T 705CAS# 259793-96-9 |
- SR 11302
Catalog No.:BCC3607
CAS No.:160162-42-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 259793-96-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 492405 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C5H4FN3O2 | M.Wt | 157.1 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (636.54 mM) H2O : 6.25 mg/mL (39.78 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
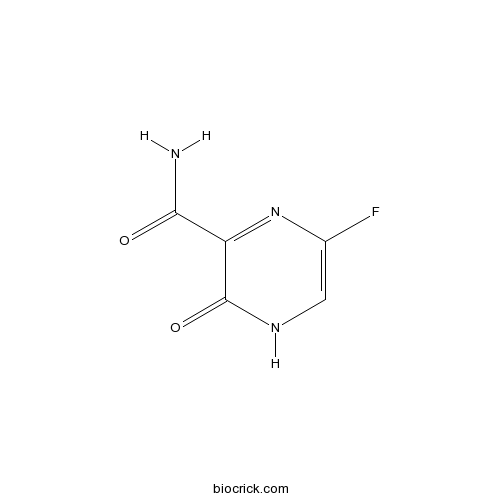
| Chemical Name | 5-fluoro-2-oxo-1H-pyrazine-3-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=C(N=C(C(=O)N1)C(=O)N)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZCGNOVWYSGBHAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H4FN3O2/c6-2-1-8-5(11)3(9-2)4(7)10/h1H,(H2,7,10)(H,8,11) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

T 705 Dilution Calculator

T 705 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.3654 mL | 31.8269 mL | 63.6537 mL | 127.3074 mL | 159.1343 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2731 mL | 6.3654 mL | 12.7307 mL | 25.4615 mL | 31.8269 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6365 mL | 3.1827 mL | 6.3654 mL | 12.7307 mL | 15.9134 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1273 mL | 0.6365 mL | 1.2731 mL | 2.5461 mL | 3.1827 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0637 mL | 0.3183 mL | 0.6365 mL | 1.2731 mL | 1.5913 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
T 705(Favipiravir) is a RNA-directed RNA polymerase NS5B inhibitor.
- 2-Deacetyltaxuspine X
Catalog No.:BCN7375
CAS No.:259678-73-4
- 5-Hydroxy-7-methoxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)chroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN1472
CAS No.:259653-54-8
- 5-Acetyl-3-chloro-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine
Catalog No.:BCC8726
CAS No.:25961-11-9
- Allura Red AC
Catalog No.:BCN2220
CAS No.:25956-17-6
- EDC.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2812
CAS No.:25952-53-8
- HOBt (anhydrous)
Catalog No.:BCC2816
CAS No.:2592-95-2
- Boc-Lys(Boc)-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3414
CAS No.:2592-19-0
- Boc-Thr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3449
CAS No.:2592-18-9
- 3'-Hydroxydehydroaglaiastatin
Catalog No.:BCN7725
CAS No.:259143-58-3
- D-Luciferin
Catalog No.:BCC6535
CAS No.:2591-17-5
- Yunaconitoline
Catalog No.:BCN6703
CAS No.:259099-25-7
- Hoechst 33258 analog
Catalog No.:BCC1624
CAS No.:258843-62-8
- Hyponine D
Catalog No.:BCC8998
CAS No.:259823-31-9
- 4-Hydroxythiobenzamide
Catalog No.:BCC8709
CAS No.:25984-63-8
- Nimbolide
Catalog No.:BCN8053
CAS No.:25990-37-8
- Xylose
Catalog No.:BCC4880
CAS No.:25990-60-7
- GI 254023X
Catalog No.:BCC2374
CAS No.:260264-93-5
- Zamanic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5131
CAS No.:260393-05-3
- Dihydroisotanshinone II
Catalog No.:BCN5132
CAS No.:260397-58-8
- Ligustroflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2370
CAS No.:260413-62-5
- PD173955
Catalog No.:BCC3999
CAS No.:260415-63-2
- Beauvericin
Catalog No.:BCC6546
CAS No.:26048-05-5
- Boc-Asp(OBzl)-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3364
CAS No.:26048-69-1
- 1-Isomangostin hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN5133
CAS No.:26063-95-6
Synthesis of T-705-Ribonucleoside and T-705-Ribonucleotide and Studies of Chemical Stability.[Pubmed:28324644]
ChemMedChem. 2017 May 9;12(9):652-659.
T-705 (favipiravir) is a fluorinated hydroxypyrazine carboxamide that exhibits antiviral activities against a variety of RNA viruses. Given the lack of potent agents to combat these infections caused by a large number of high-impact pathogens, significant emphasis has been put on studies of the antiviral properties of T-705 and its mechanism of action. T-705 acts as a nucleobase analogue; it is therefore metabolized to the corresponding ribonucleoside triphosphate intracellularly. Herein we report a reliable synthesis of T-705-ribonucleoside as well as its 5'-monophosphate. Moreover, we disclose detailed studies on the remarkable lability of the heterocycle when attached to ribose under very mild conditions, as typically applied in biochemical studies.
