Methyl pentadecanoateCAS# 7132-64-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 7132-64-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23518.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H32O2 | M.Wt | 256.43 |
| Type of Compound | Aliphatics | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | methyl pentadecanoate | ||
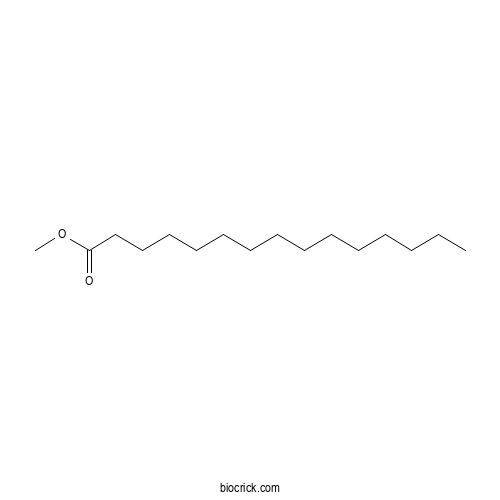
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XIUXKAZJZFLLDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H32O2/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16(17)18-2/h3-15H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Methyl pentadecanoate Dilution Calculator

Methyl pentadecanoate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8997 mL | 19.4985 mL | 38.997 mL | 77.994 mL | 97.4925 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7799 mL | 3.8997 mL | 7.7994 mL | 15.5988 mL | 19.4985 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.39 mL | 1.9498 mL | 3.8997 mL | 7.7994 mL | 9.7492 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.078 mL | 0.39 mL | 0.7799 mL | 1.5599 mL | 1.9498 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.039 mL | 0.195 mL | 0.39 mL | 0.7799 mL | 0.9749 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Saikogenin A
Catalog No.:BCX1580
CAS No.:5092-09-1
- 3-epi-Pumiloside
Catalog No.:BCX1579
CAS No.:126624-21-3
- 2'-Deoxyadenosine monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCX1578
CAS No.:16373-93-6
- Uvarigranol F
Catalog No.:BCX1577
CAS No.:176598-10-0
- 3-Hydroxy-3-methylpentanedioic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1576
CAS No.:503-49-1
- Gelsemicine
Catalog No.:BCX1575
CAS No.:6887-28-1
- Hydroxyl-γ-isosanshool
Catalog No.:BCX1574
CAS No.:127514-62-9
- Uridine diphosphate xylose
Catalog No.:BCX1573
CAS No.:3616-06-6
- Uridine diphosphate rhamnose
Catalog No.:BCX1572
CAS No.:1955-26-6
- Trisodium UDP-glucuronic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1571
CAS No.:63700-19-6
- Escin Ie
Catalog No.:BCX1570
CAS No.:1613506-26-5
- α-Sanshool
Catalog No.:BCX1569
CAS No.:504-97-2
- Phosphatidylserine
Catalog No.:BCX1582
CAS No.:51446-62-9
- 4-(3-Oxobutyl)phenyl 6-O-[(2E)-3-phenyl-2-propenoyl]-2-O-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1583
CAS No.:356517-93-6
- Bacdanol
Catalog No.:BCX1584
CAS No.:28219-61-6
- β-Sanshool
Catalog No.:BCX1585
CAS No.:10076-00-3
- Timosaponin H1
Catalog No.:BCX1586
CAS No.:288142-06-3
- Trikamsteroside A
Catalog No.:BCX1587
CAS No.:942916-76-9
- Thalictricoside
Catalog No.:BCX1588
CAS No.:649758-25-8
- HuangjiangSu A
Catalog No.:BCX1589
CAS No.:1026020-27-8
- Telephiose A
Catalog No.:BCX1590
CAS No.:297749-29-2
- Wuweizidilactone A
Catalog No.:BCX1591
CAS No.:945610-99-1
- Daphneticin
Catalog No.:BCX1592
CAS No.:83327-22-4
- Telephiose C
Catalog No.:BCX1593
CAS No.:297749-31-6
Chemical Constituents and in vitro Antibacterial Activity of Fixed Oils from Different Parts of Bridelia stipularis (L.) Blume.[Pubmed:38193369]
Pak J Biol Sci. 2023 Oct;26(11):549-556.
<b>Background and Objective:</b> Fixed oils used in traditional therapies also called volatile oils are generally aromatic oils obtained by the steam or hydrodistillation of plants. Different parts of plants have been used to obtain fixed oils. This study estimates the chemical constituents and <i>in vitro</i> antibacterial activity of fixed oils extracted by petroleum ether from the leaves, roots, stems and fruit part of <i>Bridelia stipularis</i> (L.). <b>Materials and Methods:</b> The natural fatty acids were extracted from different parts of <i>B. stipularis</i> by using petroleum ether. The fixed oils were studied by gas chromatography-mass spectrophotometry. The antibacterial test was carried out by the agar disc diffusion method. A Student's t-test was computed for the statistical significance of the results. <b>Results:</b> It showed 10 compounds from the leaf and 5 compounds from the stem. In both cases, the major components were methyl decanoate 93.56 and 74.98%, respectively. From the root parts, 6 compounds were identified in which the major compound was methyl linolelaidate (36.86%). Two compounds were identified from the fruit part and the major portion was Methyl pentadecanoate (98.20%). The <i>in vitro</i> antibacterial potentials of the oils were tested against four pathogenic bacteria. Among the four fixed oils, the stem, leaf and root showed the strongest activity against <i>E. coli</i> (30, 21 and 15 mm). On the other hand, fruit fixed oil showed the highest zone of inhibition against <i>Bacillus cereus</i> (25 mm). <b>Conclusion:</b> The fixed oils of <i>B. stipularis</i> plant have the potential to be applied as an antibacterial agent, which can be selected for further analysis and can be used to discover bioactive natural products that may serve as leads in the development of new pharmaceuticals that address unmet therapeutic needs.


