Prosaikogenin ACAS# 99365-21-6 |
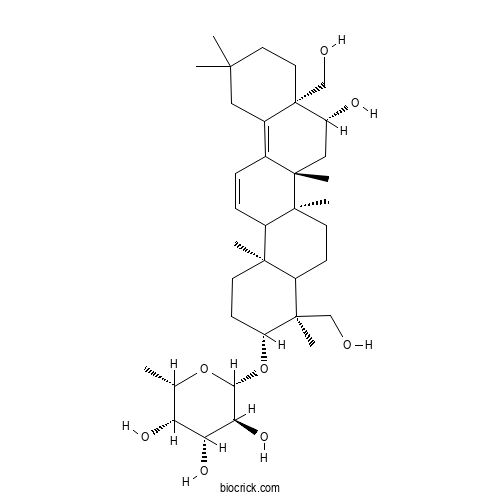
- Prosapogenin D
Catalog No.:BCX0762
CAS No.:103629-72-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 99365-21-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 154831769.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C36H58O8 | M.Wt | 618.85 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S,4R,5S,6S)-2-[[(3R,4S,6aS,6bR,8R,8aR,14bR)-8-hydroxy-4,8a-bis(hydroxymethyl)-4,6a,6b,11,11,14b-hexamethyl-1,2,3,4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,14a-dodecahydropicen-3-yl]oxy]-6-methyloxane-3,4,5-triol | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2CCC3(C(C2(C)CO)CCC4(C3C=CC5=C6CC(CCC6(C(CC54C)O)CO)(C)C)C)C)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UAUUFLADFXKYAU-NROHZDGNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C36H58O8/c1-20-27(40)28(41)29(42)30(43-20)44-26-11-12-32(4)23(33(26,5)18-37)10-13-34(6)24(32)9-8-21-22-16-31(2,3)14-15-36(22,19-38)25(39)17-35(21,34)7/h8-9,20,23-30,37-42H,10-19H2,1-7H3/t20-,23?,24?,25+,26+,27+,28+,29-,30+,32+,33+,34-,35-,36-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Prosaikogenin A Dilution Calculator

Prosaikogenin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6159 mL | 8.0795 mL | 16.159 mL | 32.318 mL | 40.3975 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3232 mL | 1.6159 mL | 3.2318 mL | 6.4636 mL | 8.0795 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1616 mL | 0.808 mL | 1.6159 mL | 3.2318 mL | 4.0398 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0323 mL | 0.1616 mL | 0.3232 mL | 0.6464 mL | 0.808 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0162 mL | 0.0808 mL | 0.1616 mL | 0.3232 mL | 0.404 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Resveratrol-4'-O-(6"-galloyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1519
CAS No.:928340-97-0
- Norfuronol
Catalog No.:BCX1518
CAS No.:19322-27-1
- dehydrotomatine
Catalog No.:BCX1517
CAS No.:157604-98-3
- Debenzoylpaeoniflorgenin
Catalog No.:BCX1516
CAS No.:1429403-79-1
- Paeoniflorgenin
Catalog No.:BCX1515
CAS No.:697300-41-7
- Synigrin
Catalog No.:BCX1514
CAS No.:534-69-0
- Rhetsinine
Catalog No.:BCX1513
CAS No.:526-43-2
- Smilagenin acetate
Catalog No.:BCX1512
CAS No.:4947-75-5
- Lycoramine Hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCX1511
CAS No.:89505-76-0
- Isocoptisine acetate
Catalog No.:BCX1510
CAS No.:30426-66-5
- Isoemetine hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCX1509
CAS No.:21026-77-7
- 4'-Hydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX1508
CAS No.:4143-63-9
- Nortanshinone
Catalog No.:BCX1521
CAS No.:97399-70-7
- Acetylseneciphylline N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCX1522
CAS No.:123844-00-8
- Dahurinol
Catalog No.:BCX1523
CAS No.:38908-87-1
- Luteolin 7-sulfate
Catalog No.:BCX1524
CAS No.:56857-57-9
- Bitalgenin
Catalog No.:BCX1525
CAS No.:2192-25-8
- (±)-Dihydrokaempferol
Catalog No.:BCX1526
CAS No.:104486-98-8
- Isoescin Ie
Catalog No.:BCX1527
CAS No.:1613506-28-7
- Dihydroactindiolide
Catalog No.:BCX1528
CAS No.:15356-74-8
- 4-Vinylphenol
Catalog No.:BCX1529
CAS No.:2628-17-3
- d-Epigalbacin
Catalog No.:BCX1530
CAS No.:84709-25-1
- (+)-Dehydroabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1531
CAS No.:1231-75-0
- 31-Norlanostenol
Catalog No.:BCX1532
CAS No.:16910-39-7
A new triterpenoid saponin from Clinopodium chinense (Benth.) O. Kuntze.[Pubmed:26511166]
Nat Prod Res. 2016;30(9):1001-8.
