Roridin ACAS# 14729-29-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

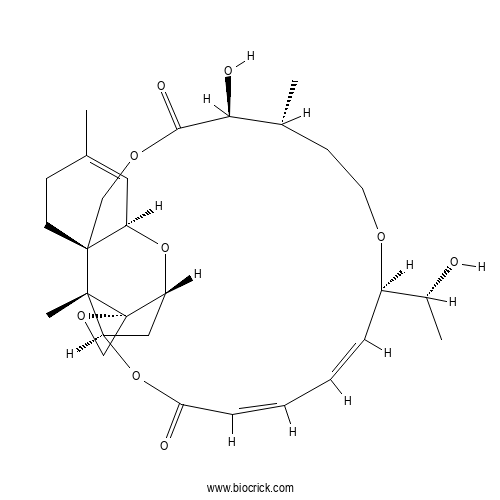
| Cas No. | 14729-29-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9915017 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C29H40O9 | M.Wt | 532.6 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (1R,3R,8R,12S,13R,17R,18E,20Z,24R,25S,26S)-12-hydroxy-17-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-5,13,25-trimethylspiro[2,10,16,23-tetraoxatetracyclo[22.2.1.03,8.08,25]heptacosa-4,18,20-triene-26,2'-oxirane]-11,22-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCOC(C=CC=CC(=O)OC2CC3C4(C2(C5(CCC(=CC5O3)C)COC(=O)C1O)C)CO4)C(C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NSFWWJIQIKBZMJ-PAGWOCKZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H40O9/c1-17-9-11-28-15-35-26(33)25(32)18(2)10-12-34-20(19(3)30)7-5-6-8-24(31)38-21-14-23(37-22(28)13-17)29(16-36-29)27(21,28)4/h5-8,13,18-23,25,30,32H,9-12,14-16H2,1-4H3/b7-5+,8-6-/t18-,19-,20-,21-,22-,23-,25+,27-,28-,29+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Roridin A Dilution Calculator

Roridin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8776 mL | 9.3879 mL | 18.7758 mL | 37.5516 mL | 46.9395 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3755 mL | 1.8776 mL | 3.7552 mL | 7.5103 mL | 9.3879 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1878 mL | 0.9388 mL | 1.8776 mL | 3.7552 mL | 4.694 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0376 mL | 0.1878 mL | 0.3755 mL | 0.751 mL | 0.9388 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0188 mL | 0.0939 mL | 0.1878 mL | 0.3755 mL | 0.4694 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Incarvilone A
Catalog No.:BCN0286
CAS No.:
- Incarvine F
Catalog No.:BCN0285
CAS No.:
- Incarvine E
Catalog No.:BCN0284
CAS No.:
- Incarvine D
Catalog No.:BCN0283
CAS No.:
- Incarvine C
Catalog No.:BCN0282
CAS No.:
- Incarvine A
Catalog No.:BCN0281
CAS No.:
- Vatalbinoside F
Catalog No.:BCN0280
CAS No.:
- Vatalbinoside I
Catalog No.:BCN0279
CAS No.:
- Vatalbinoside J
Catalog No.:BCN0278
CAS No.:
- Vatalbinoside H
Catalog No.:BCN0277
CAS No.:
- Vatalbinoside G
Catalog No.:BCN0276
CAS No.:
- Vatalbinoside C
Catalog No.:BCN0275
CAS No.:
- Agroclavine
Catalog No.:BCN0291
CAS No.:548-42-5
- Ergocornine
Catalog No.:BCN0292
CAS No.:564-36-3
- Procyanidin A4
Catalog No.:BCN0293
CAS No.:111466-29-6
- L-(±)-Alliin
Catalog No.:BCN0294
CAS No.:17795-26-5
- Andrograpanin
Catalog No.:BCN0295
CAS No.:82209-74-3
- Anemonin
Catalog No.:BCN0296
CAS No.:508-44-1
- Anisodine hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN0297
CAS No.:76822-34-9
- (-)-Antofine
Catalog No.:BCN0298
CAS No.:32671-82-2
- Apoatropine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN0299
CAS No.:5978-81-4
- Atropine N-oxide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN0300
CAS No.:4574-60-1
- Avenanthramide D
Catalog No.:BCN0301
CAS No.:115610-36-1
- Bakuchicin
Catalog No.:BCN0302
CAS No.:4412-93-5
Occurrence of type A, B and D trichothecenes, zearalenone and stachybotrylactam in straw.[Pubmed:33615927]
Arch Anim Nutr. 2021 Apr;75(2):105-120.
