D-Luciferincell-permeable chemiluminescent luciferase substrate CAS# 2591-17-5 |
- Mc-MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1735
CAS No.:1401963-15-2
- Monomethyl auristatin E
Catalog No.:BCC1775
CAS No.:474645-27-7
- CYT997 (Lexibulin)
Catalog No.:BCC4601
CAS No.:917111-44-5
- MPC 6827 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8040
CAS No.:917369-31-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2591-17-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5459882 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C11H8N2O3S2 | M.Wt | 280.32 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | D-(-)-Luciferin; Firefly luciferin | ||
| Solubility | >28mg/mL in DMSO | ||
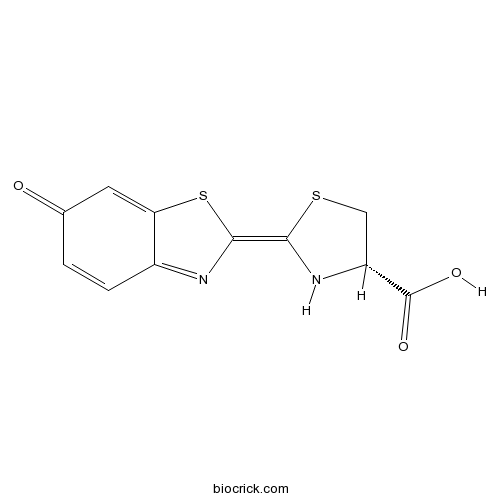
| Chemical Name | (2Z,4S)-2-(6-oxo-1,3-benzothiazol-2-ylidene)-1,3-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C(NC(=C2N=C3C=CC(=O)C=C3S2)S1)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IWJYWBVPCGUPLO-BFUDMSGGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H8N2O3S2/c14-5-1-2-6-8(3-5)18-10(12-6)9-13-7(4-17-9)11(15)16/h1-3,7,13H,4H2,(H,15,16)/b10-9-/t7-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | D-luciferin is the natural substrate of luciferases that catalyze the production of light in bioluminescent insects.In Vitro:D-luciferin is the natural substrate of the enzyme luciferase (Luc), that catalyzes the production of the typical yellowgreen light of fireflies.The present review covers the synthesis of D-luciferin and derivatives or analogues that are substrates or inhibitors of the luciferase from the American firefly Photinus pyralis, the enzyme more frequently used in techniques of in vitro and optical imaging[1].In Vivo:Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) using the firefly luciferase (Fluc) as a reporter gene and D-luciferin as a substrate is currently the most widely employed technique. The total signal intensity is plotted against the time after D-luciferin injection to generate a time-intensity curve. In addition to the peak signal, the signals at fixed time points (5, 10, 15, and 20 min) after D-luciferin injection are determined as alternatives to the peak signal. The signal in a given time-intensity curve is normalized for the peak signal in the curve to represent the pattern of temporal changes after D-luciferin injection[2]. References: | |||||

D-Luciferin Dilution Calculator

D-Luciferin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5674 mL | 17.8368 mL | 35.6735 mL | 71.347 mL | 89.1838 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7135 mL | 3.5674 mL | 7.1347 mL | 14.2694 mL | 17.8368 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3567 mL | 1.7837 mL | 3.5674 mL | 7.1347 mL | 8.9184 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0713 mL | 0.3567 mL | 0.7135 mL | 1.4269 mL | 1.7837 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0357 mL | 0.1784 mL | 0.3567 mL | 0.7135 mL | 0.8918 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
D-luciferin is a cell-permeable chemiluminescent luciferase substrate with a Km of approximately 2 μM. D-luciferin could emit lights upon oxidative decarboxylation in the presence of ATP. D-luciferin provides a bioluminescent signal for in vivo and in vitro detection of cellular ATP levels. D-Luciferin chould be used to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays. D-luciferin could be administrated intravenously or intraperitonealy. In vivo and in vitro bioluminescence imaging (BLI) is a promising technique for non-invasive tumour imaging. The repeatability coefficients of intravenously and intraperitonealy was 80.2% and 95.0%, respectively. PEmax of IP was 5.6 times higher for IV. When compared with IP, IV administration showed better repeatability and better sensitivity. It would be more beneficial to evaluate the accurate tumor burden of the small tumors rather than the larger tumors [1].
