SID 7969543Selective steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, NR5A1) inhibitor CAS# 868224-64-0 |
- PHA-665752
Catalog No.:BCC1181
CAS No.:477575-56-7
- (R)-Crizotinib
Catalog No.:BCC1284
CAS No.:877399-52-5
- Tivantinib (ARQ 197)
Catalog No.:BCC3688
CAS No.:905854-02-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 868224-64-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4076092 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H24N2O7 | M.Wt | 452.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
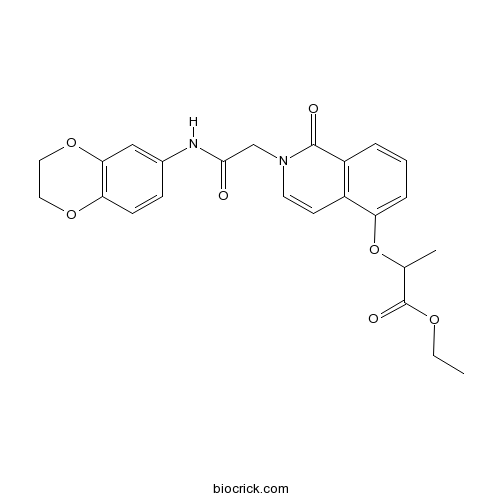
| Chemical Name | ethyl 2-[2-[2-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-ylamino)-2-oxoethyl]-1-oxoisoquinolin-5-yl]oxypropanoate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C(C)OC1=CC=CC2=C1C=CN(C2=O)CC(=O)NC3=CC4=C(C=C3)OCCO4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KWMBIIQCLUIHDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H24N2O7/c1-3-30-24(29)15(2)33-19-6-4-5-18-17(19)9-10-26(23(18)28)14-22(27)25-16-7-8-20-21(13-16)32-12-11-31-20/h4-10,13,15H,3,11-12,14H2,1-2H3,(H,25,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, NR5A1) inhibitor (IC50 values are 0.76, >33 and >33 μM at SF-1, RORα and VP16 respectively). Inhibits SF-1-dependent luciferase expression in HEK 293T cells in vitro (IC50 = 30 nM). |

SID 7969543 Dilution Calculator

SID 7969543 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2101 mL | 11.0507 mL | 22.1014 mL | 44.2028 mL | 55.2535 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.442 mL | 2.2101 mL | 4.4203 mL | 8.8406 mL | 11.0507 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.221 mL | 1.1051 mL | 2.2101 mL | 4.4203 mL | 5.5254 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0442 mL | 0.221 mL | 0.442 mL | 0.8841 mL | 1.1051 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0221 mL | 0.1105 mL | 0.221 mL | 0.442 mL | 0.5525 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Carasiphenol C
Catalog No.:BCN8251
CAS No.:868168-04-1
- H-Cys-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2904
CAS No.:868-59-7
- CRF (human, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5710
CAS No.:86784-80-7
- Astrasieversianin VII
Catalog No.:BCN2788
CAS No.:86764-11-6
- TG 100572
Catalog No.:BCC1994
CAS No.:867334-05-2
- TG 100801
Catalog No.:BCC1996
CAS No.:867331-82-6
- TG 100572 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1995
CAS No.:867331-64-4
- TRC 051384
Catalog No.:BCC7968
CAS No.:867164-40-7
- Linsitinib
Catalog No.:BCC3697
CAS No.:867160-71-2
- Colivelin
Catalog No.:BCC7821
CAS No.:867021-83-8
- Tropanyl 3-hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN1325
CAS No.:86702-58-1
- Magnoshinin
Catalog No.:BCC8205
CAS No.:86702-02-5
- Pam2CSK4
Catalog No.:BCC6247
CAS No.:868247-72-7
- LY 2365109 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7677
CAS No.:868265-28-5
- Org 27569
Catalog No.:BCC4411
CAS No.:868273-06-7
- Rhodiolin
Catalog No.:BCC8356
CAS No.:86831-53-0
- Rhodiosin; Herbacetin-7-O-glucorhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8478
CAS No.:86831-54-1
- WAY 213613
Catalog No.:BCC7442
CAS No.:868359-05-1
- 2,2,5,5-Tetramethylcyclohexane-1,4-dione
Catalog No.:BCN1324
CAS No.:86838-54-2
- Protosappanin A dimethyl acetal
Catalog No.:BCN6517
CAS No.:868405-37-2
- (+)-Puerol B 2''-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4561
CAS No.:868409-19-2
- Iristectorigenin B
Catalog No.:BCN8391
CAS No.:39012-01-6
- Carfilzomib (PR-171)
Catalog No.:BCC1145
CAS No.:868540-17-4
- 3',5'-Dimethoxybiphenyl-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN7529
CAS No.:868666-20-0
Thoracic Injury Risk Curves for Rib Deflections of the SID-IIs Build Level D.[Pubmed:27871106]
Stapp Car Crash J. 2016 Nov;60:545-580.
