RhodioninCAS# 85571-15-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 85571-15-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 21626477 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C21H20O11 | M.Wt | 448.38 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
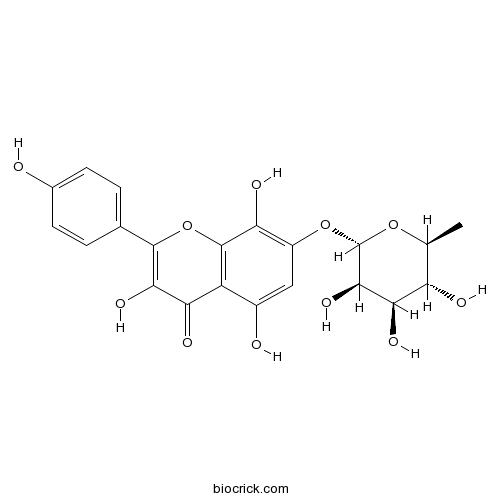
| Chemical Name | 3,5,8-trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2=C(C3=C(C(=C2)O)C(=O)C(=C(O3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)O)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CIAXXTSXVCLEJK-JOEVVYSCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H20O11/c1-7-13(24)16(27)18(29)21(30-7)31-11-6-10(23)12-15(26)17(28)19(32-20(12)14(11)25)8-2-4-9(22)5-3-8/h2-7,13,16,18,21-25,27-29H,1H3/t7-,13-,16+,18+,21-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Rhodionin and rhodionin can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 non-competitively with high specificity which could have implications for interactions with co-administered drugs; they can significantly suppress the elevation of the postprandial blood triglyceride level, suggests that they may be to the treatment of lifestyle-related diseases such as hyperlipidemia and exogeneous obesity and to health foods. Rhodionin has antioxidant activity, it exhibits potent 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging activities, with IC50 values of 19.49 ± 0.21 uM. |
| Targets | CYP450 2D6 |
| In vitro | The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis A. BOR.[Pubmed: 23018923]Molecules. 2012 Sep 27;17(10):11484-94.Isolation of compounds from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis (RRS) yielded tyrosol (1), salidroside (2), multiflorin B (3), kaempferol-3,4'-di-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (4), afzelin (5), kaempferol (6), Rhodionin (7), and rhodiosin (8). |
| In vivo | Constituents of Rhodiola rosea showing inhibitory effect on lipase activity in mouse plasma and alimentary canal.[Pubmed: 18982538 ]Planta Med. 2008 Nov;74(14):1716-9.As a methanol extract of the rhizome of Rhodiola rosea inhibits the activity of lipase in isolated mouse plasma in vitro and in the mouse gastrointestinal tube in vivo, the active components in this plant were investigated. |
| Kinase Assay | Two potent cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitors found in Rhodiola rosea.[Pubmed: 24400445]Pharmazie. 2013 Dec;68(12):974-6.
Throughout the world, in particular in Russia, Northern Europe and China, Rhodiola species are used as herb supplements. Previously, we found that the extract of Rhodiola rosea, one of the most widely used Rhodiola species, had an inhibitory effect on the catalytic activity of cytochrome P450 2D6. Here, its inhibitory components were identified.
|
| Structure Identification | Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008 Jun;56(6):807-14.Identification and comparative determination of rhodionin in traditional tibetan medicinal plants of fourteen Rhodiola species by high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 18520085]
J Sep Sci. 2014 Sep;37(17):2314-21.Application and recovery of ionic liquids in the preparative separation of four flavonoids from Rhodiola rosea by on-line three-dimensional liquid chromatography.[Pubmed: 24916654]
|

Rhodionin Dilution Calculator

Rhodionin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2303 mL | 11.1513 mL | 22.3025 mL | 44.605 mL | 55.7563 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4461 mL | 2.2303 mL | 4.4605 mL | 8.921 mL | 11.1513 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.223 mL | 1.1151 mL | 2.2303 mL | 4.4605 mL | 5.5756 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0446 mL | 0.223 mL | 0.4461 mL | 0.8921 mL | 1.1151 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0223 mL | 0.1115 mL | 0.223 mL | 0.4461 mL | 0.5576 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- NBI-74330
Catalog No.:BCC4111
CAS No.:855527-92-3
- Safflor Yellow A
Catalog No.:BCN2408
CAS No.:85532-77-0
- PK 11195
Catalog No.:BCC6745
CAS No.:85532-75-8
- Eupatorin
Catalog No.:BCN4405
CAS No.:855-96-9
- 4-Chlorotestosterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8705
CAS No.:855-19-6
- Ajugamarin chlorohydrin
Catalog No.:BCN3664
CAS No.:85447-27-4
- Caffeic anhydride
Catalog No.:BCN3295
CAS No.:854237-32-4
- (R)-(-)-Rolipram
Catalog No.:BCC5429
CAS No.:85416-75-7
- S- (+)-Rolipram
Catalog No.:BCC2303
CAS No.:85416-73-5
- Rilmenidine Phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC5637
CAS No.:85409-38-7
- Ropivacaine mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC9137
CAS No.:854056-07-8
- (-)-Haplomyrfolin
Catalog No.:BCN3225
CAS No.:85404-48-4
- Kurarinol
Catalog No.:BCN3447
CAS No.:855746-98-4
- Zaltidine
Catalog No.:BCC2068
CAS No.:85604-00-8
- Gynuramine
Catalog No.:BCN2085
CAS No.:85611-43-4
- (2-Aminoethyl)phosphinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1761
CAS No.:85618-16-2
- Temozolomide
Catalog No.:BCC4386
CAS No.:85622-93-1
- WP1130
Catalog No.:BCC3686
CAS No.:856243-80-6
- Boc-Ala-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3046
CAS No.:85642-13-3
- Curculigoside
Catalog No.:BCN4406
CAS No.:85643-19-2
- Laurycolactone A
Catalog No.:BCN3109
CAS No.:85643-76-1
- Laurycolactone B
Catalog No.:BCN3110
CAS No.:85643-77-2
- Mirtazapine
Catalog No.:BCC4923
CAS No.:85650-52-8
- Asenapine
Catalog No.:BCC2476
CAS No.:85650-56-2
Two potent cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitors found in Rhodiola rosea.[Pubmed:24400445]
Pharmazie. 2013 Dec;68(12):974-6.
