2,2,5,5-Tetramethylcyclohexane-1,4-dioneCAS# 86838-54-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 86838-54-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 13390715 | Appearance | Powder |
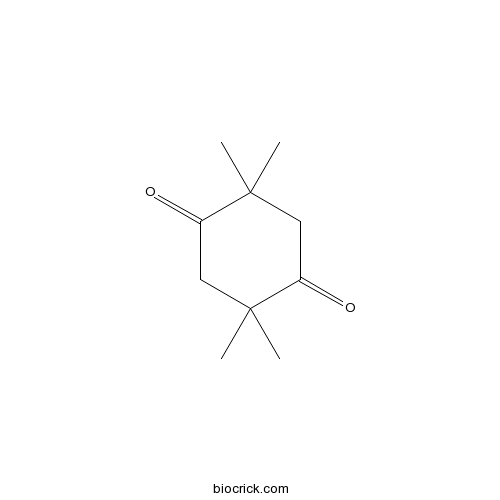
| Formula | C10H16O2 | M.Wt | 168.2 |
| Type of Compound | Monoterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2,2,5,5-tetramethylcyclohexane-1,4-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CC(=O)C(CC1=O)(C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OTQZSPVHJYLKOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

2,2,5,5-Tetramethylcyclohexane-1,4-dione Dilution Calculator

2,2,5,5-Tetramethylcyclohexane-1,4-dione Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.9453 mL | 29.7265 mL | 59.453 mL | 118.9061 mL | 148.6326 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1891 mL | 5.9453 mL | 11.8906 mL | 23.7812 mL | 29.7265 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5945 mL | 2.9727 mL | 5.9453 mL | 11.8906 mL | 14.8633 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1189 mL | 0.5945 mL | 1.1891 mL | 2.3781 mL | 2.9727 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0595 mL | 0.2973 mL | 0.5945 mL | 1.1891 mL | 1.4863 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- WAY 213613
Catalog No.:BCC7442
CAS No.:868359-05-1
- Rhodiosin; Herbacetin-7-O-glucorhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8478
CAS No.:86831-54-1
- Rhodiolin
Catalog No.:BCC8356
CAS No.:86831-53-0
- Org 27569
Catalog No.:BCC4411
CAS No.:868273-06-7
- LY 2365109 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7677
CAS No.:868265-28-5
- Pam2CSK4
Catalog No.:BCC6247
CAS No.:868247-72-7
- SID 7969543
Catalog No.:BCC6026
CAS No.:868224-64-0
- Carasiphenol C
Catalog No.:BCN8251
CAS No.:868168-04-1
- H-Cys-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2904
CAS No.:868-59-7
- CRF (human, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5710
CAS No.:86784-80-7
- Astrasieversianin VII
Catalog No.:BCN2788
CAS No.:86764-11-6
- TG 100572
Catalog No.:BCC1994
CAS No.:867334-05-2
- Protosappanin A dimethyl acetal
Catalog No.:BCN6517
CAS No.:868405-37-2
- (+)-Puerol B 2''-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4561
CAS No.:868409-19-2
- Iristectorigenin B
Catalog No.:BCN8391
CAS No.:39012-01-6
- Carfilzomib (PR-171)
Catalog No.:BCC1145
CAS No.:868540-17-4
- 3',5'-Dimethoxybiphenyl-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN7529
CAS No.:868666-20-0
- (R)-(-)-α-Methylhistamine dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC5665
CAS No.:868698-49-1
- Umeclidinium bromide
Catalog No.:BCC2022
CAS No.:869113-09-7
- Eudesma-3,11-dien-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN7607
CAS No.:86917-79-5
- SB 203580 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4293
CAS No.:869185-85-3
- PF-573228
Catalog No.:BCC4496
CAS No.:869288-64-2
- Neurokinin A (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC6955
CAS No.:86933-74-6
- Neurokinin B (human, porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC7119
CAS No.:86933-75-7
Synthesis and fluorescence studies of nine 1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4-dione derivatives: Dual emission and excimer fluorescence.[Pubmed:27894000]
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017 Mar 5;174:164-170.