Injury risk curves for SID-IIs thorax and abdomen rib deflections proposed for future NCAP side impact evaluations were developed from tests conducted with the SID-IIs FRG. Since the floating rib guide is known to reduce the magnitude of the peak rib deflections, injury risk curves developed from SID-IIs FRG data are not appropriate for use with SID-IIs build level D. PMHS injury data from three series of sled tests and one series of whole-body drop tests are paired with thoracic rib deflections from equivalent tests with SID-IIs build level D. Where possible, the rib deflections of SID-IIs build level D were scaled to adjust for differences in impact velocity between the PMHS and SID-IIs tests. Injury risk curves developed by the Mertz-Weber modified median rank method are presented and compared to risk curves developed by other parametric and non-parametric methods.
Joint position statement on "Nutraceuticals for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia" of the Italian Society of Diabetology (SID) and of the Italian Society for the Study of Arteriosclerosis (SISA).[Pubmed:27956024]
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 Jan;27(1):2-17.
AIM: Evidence showed that LDL-cholesterol lowering is associated with a significant cardiovascular risk reduction. The initial therapeutic approach to hypercholesterolemia includes dietary modifications but the compliance to recommendations is often inadequate. Some dietary components with potential cholesterol-lowering activity are present in small amounts in food. Therefore, in recent years the use of "nutraceuticals" (i.e., nutrients and/or bioactive compounds with potential beneficial effects on human health) has become widespread. Such substances may be added to foods and beverages, or taken as dietary supplements (liquid preparations, tablets, capsules). In the present manuscript, the cholesterol-lowering activity of some nutraceuticals (i.e. fiber, phytosterols, soy, policosanol, red yeast rice and berberine) will be discussed along with: 1) the level of evidence on the cholesterol-lowering efficacy emerging from clinical trial; 2) the possible side effects associated with their use; 3) the categories of patients who could benefit from their use. DATA SYNTHESIS: Based on the current literature, the cholesterol-lowering effect of fiber, phytosterols and red yeast rice is consistent and supported by a good level of evidence. Over berberine, there is sufficient evidence showing significant cholesterol-lowering effects, although the results come from studies carried out almost exclusively in Asian populations. Data on the effects of soy are conflicting and, therefore, the strength of recommendation is quite low. The evidence on policosanol is inconclusive. CONCLUSION: Although health benefits may arise from the use of nutraceuticals with cholesterol-lowering activity, their use might be also associated with possible risks and pitfalls, some of which are common to all nutraceuticals whereas others are related to specific nutraceuticals.
Comparison of calculated and experimentally determined SID of CP and AA in complex diets differing in AA contents for grower finisher pigs.[Pubmed:28052453]
J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2017 Oct;101(5):e297-e302.
In practice, the content of standardized ileal digestible AA in complex feeds for pigs is calculated on the basis of tabulated values for individual feedstuffs. It comes into question, however, whether this truly reflects an accurate content based upon the estimate made for the individual feedstuffs. The objective of this study was to compare standardized ileal digestibility (SID) of crude protein (CP) and selected AA in complex feeds for grower and finisher pigs either calculated or experimentally determined. Six diets with increasing AA levels were prepared for grower (BW from 30 to 70 kg) and finisher (BW from 70 to 120 kg) feed. Crystalline L-lys, DL-met and L-thr were added to both diets, L-trp and L-val only to the grower feed. SID of both CP and AA was calculated from feed tables and experimentally determined in six adult minipigs (MINILEWE) with ileorectal anastomosis. With increasing AA levels, experimentally determined SID of supplemented AA increased (p < 0.05), but SID of CP (p >/= 0.05) was not affected. In both grower and finisher feed, calculated and experimentally determined SID of CP, Met, Cys, Trp, Ile and Tyr differed by more than 2% units, but those of Lys and His only in the finisher feed. Yet this effect was not directly consistent. The margin of error following estimation of SID of AA via tabulated values for individual feedstuffs, however, seems to be acceptable for practical use.