Straw is the main by-product of grain production, used as bedding material and animal feed. If produced or stored under adverse hygienic conditions, straw is prone to the growth of filamentous fungi. Some of them, e.g. Aspergillus, Fusarium and Stachybotrys spp. are well-known mycotoxin producers. Since studies on mycotoxins in straw are scarce, 192 straw samples (wheat n = 80; barley n = 79; triticale n = 12; oat n = 11; rye n = 12) were collected across Germany within the German official feed surveillance and screened for the presence of 21 mycotoxins. The following mycotoxins (positive samples for at least one mycotoxin n = 184) were detected: zearalenone (n = 86, 6.0-785 mug/kg), nivalenol (n = 51, 30-2,600 mug/kg), deoxynivalenol (n = 156, 20-24,000 mug/kg), 15-acetyl-deoxynivalenol (n = 34, 20-2,400 mug/kg), 3-acetyl-deoxynivalenol (n = 16, 40-340 mug/kg), scirpentriol (n = 14, 40-680 mug/kg), T-2 toxin (n = 67, 10-250 mug/kg), HT-2 toxin (n = 92, 20-800 mug/kg), T-2 tetraol (n = 13, 70-480 mug/kg). 15-monoacetoxyscirpenol (30 mug/kg) and T-2 triol (60 mug/kg) were only detected in one barley sample. Macrocyclic trichothecenes (satratoxin G, F, roridin E, and verrucarin J) were also found in only one barley sample (quantified as Roridin A equivalent: total 183 mug/kg). The occurrence of stachybotrylactam was monitored for the first time in four samples (n = 4, 0.96-7.4 mug/kg). Fusarenon-X, 4,15-diacetoxyscirpenol, neosolaniol, satratoxin H and roridin-L2 were not detectable in the samples. The results indicate a non-negligible contribution of straw to oral and possibly inhalation exposure to mycotoxins of animals or humans handling contaminated straw.
An Electrochemical Fiveplex Biochip Assay Based on Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies for Fast On-Site Detection of Bioterrorism Relevant Low Molecular Weight Toxins.[Pubmed:31795179]
Toxins (Basel). 2019 Nov 28;11(12). pii: toxins11120696.
Modern threats of bioterrorism force the need for multiple detection of biothreat agents to determine the presence or absence of such agents in suspicious samples. Here, we present a rapid electrochemical fiveplex biochip screening assay for detection of the bioterrorism relevant low molecular weight toxins saxitoxin, microcystin-LR, T-2 toxin, Roridin A and aflatoxin B1 relying on anti-idiotypic antibodies as epitope-mimicking reagents. The proposed method avoids the use of potentially harmful toxin-protein conjugates usually mandatory for competitive immunoassays. The biochip is processed and analyzed on the automated and portable detection platform pBDi within 13.4 min. The fiveplex biochip assay revealed toxin group specificity to multiple congeners. Limits of detection were 1.2 ng/mL, 1.5 ng/mL, 0.4 ng/mL, 0.5 ng/mL and 0.6 ng/mL for saxitoxin, microcystin-LR, T-2 toxin, Roridin A or aflatoxin B1, respectively. The robustness of the fiveplex biochip for real samples was demonstrated by detecting saxitoxin, microcystin-LR, HT-2 toxin, Roridin A and aflatoxin B1 in contaminated human blood serum without elaborate sample preparation. Recovery rates were between 52-115% covering a wide concentration range. Thus, the developed robust fiveplex biochip assay can be used on-site to quickly detect one or multiple low molecular weight toxins in a single run.