A new triterpene saponin, 3beta,16beta,23alpha,28beta,30beta-pentahydroxyl-olean-11,13(18)-dien-3beta-yl-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)]-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)]-beta-D-fucopyranoside, was named Clinoposaponin D (1), together with six known triterpene saponins, buddlejasaponin IVb (2), buddlejasaponin IVa (3), buddlejasaponin IV (4), clinopodisides D (5), 11alpha,16beta,23,28-Tetrahydroxyolean-12-en-3beta-yl-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)]-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)]-beta-D-fucopyranoside (6) and Prosaikogenin A (7), and two known triterpenes, saikogenin A (8) and saikogenin F (9) were isolated from Clinopodium chinense (Benth.) O. Kuntze. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of 1D, 2D NMR and MS analysis. Meanwhile, the effects of all compounds on rabbit platelet aggregation and thrombin time (TT) were investigated in vitro. Compounds 4 and 7 had significant promoting effects on platelet aggregation with EC50 value at 53.4 and 12.2 muM, respectively. In addition, the highest concentration (200 muM) of compounds 2 and 9 shortened TT by 20.6 and 25.1%, respectively.
A new saikogenin from the roots of Bupleurum bicaule.[Pubmed:24863358]
Chin J Nat Med. 2014 Apr;12(4):305-8.
AIM: To study the chemical constituents from the roots of Buleurum bicaule Helm (Apiaceae). METHOD: Silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, MPLC Rp-C18 column chromatography, and HPLC were used for isolation of compounds. The structures were elucidated on the basis of 1D- and 2D-NMR technology and HRESI-MS. Compounds were evaluated in vitro for their inhibitory ability against the proliferation of rat mesangial cells by the MTT method. RESULTS: Twelve compounds were isolated, and their structures were identified on the basis of their spectroscopic and physico-chemical properties as 13, 28-epoxy-olean-11-en-3-one (1), saikogenin E (2), saikogenin G (3), 11alpha-methoxy-3beta, 16beta, 23, 28-tetrahydroxyolean-12-ene (4), saikogenin D (5), prosaikogenin F (6), Prosaikogenin A (7), prosaikogenin G (8), prosaikogenin D (9), laccaic acid (10b), methyl gallate (11), and ethyl gallate (12). Compounds 1, 2, 7, 8, and 10 were observed to have inhibitory activity against mesangial cell proliferationin to different degrees. CONCLUSION: Compound 1, 8, and 10 exhibit significant inhibitory effects on rat mesangial cell proliferation induced by Ang II.
Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of orally administered saikosaponin b1 in conventional, germ-free and Eubacterium sp. A-44-infected gnotobiote rats.[Pubmed:9657043]
Biol Pharm Bull. 1998 Jun;21(6):588-93.
The metabolic fate of saikosaponin b1 (1) was investigated using conventional, germ-free and Eubacterium sp. A-44-infected gnotobiote rats. After the oral administration of 1 to germ-free rats at a dose of 50 mg/kg, no metabolite was detected in the plasma, the cecal contents or the cumulative feces through the experiment. On the other hand, when 1 was orally given to the Eubacterium sp. A-44-infected gnotobiote rats, considerable amounts of its metabolites, Prosaikogenin A (2) and saikogenin A (3), were detected in the rat plasma with the respective AUC0-10 h values of 17,424 and 22,260 pmol.min/ml, similar to the case of its oral administration to conventional rats (AUC0-10 h values of 9,936 and 12,414 pmol.min/ml for 2 and 3, respectively). Furthermore, significant amounts of both metabolites were detected in the cecal contents and the cumulative feces of the gnotobiote and conventional rats, but not in those of the germ-free rats, within 10 h after the administration. Fecal and cecal activities of hydrolyzing 1 and 2 were found in the gnotobiote and conventional rats, though there were no detectable activities in the germ-free rats. Accordingly, both hydrolyzing activities in the intestinal bacteria, such as Eubacterium sp. A-44, are essential for the appearance of 2 and 3 in the rat plasma and cumulative feces, since orally administered 1 was poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Triterpenoid saponins from Bupleurum smithii var. parvifolium.[Pubmed:8783839]
Phytochemistry. 1996 Aug;42(6):1673-5.
Four triterpenoidal saponins, Prosaikogenin A and saikosaponins b1, n and o, were isolated from the roots of the title plant for the first time. Saikosaponin O is a new compound, which was identified as 3 beta,16 beta,23,28-tetrahydroxyolean-11,12(18)-diene-3-O-beta-D-glucopy ran osyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1--> 6)-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)]-beta-D-glucopyranoside.
