Neurokinin B (human, porcine)Endogenous tachykinin peptide CAS# 86933-75-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
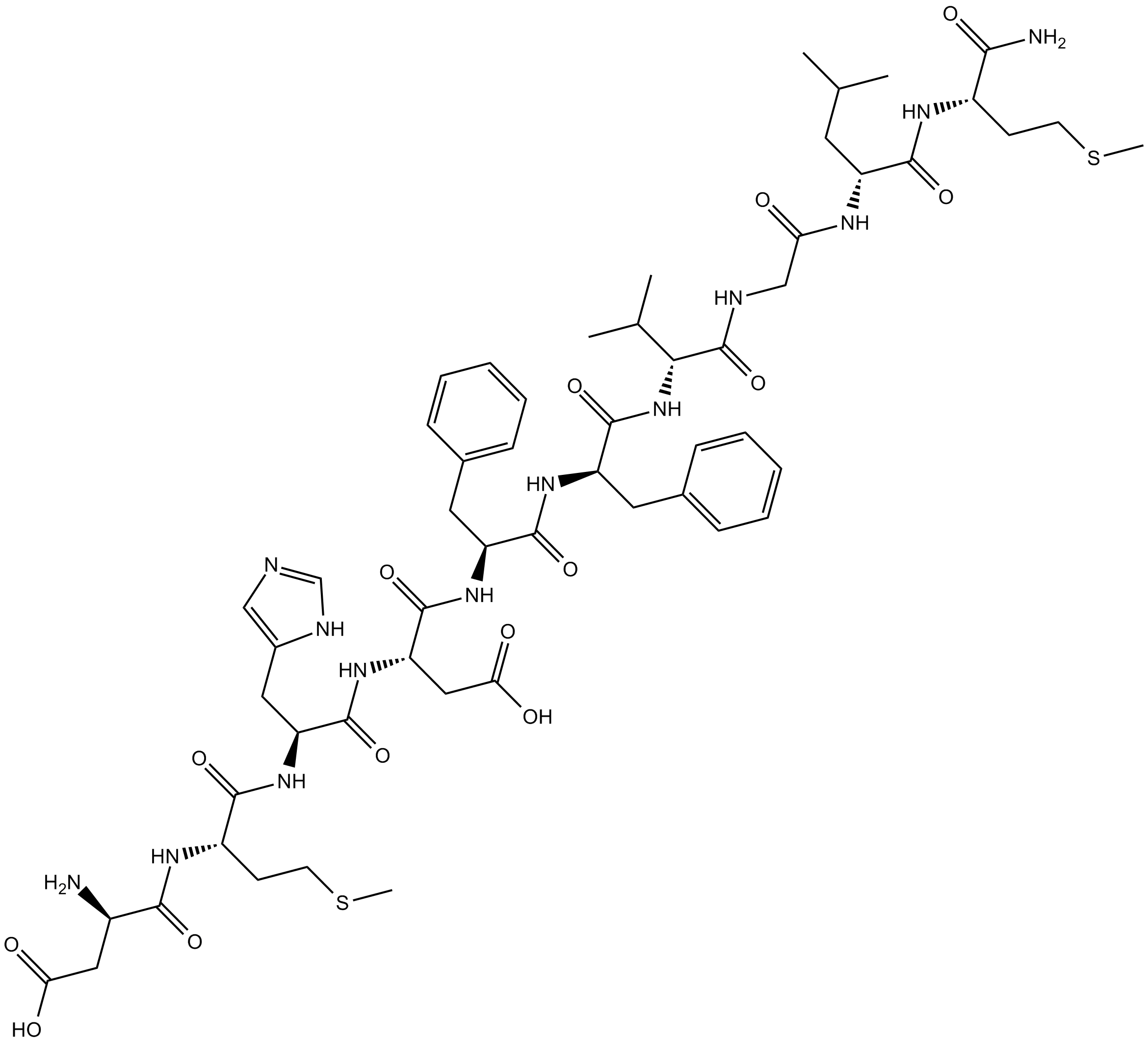
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 86933-75-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 55583 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C55H79N13O14S2 | M.Wt | 1210.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | NKB | ||
| Solubility | H2O Peptide Solubility and Storage Guidelines: 1. Calculate the length of the peptide. 2. Calculate the overall charge of the entire peptide according to the following table: 3. Recommended solution: | ||
| Sequence | DMHDFFVGLM (Modifications: Met-10 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-amino-4-[[1-[[1-[[1-[[1-[[1-[[1-[[2-[[1-[(1-amino-4-methylsulfanyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-3-carboxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-4-methylsulfanyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(C(=O)NC(CCSC)C(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)C(CC2=CC=CC=C2)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC3=CN=CN3)NC(=O)C(CCSC)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NHXYSAFTNPANFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C55H79N13O14S2/c1-30(2)21-38(50(77)62-36(47(57)74)17-19-83-5)61-43(69)28-59-55(82)46(31(3)4)68-54(81)40(23-33-15-11-8-12-16-33)65-51(78)39(22-32-13-9-7-10-14-32)64-53(80)42(26-45(72)73)67-52(79)41(24-34-27-58-29-60-34)66-49(76)37(18-20-84-6)63-48(75)35(56)25-44(70)71/h7-16,27,29-31,35-42,46H,17-26,28,56H2,1-6H3,(H2,57,74)(H,58,60)(H,59,82)(H,61,69)(H,62,77)(H,63,75)(H,64,80)(H,65,78)(H,66,76)(H,67,79)(H,68,81)(H,70,71)(H,72,73) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Endogenous tachykinin agonist peptide that shows preference for the NK3 receptor (EC50 = 1 nM). |

Neurokinin B (human, porcine) Dilution Calculator

