PPY ABl kinases inhibitor CAS# 875634-01-8 |
- Imatinib Mesylate (STI571)
Catalog No.:BCC1115
CAS No.:220127-57-1
- Dasatinib (BMS-354825)
Catalog No.:BCC1281
CAS No.:302962-49-8
- Saracatinib (AZD0530)
Catalog No.:BCC1166
CAS No.:379231-04-6
- Bosutinib (SKI-606)
Catalog No.:BCC1167
CAS No.:380843-75-4
- DPH
Catalog No.:BCC1538
CAS No.:484049-04-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 875634-01-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16750094 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H20N4O2 | M.Wt | 372.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | PPY-A | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
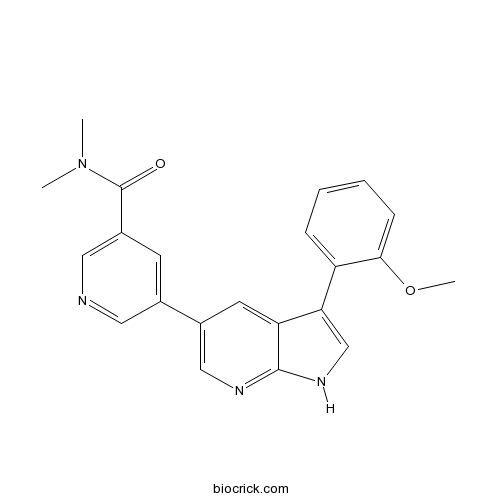
| Chemical Name | 5-[3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl]-N,N-dimethylpyridine-3-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)C(=O)C1=CN=CC(=C1)C2=CN=C3C(=C2)C(=CN3)C4=CC=CC=C4OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GYQRHHQPEMOLKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H20N4O2/c1-26(2)22(27)16-8-14(10-23-11-16)15-9-18-19(13-25-21(18)24-12-15)17-6-4-5-7-20(17)28-3/h4-13H,1-3H3,(H,24,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent inhibitor of T315l mutant and wild-type Abl kinases (IC50 values are 9 and 20 nM, respectively). Inhibits growth of cells transformed with either the Bcr-Abl T315l mutant or wild-type Bcr-Abl gene. |

PPY A Dilution Calculator

PPY A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6851 mL | 13.4257 mL | 26.8514 mL | 53.7028 mL | 67.1285 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.537 mL | 2.6851 mL | 5.3703 mL | 10.7406 mL | 13.4257 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2685 mL | 1.3426 mL | 2.6851 mL | 5.3703 mL | 6.7129 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0537 mL | 0.2685 mL | 0.537 mL | 1.0741 mL | 1.3426 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0269 mL | 0.1343 mL | 0.2685 mL | 0.537 mL | 0.6713 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
gene.Crystal structure of the T315I mutant of AbI kinase. Zhou et al.Chem.Biol.Drug.Des., 2007;70:171 Inhibitors of ABL and the ABL-T315I mutation. Noronha et al.Curr.Top.Med.Chem., 2008;8:905
- Kelampayoside A
Catalog No.:BCN4422
CAS No.:87562-76-3
- Randaiol
Catalog No.:BCN4002
CAS No.:87562-14-9
- ent-14,15-Dinor-13-oxolabda-8(17),11-dien-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1319
CAS No.:875585-30-1
- H-D-Tyr-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC3136
CAS No.:87553-74-0
- Anacetrapib (MK-0859)
Catalog No.:BCC2327
CAS No.:875446-37-0
- MGCD-265
Catalog No.:BCC2479
CAS No.:875337-44-3
- JNJ-26481585
Catalog No.:BCC2147
CAS No.:875320-29-9
- Dimethyl lithospermate B
Catalog No.:BCN2823
CAS No.:875313-64-7
- Lusianthridin
Catalog No.:BCN3689
CAS No.:87530-30-1
- YIL 781
Catalog No.:BCC7826
CAS No.:875258-85-8
- Tenacissoside X
Catalog No.:BCN8354
CAS No.:875057-87-7
- H-D-Phg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3313
CAS No.:875-74-1
- cis-3,4-Dihydroxy-beta-ionone
Catalog No.:BCN6694
CAS No.:875666-39-0
- LXR-623
Catalog No.:BCC4273
CAS No.:875787-07-8
- (+)-Lyoniresinol 9'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4832
CAS No.:87585-32-8
- Smyrindioloside
Catalog No.:BCN4423
CAS No.:87592-77-6
- Ptaquiloside
Catalog No.:BCN8159
CAS No.:87625-62-5
- Montixanthone
Catalog No.:BCN8069
CAS No.:876305-36-1
- RF 9
Catalog No.:BCC7744
CAS No.:876310-60-0
- RO-9187
Catalog No.:BCC1904
CAS No.:876708-03-1
- Trandolapril
Catalog No.:BCC5275
CAS No.:87679-37-6
- 6-Hydroxyrubiadin
Catalog No.:BCN4425
CAS No.:87686-86-0
- Pentoxyresorufin
Catalog No.:BCC6297
CAS No.:87687-03-4
- Isomagnolol
Catalog No.:BCN8325
CAS No.:87688-90-2
Constructing Hierarchical Tectorum-like alpha-Fe2 O3 /PPy Nanoarrays on Carbon Cloth for Solid-State Asymmetric Supercapacitors.[Pubmed:28000972]
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017 Jan 19;56(4):1105-1110.