Macrocyclic Trichothecenes from Myrothecium roridum Strain M10 with Motility Inhibitory and Zoosporicidal Activities against Phytophthora nicotianae.[Pubmed:26320597]
J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Oct 14;63(40):8777-86.
The cytotoxicity of the extract obtained from Myrothecium roridum M10 and a characteristic (1)H signal at deltaH approximately 8 led to the assumption that verrucarin/roridin-type compounds were present. Upscaling on rice medium led to the isolation of four new metabolites: verrucarins Y (1) and Z (6) (macrocyclic trichothecenes), bilain D (12) (a diketopiperazine derivative), and hamavellone C (14) (an unusual cyclopropyl diketone). In addition, nine known trichothecenes [verrucarin A (3), 16-hydroxyverrucarin A (5), verrucarin B (7), 16-hydroxyverrucarin B (8), verrucarin J (2), verrucarin X (4), Roridin A (9), roridin L-2 (10), and trichoverritone (11)] and a bicyclic lactone [myrotheciumone A (15)] were identified. Their structures and configurations were determined by spectroscopic methods, published data, Mosher's method, and considering biosyntheses. Some trichothecenes showed motility inhibition followed by lysis of the zoospores against devastating Phytophthora nicotianae within 5 min. Compounds 2, 3, 7, and 9 also exhibited potent activities against Candida albicans and Mucor miehei.
[Secondary fungal metabolites (mycotoxins) in lichens of different taxonomic groups].[Pubmed:25731032]
Izv Akad Nauk Ser Biol. 2014 May-Jun;(3):228-35.
Secondary fungal metabolites (mycotoxins) in 22 lichen species of the families Parmeliaceae, Nephromataceae, Umbilicariaceae, Ramalinaceae, Cladoniaceae, Peltigeraceae, and Teloschistaceae were identified determined by enzyme immunoassay enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The following mycotoxins were identified found in these lichens in a broad concentration range with a frequency of 70-100%: sterigmatocystin (7-2090 ng/g), alternariol (20-6460 ng/g), and emodin (45-94500 ng/g). Mycophenolic acid frequently occurred in 19 lichen species; citrinin, in 17 species; diacetoxyscirpenol, in 11 species; cyclopiazonic acid, in 10 species; and zearalenone, in 9 species. PR toxin was regularly detected in three lichen species; deoxynivalenol, fumonisins, and ochratoxin A, in two species; and T-2 toxin and ergot alkaloids, in one species. Aflatoxin B1 was detected in only six species with a frequency of 2-42%, whereas Roridin A was identified present in 10% of Hypogymnia physodes samples.
Trichothecene mycotoxins activate NLRP3 inflammasome through a P2X7 receptor and Src tyrosine kinase dependent pathway.[Pubmed:24269698]
Hum Immunol. 2014 Feb;75(2):134-40.
Inflammasome is an intracellular molecular platform of the innate immunity that is a key mediator of inflammation. The inflammasome complex detects pathogens and different danger signals, and triggers cysteine protease caspase-1-dependent processing of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta, and IL-18 in dendritic cells and macrophages. Previously, we have shown that water-damaged building associated trichothecene mycotoxins, including Roridin A, trigger IL-1beta and IL-18 secretion in human macrophages. However, the molecular basis as well as mechanism behind this trichothecene-induced cytokine secretion has remained uncharacterized. Here, we show that the trichothecene-induced IL-1beta secretion is dependent on NLRP3 inflammasome in human primary macrophages. Pharmacological inhibition and small interfering RNA approach showed that the trichothecene-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation is mediated through ATP-gated P2X7 receptor. Moreover, we show that trichothecene-triggered NLRP3 inflammasome activation is dependent on Src tyrosine kinase activity. In addition, gene silencing of c-Cbl, a negative autophagy-related regulator of c-Src, resulted in enhanced secretion of IL-1beta and IL-18 in response to trichothecene mycotoxin stimulation in human macrophages. In conclusion, our results suggest that Roridin A, a fungal trichothecene mycotoxin, acts as microbial danger signals that trigger activation of NLRP3 inflammasome through P2X7R and Src tyrosine kinase signaling dependent pathway in human primary macrophages.