Neurokinin B (human, porcine) Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Neurokinin A (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC6955
CAS No.:86933-74-6
- PF-573228
Catalog No.:BCC4496
CAS No.:869288-64-2
- SB 203580 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4293
CAS No.:869185-85-3
- Eudesma-3,11-dien-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN7607
CAS No.:86917-79-5
- Umeclidinium bromide
Catalog No.:BCC2022
CAS No.:869113-09-7
- (R)-(-)-α-Methylhistamine dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC5665
CAS No.:868698-49-1
- 3',5'-Dimethoxybiphenyl-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN7529
CAS No.:868666-20-0
- Carfilzomib (PR-171)
Catalog No.:BCC1145
CAS No.:868540-17-4
- Iristectorigenin B
Catalog No.:BCN8391
CAS No.:39012-01-6
- (+)-Puerol B 2''-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4561
CAS No.:868409-19-2
- Protosappanin A dimethyl acetal
Catalog No.:BCN6517
CAS No.:868405-37-2
- 2,2,5,5-Tetramethylcyclohexane-1,4-dione
Catalog No.:BCN1324
CAS No.:86838-54-2
- AZD8330
Catalog No.:BCC3733
CAS No.:869357-68-6
- MLN8054
Catalog No.:BCC2170
CAS No.:869363-13-3
- 14-Deoxy-17-hydroxyandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN4560
CAS No.:869384-82-7
- Praeroside II
Catalog No.:BCN7001
CAS No.:86940-46-7
- JNJ 10191584 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC7362
CAS No.:869497-75-6
- Tecovirimat
Catalog No.:BCC5518
CAS No.:869572-92-9
- Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2572
CAS No.:86967-51-3
- Obestatin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5912
CAS No.:869705-22-6
- A-770041
Catalog No.:BCC1323
CAS No.:869748-10-7
- threo-Guaiacylglycerol beta-coniferyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN1323
CAS No.:869799-76-8
- A 841720
Catalog No.:BCC7550
CAS No.:869802-58-4
- Andropanolide
Catalog No.:BCN4559
CAS No.:869807-57-8
The tachykinin peptide family.[Pubmed:12037144]
Pharmacol Rev. 2002 Jun;54(2):285-322.
