as well as in highly enriched CD34(+)/CD38(-) and CD34(+)/CD38(+) stem- and progenitor cells in all patients examined. In unfractionated leukemic cells, submicromolar concentrations of JQ1 induced major growth-inhibitory effects (IC(5)(0) 0.05-0.5 microM) in most samples, including cells derived from relapsed or refractory patients. In addition, JQ1 was found to induce apoptosis in CD34+/CD38(-) and CD34(+)/CD38(+) stem- and progenitor cells in all donors examined as evidenced by combined surface/Annexin-V staining. Moreover, we were able to show that JQ1 synergizes with ARA-C in inducing growth inhibition in AML cells. Together, the BRD4-targeting drug JQ1 exerts major anti-leukemic effects in a broad range of human AML subtypes, including relapsed and refractory patients and all relevant stem- and progenitor cell compartments, including CD34(+)/CD38(-) and CD34(+)/CD38(+) AML cells. These results characterize BRD4-inhibition as a promising new therapeutic approach in AML which should be further investigated in clinical trials.
Small-molecule inhibition of BRDT for male contraception.[Pubmed:22901802]
Cell. 2012 Aug 17;150(4):673-84.
A pharmacologic approach to male contraception remains a longstanding challenge in medicine. Toward this objective, we explored the spermatogenic effects of a selective small-molecule inhibitor (JQ1) of the bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) subfamily of epigenetic reader proteins. Here, we report potent inhibition of the testis-specific member BRDT, which is essential for chromatin remodeling during spermatogenesis. Biochemical and crystallographic studies confirm that occupancy of the BRDT acetyl-lysine binding pocket by JQ1 prevents recognition of acetylated histone H4. Treatment of mice with JQ1 reduced seminiferous tubule area, testis size, and spermatozoa number and motility without affecting hormone levels. Although JQ1-treated males mate normally, inhibitory effects of JQ1 evident at the spermatocyte and round spermatid stages cause a complete and reversible contraceptive effect. These data establish a new contraceptive that can cross the blood:testis boundary and inhibit bromodomain activity during spermatogenesis, providing a lead compound targeting the male germ cell for contraception.
Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains.[Pubmed:20871596]
Nature. 2010 Dec 23;468(7327):1067-73.
Epigenetic proteins are intently pursued targets in ligand discovery. So far, successful efforts have been limited to chromatin modifying enzymes, or so-called epigenetic 'writers' and 'erasers'. Potent inhibitors of histone binding modules have not yet been described. Here we report a cell-permeable small molecule (JQ1) that binds competitively to acetyl-lysine recognition motifs, or bromodomains. High potency and specificity towards a subset of human bromodomains is explained by co-crystal structures with bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) family member BRD4, revealing excellent shape complementarity with the acetyl-lysine binding cavity. Recurrent translocation of BRD4 is observed in a genetically-defined, incurable subtype of human squamous carcinoma. Competitive binding by JQ1 displaces the BRD4 fusion oncoprotein from chromatin, prompting squamous differentiation and specific antiproliferative effects in BRD4-dependent cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models. These data establish proof-of-concept for targeting protein-protein interactions of epigenetic 'readers', and provide a versatile chemical scaffold for the development of chemical probes more broadly throughout the bromodomain family.