The photophysical properties of nine 1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4-dione (BZD) derivatives were investigated using absorption and fluorescence spectral techniques in dimethyl sulfoxide. The trend of red shifts caused by the substitutions had full compliance with the trend of decreasing the calculated band gap (DeltaELUMO-HOMO) by semi-empirical AM1 and DFT/B3LYP/6-311+G* computational methods. The positive solvatochromism of BZD a demonstrated the pi-pi* nature of the singlet excited state. Dual fluorescence was observed in the emission spectra of BZD f and g, while their spectrum in different concentration showed only one peak short wavelength (SW) in dilute solutions. The main peak in SW around 370nm was attributed to the monomer of BZD (f* or g*) and the broader emission shifted to the visible region around 400nm in middle wavelength (MW) to the intermolecular excimer emission of BZD ([f/f]*or [g/g]*). The observed phenomena, such as solvatochromism, dual fluorescence, some red shifts caused by substitution, and larger Stokes shift indicated the existence of intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) in the BZDs series. The phosphorescence emission of the BZDs demonstrated their intersystem crossing (ISC) process.
Synthesis, biological evaluation and in silico studies of 5-(3-methoxybenzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione analogues as PTP1B inhibitors.[Pubmed:28126289]
Bioorg Chem. 2017 Apr;71:1-9.
PTP1B (protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B) dephosphorylates the insulin receptor substrate and thus acts as a negative regulator of the insulin and leptin signalling pathway. Recently, it has been considered as a new therapeutic target of intervention for the treatment of type2 diabetes. A series of aryl/alkylsulfonyloxy-5-(3-methoxybenzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives were synthesized, screened in vitro for their PTP1B inhibitory activity and in vivo for anti-hyperglycaemic activity. Docking results further helped in understanding the nature of interactions governing the binding mode of ligands inside the active site of PTP1B. Among the synthesized compounds, 13 and 16 were found to be potent PTP1B inhibitors having IC50 of 7.31 and 8.73muM respectively. Significant lowering of blood glucose level was observed in some of the synthesized compounds in in vivo study.
Programmable self-assembly of water-soluble organo-heterometallic cages [M12M'4L12] using 3-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)pentane-2,4-dione (H2L).[Pubmed:28361135]
Chem Commun (Camb). 2017 Apr 11;53(30):4238-4241.
A bifunctional ligand H2L featuring primary (pyrazole) and secondary (acetylacetone) coordination sites was preferentially reacted with dimetallic [M2(NO3)2](NO3)2 linkers at the pyrazolyl end of H2L, giving rise to dimetallic corners. Subsequently, the corners serve as the secondary site with M' to form water-soluble organo-heterometallic [M12M'4L12] cages in a stepwise mode.
Protective Effects of 2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2,5 -Diene-1,4-Dione Isolated from Averrhoa Carambola L. (Oxalidaceae) Roots on High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Mice.[Pubmed:27941348]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(5):993-1004.
BACKGROUND/AIMS: The roots of Averrhoa carambola L. (Oxalidaceae) have long been used as a traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of diabetes and diabetes-related diseases. 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycycyclohexa-2,5-1,4-dione (DMDD) has been isolated from A. carambola L. roots, and this study was carried out to investigate the potential beneficial effects of DMDD on obesity and insulin resistance induced by a high-fat diet (HFD) in mice. METHODS: C57BL/6J mice were fed a HFD for 16 weeks and orally administered DMDD (12.5, 25, or 50 mg/kg of body weight per day) and metformin (280 mg/kg of body weight per day) for the last 4 weeks. RESULTS: The body weights and adipose tissue weights as well as the serum levels of blood glucose, total cholesterol, triglycerides, free fatty acids, insulin, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha were significantly decreased by DMDD, and the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and myeloid differentiation factor (Myd88) in the epididymal adipose tissue was downregulated by DMDD. In contrast, insulin sensitivity was enhanced. The results of the glucose tolerance tests, insulin tolerance tests, and insulin release tests indicated that there was a marked improvement in insulin secretion, and the areas under the curve corresponding to the three tests were also significantly decreased by DMDD. The activities of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase were simultaneously enhanced, whereas the content of malondialdehyde was decreased by DMDD in the liver homogenates of the C57BL/6J mice. In addition, hepatic steatosis and adipocyte hypertrophy, as assessed by H&E staining of liver and adipose tissues, were significantly improved by DMDD. CONCLUSION: These data suggest that MDD has potential benefits for the treatment of HFD-induced obesity and insulin resistance, and its effects may be associated with improvements in lipid metabolism and inhibition of the expression of TLR4 in adipose tissues.