SID lysine requirement of immunologically and physically castrated male pigs during the grower, early and late finisher periods.[Pubmed:28380505]
J Anim Sci. 2017 Mar;95(3):1253-1263.
The main objective of this experiment was to determine the standardized ileal digestible (SID) Lys requirement of immunologically castrated (IC) and physically castrated (PC) male pigs during 3 growth phases. An additional objective was to compare the ADFI of PC and IC after the second anti-gonadotropin releasing factor (GnRF) injection. Three hundred male pigs (PIC 359 x C29), 150 each of IC and PC, were allotted to 1 of 5 treatments: 80, 90, 100, 110, or 120% of the estimated Lys requirement using the modeling program. Pigs remained on the same treatment throughout each of the 3 phases. Lysine requirements were determined at 3 stages of growth starting at a BW of 30.0 +/- 0.8, 64.7 +/- 1.4, and 111.9 +/- 1.9 kg for IC and 32.4 +/- 0.6, 69.8 +/- 1.0, and 114.5 +/- 1.3 kg for PC. Anti-GnRF injections were administered to IC at 11.5 and 19 wk (average BW = 96.3 +/- 1.8 kg) of age. The one-slope broken line regression and quadratic plateau models were used, and the best model was selected based on the Akaike information criterion. The IC SID Lys requirements based on ADG were 1.03, 0.97, and 0.55% and for G:F, the requirements were 0.99, 0.72, and 0.55% for phases 1, 2, and 3, respectively. For PC, the SID Lys requirements based on ADG were 0.86, 0.62, and 0.47% and for G:F were 0.86, 0.58, and 0.47% for phases 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Immunologically castrated pigs had greater SID Lys requirements for phases 1 and 2 compared to PC (0.17 and 0.35% points greater for ADG and 0.13 and 0.14% points greater for G:F for phases 1 and 2, respectively). After the second injection, when IC pigs are believed to become physiologically more similar to PC pigs, the SID Lys requirements continue to be greater for IC (0.55 vs. 0.47% for both ADG and G:F). The ADFI of IC increased 4 d after the second injection relative to PC. By 2 wk post second injection, the ADFI of IC exceeded that of PC ( < 0.05). Adopting immunological castration as a management tool requires an understanding that IC need to be fed differently compared to PC, to maximize growth performance. Immunologically castrated pigs have a greater SID Lys requirement throughout the grower and finishing periods compared to the PC.
Potent, selective and cell penetrant inhibitors of SF-1 by functional ultra-high-throughput screening.[Pubmed:18334597]
Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;73(6):1776-84.
The steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1, also known as NR5A1) is a transcription factor belonging to the nuclear receptor superfamily. Whereas most of the members of this family have been extensively characterized, the therapeutic potential and pharmacology of SF-1 still remains elusive. Described here is the identification and characterization of selective inhibitory chemical probes of SF-1 by a rational ultra-high-throughput screening (uHTS) strategy. A set of 64,908 compounds from the National Institute of Health's Molecular Libraries Small Molecule Repository was screened in a transactivation cell-based assay employing a chimeric SF-1 construct. Two analogous isoquinolinones, ethyl 2-[2-[2-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-7-ylamino)-2-oxoethyl]-1-oxoisoquinolin-5-yl ]oxypropanoate (SID7969543) and ethyl 2-[2-[2-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethylamino)-2-oxoethyl]-1-oxoisoquinolin-5-yl]oxypr opanoate and (SID7970631), were identified as potent submicromolar inhibitors, yielding IC(50) values of 760 and 260 nM. The compounds retained their potency in a more physiologic functional assay employing the full-length SF-1 protein and its native response element, yielding IC(50) values of 30 and 16 nM, respectively. The selectivity of these isoquinolinones was confirmed via transactivation-based functional assays for RAR-related orphan receptor A (RORA), Herpes simplex virus transcriptional activator protein Vmw65 (VP16), and liver receptor homolog 1 (LRH-1). Their cytotoxicity, solubility, permeability and metabolic stability were also measured. These isoquinolinones represent valuable chemical probes to investigate the therapeutic potential of SF-1.
Synthesis of small molecule inhibitors of the orphan nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor-1 (NR5A1) based on isoquinolinone scaffolds.[Pubmed:18374567]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Apr 15;18(8):2628-32.
Three synthetic routes were developed for structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies of HTS-derived isoquinolinone inhibitor probes for the orphan nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor-1 (NR5A1). Among the new analogs reported herein, 31 and 32 have improved potency, lower cellular toxicity, and improved selectivity compared to the initial HTS-derived leads 1 and 2.