A new trichothecene from Myrothecium roridum QDFE005, a symbiotic fungus isolated from Mactra chinensis.[Pubmed:24152038]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2013;15(12):1284-9.
A new trichothecene, 12'-episatratoxin H (1), together with three known analogs: Roridin A (2), 16-hydroxyroridin E (3), and roridin E (4), was isolated from the culture broth of the symbiotic fungus Myrothecium roridum QDFE005, which was isolated from Mactra chinensis. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods, including 1D and 2D NMR (COSY, HMQC, and HMBC) techniques. Compound 1 exhibited significant cytotoxicity against the human tumor cell lines KB and HepG2 with IC(5)(0) values of 1.42 and 2.27 muM, respectively.
Enzymatic and toxigenic ability of opportunistic fungi contaminating intensive care units and operation rooms at Assiut University Hospitals, Egypt.[Pubmed:23961411]
Springerplus. 2013 Jul 29;2:347.
Total of 110 isolates belonging to 8 fungal species collected from intensive care units (ICUs) and operation rooms (ORs) at Assiut University hospitals were examined for their ability to produce some extracellular enzymes and mycotoxins which are considered as important factors involved in for fungal pathogenicity. The results revealed that 73, 92 and 78 out of the 110 tested isolates produced protease, lipase and urease respectively; meanwhile, 77 of the tested isolates exhibited some hemolytic activities. Chromatographic analysis (TLC) of the crude extract of the fungal isolates tested revealed that 79 isolates of them had the ability to produce at least one of these mycotoxic compounds (aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, gliotoxin, fumigillin, T-2, zearalenone, Roridin A & E, verrucarin A & J, trichoveroids, satratoxin H & E). These results demonstrate that the opportunistic fungal species isolated from (ICUs) and (ORs) and tested exhibited some enzymatic and mycotoxic ability which are the most effective virulence factors contributing to fungal pathogenicity indicating that the management of infection control unit at Assiut University hospitals must be aware of not only bacterial but also fungal contamination.
Bioherbicidal activity from washed spores of Myrothecium verrucaria.[Pubmed:22806015]
World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 May;28(5):1941-6.
The fungal plant pathogen, Myrothecium verrucaria, is highly virulent to several important weed species and has potential utility as a bioherbicide. However the production of macrocyclic trichothecene mycotoxins by this fungus presents significant safety concerns. It was discovered that trichothecenes are removed from M. verrucaria spores by repeated washes with water. These washed spores retained bioherbicidal efficacy against kudzu when tested in field trials and on sicklepod when tested under greenhouse conditions. Changes in the growth medium combined with washing spores with water resulted in greater than 95% reduction in Roridin A and verrucarin A. Washing spores reduced trichothecene concentrations in spore preparations with no significant effect on plant biomass reduction, thus demonstrating the possibility of M. verrucaria formulations with improved safety to researchers, producers and applicators.
Neurotoxic, inflammatory, and mucosecretory responses in the nasal airways of mice repeatedly exposed to the macrocyclic trichothecene mycotoxin roridin A: dose-response and persistence of injury.[Pubmed:20430879]
Toxicol Pathol. 2010 Apr;38(3):429-51.
Macrocyclic trichothecene mycotoxins encountered in water-damaged buildings have been suggested to contribute to illnesses of the upper respiratory tract. Here, the authors characterized the adverse effects of repeated exposures to Roridin A (RA), a representative macrocyclic trichothecene, on the nasal airways of mice and assessed the persistence of these effects. Young, adult, female C57BL/6 mice were exposed to single daily, intranasal, instillations of RA (0.4, 2, 10, or 50 microg/kg body weight [bw]) in saline (50 microl) or saline alone (controls) over 3 weeks or 250 microg/kg RA over 2 weeks. Histopathologic, immunohistochemical, and morphometric analyses of nasal airways conducted 24 hr after the last instillation revealed that the lowest-effect level was 10 microg/kg bw. RA exposure induced a dose-dependent, neutrophilic rhinitis with mucus hypersecretion, atrophy and exfoliation of nasal transitional and respiratory epithelium, olfactory epithelial atrophy and loss of olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs). In a second study, the persistence of lesions in mice instilled with 250 microg/kg bw RA was assessed. Nasal inflammation and excess luminal mucus were resolved after 3 weeks, but OSN loss was still evident in olfactory epithelium (OE). These results suggest that nasal inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, and olfactory neurotoxicity could be important adverse health effects associated with short-term, repeated, airborne exposures to macrocyclic trichothecenes.