OBJECTIVES: Throughout the world, in particular in Russia, Northern Europe and China, Rhodiola species are used as herb supplements. Previously, we found that the extract of Rhodiola rosea, one of the most widely used Rhodiola species, had an inhibitory effect on the catalytic activity of cytochrome P450 2D6. Here, its inhibitory components were identified. METHODS: A human liver microsomal in vitro system was used with dextromethorphan as substrate. The production rate of destrorphan, a metabolite of dextromethorphan, was used to measure enzyme activity. The concentration of destrorphan in the samples was measured using LC-MS/MS. Inhibitory activity of eight main components from Rhodiola rosea was evaluated. RESULTS: Rhodiosin and Rhodionin showed inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 0.761 microM and 0.420 microM, respectively. The other components showed no obvious inhibition (with a residual enzyme activity of more than 90%). Both rhodiosin and Rhodionin were determined to be non-competitive inhibitors with Ki values of 0.769 microM and 0.535 microM. CONCLUSION: Two of the main Rhodiola rosea compounds, rhodiosin and Rhodionin, can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 non-competitively with high specificity which could have implications for interactions with co-administered drugs.
The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis A. BOR.[Pubmed:23018923]
Molecules. 2012 Sep 27;17(10):11484-94.
Isolation of compounds from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis (RRS) yielded tyrosol (1), salidroside (2), multiflorin B (3), kaempferol-3,4'-di-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (4), afzelin (5), kaempferol (6), Rhodionin (7), and rhodiosin (8). Quantification of these compounds was performed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). To investigate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of the compounds, DPPH radical scavenging, NBT superoxide scavenging and nitric oxide production inhibitory activities were examined in LPS-stimulated Raw 264.7 cells. We suggest that the major active components of RRS are herbacetin glycosides, exhibiting antioxidant activity, and kaempferol, exhibiting anti-inflammatory activity.
Constituents of Rhodiola rosea showing inhibitory effect on lipase activity in mouse plasma and alimentary canal.[Pubmed:18982538]
Planta Med. 2008 Nov;74(14):1716-9.
As a methanol extract of the rhizome of Rhodiola rosea inhibits the activity of lipase in isolated mouse plasma in vitro and in the mouse gastrointestinal tube in vivo, the active components in this plant were investigated. After fractionation and separation processes, Rhodionin and rhodiosin were isolated as active ingredients. Their IC50 values were 0.093 mM and 0.133 mM in vitro, respectively. Both compounds significantly suppressed the elevation of the postprandial blood triglyceride level, e.g., by 45.6 % (150 mg/kg, 60 min after oral administration) and 57.6 % (200 mg/kg, 180 min after oral administration), respectively. Consequently, we anticipate the application of this plant and its constituents to the treatment of lifestyle-related diseases such as hyperlipidemia and exogeneous obesity and to health foods.
Identification and comparative determination of rhodionin in traditional tibetan medicinal plants of fourteen Rhodiola species by high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:18520085]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008 Jun;56(6):807-14.
Using the HPLC/PDA/ESI/MS method, a comparative analysis of Rhodionin (RH) was undertaken in order to conduct a qualitative and quantitative study in 38 batches of fourteen species of Rhodiola for quality control purposes. Alongside of this RH analysis, a simultaneous determination of salidroside (SA), tyrosol (TY), and gallic acid (GA) was carried out. Rhodiola plants are a popularly used ethnodrug from the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau of China. The identity of RH was unambiguously determined based on the quasimolecular ions in negative ESI-MS mode. This method was validated in respect to sensitivity, linearity, precision, repeatability and recovery using optimized chromatographic conditions. The linear calibration curve was acquired with R(2)>0.999, and the limit of detection (S/N=3) was estimated to be 43.75 microg/g. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) of the intra- and inter-day precisions were 0.75% and 0.50%, respectively. The repeatability was evaluated by a replicated analysis of samples with the RSD value found within 0.67%. The recovery rates varied within the range of 98.79-100.08% with RSD less than 1.10%. In the present study, the content of RH was quantified within 0.4192-4.7260 mg/g for 16 batches of R. crenulata. It was also found in eight other species plants. The results demonstrated that RH is a useful characteristic standard compound for quality evaluation and chemical differentiation among species of Rhodiola. The study also indicated that the analytical procedure is precise, reproducible and a potential tool for both quality assessment and species identification.