The tachykinin peptide family certainly represents one of the largest peptide families described in the animal organism. So far, more than 40 tachykinins have been isolated from invertebrate (insects, worms, and molluscs), protochordate, and vertebrate (skin, gastrointestinal tract, peripheral and central nervous system) tissues. Substance P (SP), first identified by bioassay as early as 1931 but sequenced only in 1971, several years after the elucidation of the structure of eledoisin from molluscan tissues and of physalaemin from amphibian skin, may be considered as a prototype of the tachykinins. Hitherto, as many as 19 tachykinins have been isolated from amphibian integument, and eight additional peptides have been isolated from amphibian gut and brain. Counterparts of skin tachykinins in mammalian tissues are SP, neurokinin A, and neurokinin B. Three main receptor subtypes for the tachykinins have been identified (NK1, NK2, and NK3), but their number is probably destined to increase. It is obvious that the peripheral and central effects of the tachykinins may substantially vary depending on the activation of different receptor subtypes. Matters are further complicated by the frequent capacity of the single tachykinins to bind, although with different affinity, to more receptors. It has been recognized that tachykinins have a variety of effects in physiological and pathological conditions, and there is evidence suggesting intrinsic neuroprotective and neurodegenerative properties of these neuropeptides. This review provides an update on the current body of knowledge regarding tachykinin occurrence and distribution in the animal kingdom, from the lowest invertebrates to man, and the physiological and pharmacological actions of tachykinins outlining the pregnant importance of this large peptide family.
Neurokinin B potentiates ATP-activated currents in rat DRG neurons.[Pubmed:11743983]
Brain Res. 2001 Dec 27;923(1-2):157-62.
This study aimed to explore whether NKB could modulate the responses mediated by ATP receptor (P2X purinoceptor). Whole-cell patch clamp and repatch experiments were performed on cultured rat DRG neurons. The majority of neurons examined were sensitive both to ATP and to NKB (77.1%, 54/70). NKB preapplied could potentiate ATP-activated currents (I(ATP)) markedly; this effect was concentration-dependent and could be blocked by SR 142801, an NK3 receptor antagonist. Preapplication of 0.001, 0.01, 0.1 and 1.0 microM NKB increased ATP-activated currents by 55.1+/-18.8, 75.2+/-17.4, 84.1+/-18.8 and 81.0+/-21.7%, respectively. The concentration-response curves for ATP with and without preapplication of NKB show that: (1) preapplication of NKB shifted the curve upwards; (2) the maximal amplitude of I(ATP) with NKB preapplication increased by 78.5%, while the threshold value remained unchanged; (3) the EC(50) values of the two curves were very close (44 vs. 42 microM). Intracellular dialysis of H-7 by using repatch clamp technique could block the potentiation of I(ATP) by NKB. It suggests that this potentiating effect was caused by phosphorylation of ATP receptor, which resulted from the activation of G protein coupled NK3 receptor and consequential intracellular signal transduction cascade.
Neurokinin B is a preferred agonist for a neuronal substance P receptor and its action is antagonized by enkephalin.[Pubmed:2414777]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7444-8.
Receptor specificity of the substance P-related peptides neurokinin A and neurokinin B was studied in the isolated guinea pig ileum. Substance P and the recently discovered neurokinins elicit contraction of the ileum both directly through action on a muscle cell receptor and indirectly through stimulation of a neuronal receptor, leading to release of acetylcholine, which causes muscle contraction via muscarinic receptors. Two specific assay procedures for the function of the neuronal receptor were developed. The muscular receptor was inactivated either by desensitization with the selective agonist substance P methyl ester or by receptor blockade with the selective antagonist [Arg6, D-Trp7,9, Me-Phe8]substance P-(6-11) hexapeptide. Both procedures revealed that the neuronal receptor is clearly distinct from the muscular receptor, since it exhibits different agonist specificity and is insensitive to antagonists of the muscular receptor. Neurokinin B was found to be the most potent agonist (EC50 = 1 nM) for the neuronal receptor. Furthermore, [D-Ala2, Met5]enkephalinamide inhibited in a naloxone-sensitive manner the effect of neurokinin B mediated via the neuronal receptor. These results suggest that the different mammalian tachykinins can play specific physiological roles by virtue of their distinct receptor specificities.