[Study of specificity of fungistatic effect of trichothecene mycotoxins].[Pubmed:19938595]
Mikrobiol Z. 2009 Mar-Apr;71(2):57-62.
In attempt to realize the purposeful search of highly sensitive and highly specific microbial test-cultures the authors studied the ratio between selected before species of yeast to the wide set of different mycotoxins including macrocyclic trichothecenes (T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, T-2 triol, T-2 tetraol, NT-1 toxin, NT-2 toxin, fusarenon-X, diacetoxyscirpenol, deoxynivalenol, trichothecin, trichothecolon, neosolaniol, verrucarin A, Roridin A, roridin H, aflatoxins, B1, B2, G1 and G2, sterigmatocystin, patulin, fusaric acid, ochratoxin A, zearalenon and their derivatives). It was supposed to define borders of specific sensitivity of test-cultures. The value of minimal inhibiting concentration (MIC) of mycotoxins, which caused fungicide action in respect of the investigated yeast strains, was used as the estimation criterion. Extremely few species with narrow specific sensitivity to individual trichothecenes were found. Strains with group sensitivity to investigated trichothecene mycotoxins (MCTC) were more widely presented. Selectivity in respect of either simple (T-2 toxin), or MCTC (verrucarin A, Roridin A, roridin H) is traced for some species. Taxons with mixed selectivity were discovered. Exceptionally high fungistatic activity was characteristic of the investigated MCTC, T-2 toxin, trichothecin. Values of MCTC for these substances in respect of more sensitive strains varied in the borders of 0.03-0.1; 0.1-1.0 and 0.02-0.1 mcg/disk, correspondingly. It was less expressed for diacetoxyscirpenol, deoxynivalenol, trichothecolon (0.8-5.0; 0.1-2.0 and 0.8-4.0 mcg/disk, correspondingly). The data obtained give reasons for completing the bank of yeast test-cultures with wide potentialities of mycotoxins indication in various food and fodder substrates.
The biocontaminants and complexity of damp indoor spaces: more than what meets the eyes.[Pubmed:19793773]
Toxicol Ind Health. 2009 Oct-Nov;25(9-10):583-615.
Nine types of biocontaminants in damp indoor environments from microbial growth are discussed: (1) indicator molds; (2) Gram negative and positive bacteria; (3) microbial particulates; (4) mycotoxins; (5) volatile organic compounds, both microbial (MVOCs) and non-microbial (VOCs); (6) proteins; (7) galactomannans; (8) 1-3-beta-D-glucans (glucans) and (9) lipopolysaccharides (LPS--endotoxins). When mold species exceed those outdoors contamination is deduced. Gram negative bacterial endotoxins, LPS in indoor environments, synergize with mycotoxins. The gram positive Bacillus species, Actinomycetes (Streptomyces, Nocardia and Mycobacterium), produce exotoxins. The Actinomycetes are associated with hypersensitivity pneumonitis, lung and invasive infections. Mycobacterial mycobacterium infections not from M. tuberculosis are increasing in immunocompetent individuals. In animal models, LPS enhance the toxicity of Roridin A, satratoxins G and aflatoxin B1 to damage the olfactory epithelium, tract and bulbs (Roridin A, satratoxin G) and liver (aflatoxin B1). Aflatoxin B1 and probably trichothecenes are transported along the olfactory tract to the temporal lobe. Co-cultured Streptomyces californicus and Stachybotrys chartarum produce a cytotoxin similar to doxorubicin and actinomycin D (chemotherapeutic agents). Trichothecenes, aflatoxins, gliotoxin and other mycotoxins are found in dust, bulk samples, air and ventilation systems of infested buildings. Macrocyclic trichothecenes are present in airborne particles <2 microm. Trichothecenes and stachylysin are present in the sera of individuals exposed to S. chartarum in contaminated indoor environments. Haemolysins are produced by S. chartarum, Memnoniella echinata and several species of Aspergillus and Penicillium. Galactomannans, glucans and LPS are upper and lower respiratory tract irritants. Gliotoxin, an immunosuppressive mycotoxin, was identified in the lung secretions and sera of cancer patients with aspergillosis produced by A. fumigatus, A. terreus, A. niger and A. flavus.