The design of complex heterostructured electrode materials that deliver superior electrochemical performances to their individual counterparts has stimulated intensive research on configuring supercapacitors with high energy and power densities. Herein we fabricate hierarchical tectorum-like alpha-Fe2 O3 /polypyrrole (PPy) nanoarrays (T-Fe2 O3 /PPy NAs). The 3D, and interconnected T-Fe2 O3 /PPy NAs are successfully grown on conductive carbon cloth through an easy self-sacrificing template and in situ vapor-phase polymerization route under mild conditions. The electrode made of the T-Fe2 O3 /PPy NAs exhibits a high areal capacitance of 382.4 mF cm(-2) at a current density of 0.5 mA cm(-2) and excellent reversibility. The solid-state asymmetric supercapacitor consisting of T-Fe2 O3 /PPy NAs and MnO2 electrodes achieves a high energy density of 0.22 mWh cm(-3) at a power density of 165.6 mW cm(-3) .
Sensor development of 1,2 Dichlorobenzene based on polypyrole/Cu-doped ZnO (PPY/CZO) nanocomposite embedded silver electrode and their antimicrobial studies.[Pubmed:28163125]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 May;98:256-267.
Cu-doped ZnO nanopowders and their composites of polypyrole (PPY)/CZO were prepared by a gel combustion method and an in-situ polymerization process, respectively. The synthesized nanocomposite are characterized by X-ray powder diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), FTIR, and TGA studies. Then the PPY/CZO/AgE nanocomposites were used for potential application in chemical sensing by easy and reliable I-V method, where 1,2 dichlorobenzene (1,2-DCB) is considered as a model target compound. The chemical sensor performances are exhibited the higher sensitivity, good stability, and repeatability of the sensor enhanced significantly using PPY/CZO/AgE of thin-film with conducting binders on silver electrodes (AgE; Surface area: 0.0216cm(2)). The calibration plot is linear over the large dynamic range (0.35nM approximately 3.5mM), where the sensitivity ( approximately 2.702muAmM(-1)cm(-2)) and detection limit ( approximately 0.34nM) is calculated based on signal/noise ratio ( approximately (3N)/S) in short response time. Finally, it is concluded that the structural and optical characteristics could be encompassed to a broad-scale in PPY/CZO/AgE composites and efficient chemical sensor applications for environmental fields. Simultaneously PPY/CZO composites was also evaluated against Gram positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis, Gram negative bacteria Escherichia coli and antibiotics (Amoxicillin) using the agar plate.
Regioselective Photoisomerization/C-C Bond Formation of Asymmetric B(ppy)(Mes)(Ar): The Role of the Aryl Groups on Boron.[Pubmed:28295925]
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017 May 22;56(22):6093-6097.
Asymmetric N,C-chelate organoboron compounds bearing two different aryl groups at the boron center undergo photoisomerization reactions that involve exclusively the less bulky aryl group, generating various strongly colored "dark isomers". These species thermally isomerize to 4bH-azaborepin molecules by direct hydrogen atom transfer from a borirane cycle to the pyridyl moiety and ring expansion. Mechanistic insight into these highly regioselective transformations was obtained from kinetic data and through computational studies.