Distinct Effects of T-705 (Favipiravir) and Ribavirin on Influenza Virus Replication and Viral RNA Synthesis.[Pubmed:27572398]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Oct 21;60(11):6679-6691.
T-705 (favipiravir) is a new antiviral agent in advanced clinical development for influenza therapy. It is supposed to act as an alternative substrate for the viral polymerase, causing inhibition of viral RNA synthesis or virus mutagenesis. These mechanisms were also proposed for ribavirin, an established and broad antiviral drug that shares structural similarity with T-705. We here performed a comparative analysis of the effects of T-705 and ribavirin on influenza virus and host cell functions. Influenza virus-infected cell cultures were exposed to T-705 or ribavirin during single or serial virus passaging. The effects on viral RNA synthesis and infectious virus yield were determined and mutations appearing in the viral genome were detected by whole-genome virus sequencing. In addition, the cellular nucleotide pools as well as direct inhibition of the viral polymerase enzyme were quantified. We demonstrate that the anti-influenza virus effect of ribavirin is based on IMP dehydrogenase inhibition, which results in fast and profound GTP depletion and an imbalance in the nucleotide pools. In contrast, T-705 acts as a potent and GTP-competitive inhibitor of the viral polymerase. In infected cells, viral RNA synthesis is completely inhibited by T-705 or ribavirin at >/=50 muM, whereas exposure to lower drug concentrations induces formation of noninfectious particles and accumulation of random point mutations in the viral genome. This mutagenic effect is 2-fold higher for T-705 than for ribavirin. Hence, T-705 and ribavirin both act as purine pseudobases but profoundly differ with regard to the mechanism behind their antiviral and mutagenic effects on influenza virus.
Clinical and Virological Characteristics of Ebola Virus Disease Patients Treated With Favipiravir (T-705)-Sierra Leone, 2014.[Pubmed:27553371]
Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Nov 15;63(10):1288-1294.
BACKGROUND: During 2014-2015, an outbreak of Ebola virus disease (EVD) swept across parts of West Africa. No approved antiviral drugs are available for Ebola treatment currently. METHODS: A retrospective clinical case series was performed for EVD patients in Sierra Leone-China Friendship Hospital. Patients with confirmed EVD were sequentially enrolled and treated with either World Health Organization (WHO)-recommended supportive therapy (control group) from 10 to 30 October, or treated with WHO-recommended therapy plus favipiravir (T-705) from 1 to 10 November 2014. Survival and virological characteristics were observed for 85 patients in the control group and 39 in the T-705 treatment group. RESULTS: The overall survival rate in the T-705 treatment group was higher than that of the control group (56.4% [22/39] vs 35.3% [30/85]; P = .027). Among the 35 patients who finished all designed endpoint observations, the survival rate in the T-705 treatment group (64.8% [11/17]) was higher than that of the control group (27.8% [5/18]). Furthermore, the average survival time of the treatment group (46.9 +/- 5.6 days) was longer than that of the control group (28.9 +/- 4.7 days). Most symptoms of patients in the treatment group improved significantly. Additionally, 52.9% of patients who received T-705 had a >100-fold viral load reduction, compared with only 16.7% of patients in the control group. CONCLUSIONS: Treatment of EVD with T-705 was associated with prolonged survival and markedly reduced viral load, which makes a compelling case for further randomized controlled trials of T-705 for treating EVD.
T-705 (Favipiravir) suppresses tumor necrosis factor alpha production in response to influenza virus infection: A beneficial feature of T-705 as an anti-influenza drug.[Pubmed:28105854]
Acta Virol. 2017;61(1):48-55.
Influenza virus infection induces the production of various cytokines, which play important roles in the pathogenesis of infection. Among the cytokines induced by influenza, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) production has been correlated with the severity of lung lesions. We investigated the effects of T-705 (Favipiravir, 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazinecarboxamide) on cytokine production due to influenza virus infection in vitro and in vivo, compared with oseltamivir or GS 4071, an active form of oseltamivir. TNF-alpha production in mouse macrophage-derived P388D1 cells infected with the influenza virus was lower following treatment with T-705 at concentrations of 0.3 to 100 microg/ml than treatment with GS 4071 at the same concentrations. The effect of treatment with T-705 on the cytokine production induced by the influenza virus infection was investigated in mouse influenza virus infection model. At 48 h post-infection (p.i.) T-705 significantly suppressed the viral load in the lungs and TNF-alpha production in the airways of infected mice even when viral loads were high. Furthermore, T-705 suppressed only TNF-alpha production from the early phase of infection. In this study, T-705 showed the antiviral activity of reducing pulmonary viral load compared with oseltamivir, thereby suppressing the TNF-alpha production. This feature of T-705 is benefit against severe influenza infection.