Trichothecene mycotoxins activate inflammatory response in human macrophages.[Pubmed:19414795]
J Immunol. 2009 May 15;182(10):6418-25.
Damp building-related illnesses have caused concern for years in many countries. Although the problem is extensive, the knowledge of the immunological reactions behind damp building-related illnesses is still quite limited. Trichothecene mycotoxins form one major group of toxins, which possibly contribute to the illnesses. Stachybotrys chartarum is a well-known, but also controversial damp building mold and many strains of this mold are capable of producing trichothecenes. In this report, we have examined the effect of S. chartarum and trichothecene mycotoxins on the proinflammatory cytokine response in human macrophages. As a result, satratoxin-positive S. chartarum activated inflammasome-associated caspase-1, which is needed for proteolytic processing of IL-1beta and IL-18. Furthermore, purified trichothecene mycotoxins, Roridin A, verrucarin A, and T-2 toxin activated caspase-1, and these mycotoxins also strongly enhanced LPS-dependent secretion of IL-1beta and IL-18. The satratoxin-positive strain of S. chartarum and the trichothecenes also triggered the activation of caspase-3, which is an effector caspase of apoptosis. Satratoxin-negative S. chartarum was not able to activate either caspase-1 or caspase-3. In conclusion, our results indicate that human macrophages sense trichothecene mycotoxins as a danger signal, which activates caspase-1, and further enables the secretion of IL-1beta and IL-18 from the LPS-primed cells.
Cytotoxicity and phytotoxicity of trichothecene macrolides from Myrothecium gramminum.[Pubmed:19097001]
Planta Med. 2009 Feb;75(3):227-9.
(1)H-NMR guided fractionation of the EtOAc extract from the culture of Myrothecium gramminum (strain no. 3.1968) led to the isolation of eight cytotoxic trichothecene macrolides ( 1 - 8), all being substantially inhibitory against HepG2 (human hepatocellular carcinoma) and KB (human nasopharynyeal epidermoid tumor) cell lines with IC (50) values ranging from 2.2 to 12.2 mug/mL. Their inactivity to or weaker action on Vero cells (IC (50) values > 20 microg/mL, originated from the African green monkey kidney) highlighted preliminarily the nature of the selective cytotoxicity of the fungal metabolites against the test cancer cell lines. In addition, verrucarin A ( 1) and Roridin A ( 5) were found to be potent inhibitors of the radial growth of Echinochloa crusgalli with corresponding IC (50) values of (7.96 +/- 0.31) x 10 ( - 6) and (9.18 +/- 0.44) x 10 ( - 6) M, respectively, which were more potent than that of the positive control (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) [(9.40 +/- 0.04) x 10 ( - 5) M].
[Biosynthesis of macrocyclic trichothecenes: some aspects of physiology].[Pubmed:18663931]
Mikrobiol Z. 2008 Mar-Apr;70(2-3):116-21.
The data of long-term investigations of the control of macrocyclic trichothecenes biosynthesis by means ofthe elements of mineral nutrition, microelements in particular in Dendrodochium toxicum Pidopl. et Bilai are presented. The media for providing the dominant synthesis (50-70 %) of certain component from the composite complex of dendrodochins and so for obtaining the fractions enriched with this component, have been worked out. This method simplifies considerably the isolation of components in the crystal state. The media for obtaining verrucarin A, Roridin A and roridin H are proposed.