Evaluation of a New Biosensor Based on in Situ Synthesized PPy-Ag-PVP Nanohybrid for Selective Detection of Dopamine.[Pubmed:28080061]
J Phys Chem B. 2017 Feb 9;121(5):1118-1127.
In the present work, in situ synthesis of polypyrrole-silver-polyvinylpyrrolidone (PPy-Ag-PVP) nanohybrid using AgNO3 as an oxidant and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a stabilizer and surfactant is demonstrated. The obtained ternary PPy-Ag-PVP nanohybrid was characterized by UV-vis, FT-IR, XRD, Raman, TGA, SEM, and HR-TEM analysis. Further the synthesized PPy-Ag-PVP has been investigated for its selective and sensitive sensing of dopamine (DA). The PPy-Ag-PVP modified glassy carbon electrode shows a reversible electrochemical behavior with superior response for DA. The limit of detection and limit of quantification are found to be 0.0126 and 0.042 muM (S/N = 3 and 10), respectively, with remarkable sensitivity (7.26 muA mM(-1) cm(-2)). The practical application of the present modified electrode has been validated by determining the concentration of DA in human urine samples of different age group.
Inhibitors of ABL and the ABL-T315I mutation.[Pubmed:18673174]
Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(10):905-21.
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a hematological stem cell disorder caused by increased and unregulated growth of myeloid cells in the bone marrow, and the accumulation of excessive white blood cells. Abelson tyrosine kinase (ABL) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase involved in cell growth and proliferation and is usually under tight control. However, 95% of CML patients have the ABL gene from chromosome 9 fused with the breakpoint cluster (BCR) gene from chromosome 22, resulting in a short chromosome known as the Philadelphia chromosome. This Philadelphia chromosome is responsible for the production of BCR-ABL, a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that causes uncontrolled cellular proliferation. An ABL inhibitor, imatinib, was approved by the FDA for the treatment of CML, and is currently used as first line therapy. However, a high percentage of clinical relapse has been observed due to long term treatment with imatinib. A majority of these relapsed patients have several point mutations at and around the ATP binding pocket of the ABL kinase domain in BCR-ABL. In order to address the resistance of mutated BCR-ABL to imatinib, 2(nd) generation inhibitors such as dasatinib, and nilotinib were developed. These compounds were approved for the treatment of CML patients who are resistant to imatinib. All of the BCR-ABL mutants are inhibited by the 2(nd) generation inhibitors with the exception of the T315I mutant. Several 3(rd) generation inhibitors such as AP24534, VX-680 (MK-0457), PHA-739358, PPY-A, XL-228, SGX-70393, FTY720 and TG101113 are being developed to target the T315I mutation. The early results from these compounds are encouraging and it is anticipated that physicians will have additional drugs at their disposal for the treatment of patients with the mutated BCR-ABL-T315I. The success of these inhibitors has greater implication not only in CML, but also in other diseases driven by kinases where the mutated gatekeeper residue plays a major role.
Crystal structure of the T315I mutant of AbI kinase.[Pubmed:17718712]
Chem Biol Drug Des. 2007 Sep;70(3):171-81.
Imatinib (Gleevec) is currently the frontline therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a disease characterized by the presence of a constitutively activated chimeric tyrosine kinase protein Bcr-AbI. However, drug resistance often occurs at later stages of the disease, principally because of the occurrence of mutations in the kinase domain. Second generation Bcr-AbI inhibitors, such as dasatinib and nilotinib are capable of inhibiting many imatinib-resistant forms of the kinase but not the form in which threonine is mutated to isoleucine at the gatekeeper position (T315I). In this study, we present the crystal structure of the kinase domain of the c-AbI T315I mutant, as well as the wild-type form, in complex with a pyrrolopyridine inhibitor, PPY-A. The side chain of Ile315 is accommodated in the AbI T315I mutant structure without large conformational changes proximal to the site of mutation. In contrast to other inhibitors, such as imatinib and dasatinib, PPY-A does not occupy the hydrophobic pocket behind the gatekeeper residue. This binding mode, coupled with augmented contacts with the glycine-rich loop, appears to be critical for its ability to override the T315I mutation. The data presented here may provide structural guidance for the design of clinically useful inhibitors of Bcr-AbI T315I.