Effects of saikosaponin metabolites on the hemolysis of red blood cells and their adsorbability on the cell membrane.[Pubmed:2632076]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1989 Dec;37(12):3306-10.
The hemolytic properties and the adsorbability on red blood cells of saikosaponin a, saikosaponin d and 13 metabolites formed in the alimentary tract were investigated. Among these compounds, saikosaponin d and its intestinal product, prosaikogenin G, which possess an alpha-hydroxyl function at C16, showed the strongest hemolytic activity at the dose range of 1.0 to 5.0 micrograms/ml. Saikosaponin a and its intestinal product, prosaikogenin F, which possess a beta-hydroxyl function at C16, showed activity above 10 micrograms/ml. In this case, the monoglycoside, prosaikogenin F, showed the stronger activity than the diglycoside, saikosaponin a. Among the gastric products whose ether ring was cleaved to produce a carbinol, the monoglycosides, Prosaikogenin A and prosaikogenin H, showed a slight activity above 25 micrograms/ml, and the saikogenins except saikogenin A were inactive. Saikogenin A, however, had hemolytic activity at a dose of 15 micrograms/ml. The adsorbabilities of these compounds on red blood cell membranes closely paralleled their degrees of hemolytic activity.
Corticosterone secretion-inducing activity of saikosaponin metabolites formed in the alimentary tract.[Pubmed:2611932]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1989 Oct;37(10):2736-40.
The corticosterone secretion-inducing activities of saikosaponin a, saikosaponin c and saikosaponin d, isolated from the root of Bupleurum falcatum L., and 27 metabolites formed in the murine alimentary tract were studied in mice. Serum corticosterone was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Intraperitoneal administration of saikosaponin a and its intestinal metabolite, prosaikogenin F, showed corticosterone secretion-inducing activity at a dose of 0.1 mmol/kg, and maximally increased it at a dose of 0.4 mmol/kg. On the other hand, the genuine sapogenin, saikogenin F, was inactive. Saikosaponin b1 and saikosaponin g, gastric metabolites of saikosaponin a, and their intestinal metabolites, Prosaikogenin A, prosaikogenin H, saikogenin A and saikogenin H, were also inactive. Serum corticosterone was increased by the administration of saikosaponin d and its intestinal metabolite, prosaikogenin G, at a dose of 0.04 mmol/kg, and it reached the maximal level at the dose of 0.1 mmol/kg. Saikogenin G also showed a slight activity. A gastric metabolite of saikosaponin d, saikosaponin b2, and its intestinal metabolites, prosaikogenin D and saikogenin D, were inactive. In the experiments on saikosaponin c and its metabolites, saikosaponin c was inactive but its intestinal metabolites, especially prosaikogenin E-2, showed activity almost equal to that of saikosaponin a. Saikosaponin h and saikosaponin i, gastric metabolites of saikosaponin c, were also inactive, but their prosaikogenins showed slight activities. When these compounds were orally administered, their corticosterone secretion-inducing activities were similar to those obtained in the intraperitoneal experiment. These results suggest that a proper polar balance between the sugar moiety and the aglycone is important for the corticosterone secretion-inducing activity of saikosaponins and their metabolites.
Structural transformation of saikosaponins by gastric juice and intestinal flora.[Pubmed:4087133]
J Pharmacobiodyn. 1985 Sep;8(9):718-25.
Structural transformation of saikosaponin a and saikosaponin d, main components of Bupleuri Radix, were investigated using rat gastric juice (pH 1.5) and mouse intestinal flora in vitro and the excretion of saikosaponin derivatives in rat feces was also studied. Quantitative analysis of saikosaponins and their derivatives was carried out by high performance liquid chromatography. By the incubation of saikosaponins in rat gastric juice, saikosaponin a decreased with time dependently. After 3 h, saikosaponin a disappeared completely and saikosaponin b1 which possessed heteroannular diene moiety at C-11,13(18) and saikosaponin g which possessed homoannular diene moiety at C-9(11),12 were detected with the ratio of 3:1. On the other hand, saikosaponin d rapidly changed to only saikosaponin b2 (heteroannular diene structure) completely 30 min after the incubation. Next, by the anaerobic incubation of saikosaponin a with mouse intestinal flora, the formation of saikogenin F, a genuine aglycone of saikosaponin a, reached to the maximum 1 h after the incubation and its yield was 80%. A minor peak of prosaikogenen F, a monofucoside of saikogenin F, was also detected at 15 min. By the same procedures, saikosaponin b1, g, d and b2 also changed to the corresponded Prosaikogenin A, H, G and D and saikogenin A, H, G and D with the almost similar pattern to that of saikosaponin a. Finally, the contents of nine excreted metabolites from saikosaponin a, 5 and 20 mg/kg, in feces after its oral administration was investigated using fasted or non-fasted rats.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)