Reference:
Keyaerts M, Verschueren J, Bos T J, et al. Dynamic bioluminescence imaging for quantitative tumour burden assessment using IV or IP administration of D-luciferin: effect on intensity, time kinetics and repeatability of photon emission[J]. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, 2008, 35(5): 999-1007.
- Yunaconitoline
Catalog No.:BCN6703
CAS No.:259099-25-7
- Hoechst 33258 analog
Catalog No.:BCC1624
CAS No.:258843-62-8
- Liensinine
Catalog No.:BCN6337
CAS No.:2586-96-1
- H-D-Cys(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2914
CAS No.:25840-82-8
- Ghrelin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5767
CAS No.:258338-12-4
- IEM 1925 dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7885
CAS No.:258282-23-4
- Ghrelin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC7076
CAS No.:258279-04-8
- LEP (116-130) (mouse)
Catalog No.:BCC1016
CAS No.:258276-95-8
- Gemfibrozil
Catalog No.:BCC4783
CAS No.:25812-30-0
- Pelitinib (EKB-569)
Catalog No.:BCC1118
CAS No.:257933-82-7
- H-D-Glu(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2939
CAS No.:2578-33-8
- CP 154526
Catalog No.:BCC7481
CAS No.:257639-98-8
- 3'-Hydroxydehydroaglaiastatin
Catalog No.:BCN7725
CAS No.:259143-58-3
- Boc-Thr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3449
CAS No.:2592-18-9
- Boc-Lys(Boc)-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3414
CAS No.:2592-19-0
- HOBt (anhydrous)
Catalog No.:BCC2816
CAS No.:2592-95-2
- EDC.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2812
CAS No.:25952-53-8
- Allura Red AC
Catalog No.:BCN2220
CAS No.:25956-17-6
- 5-Acetyl-3-chloro-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine
Catalog No.:BCC8726
CAS No.:25961-11-9
- 5-Hydroxy-7-methoxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)chroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN1472
CAS No.:259653-54-8
- 2-Deacetyltaxuspine X
Catalog No.:BCN7375
CAS No.:259678-73-4
- T 705
Catalog No.:BCC4130
CAS No.:259793-96-9
- Hyponine D
Catalog No.:BCC8998
CAS No.:259823-31-9
- 4-Hydroxythiobenzamide
Catalog No.:BCC8709
CAS No.:25984-63-8
The Drug Excipient Cyclodextrin Interacts With d-Luciferin and Interferes With Bioluminescence Imaging.[Pubmed:27030398]
Mol Imaging. 2016 Jan 27;15. pii: 15/0/1536012115625225.
Cyclodextrins are well-characterized, barrel-shaped molecules that can solubilize organic small molecules in aqueous solution via host-guest interactions. As such, cyclodextrins are used as excipients for experimental therapeutics in vivo. We observed unanticipated modifications to bioluminescence imaging (BLI) signal intensity when 2-hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HPCD) was coinjected as an excipient. We hypothesized that HPCD bindsD-Luciferin and interferes with the BLI signal. Using luciferase-expressing cell lines, we showed that HPCD lowers the BLI signal in a concentration-dependent manner. Flow cytometry revealed that HPCD resulted in reduced cellular accumulation ofD-Luciferin, and mass spectrometry revealedD-Luciferin HPCD species, confirming a direct interaction. In vivo imaging using a luciferase mouse model demonstrated that HPCD reduced luciferin-mediated BLI compared to luciferin alone. The implications of using HPCD as an excipient in BLI studies are discussed.
Hydrazide d-luciferin for in vitro selective detection and intratumoral imaging of Cu(2.).[Pubmed:27131992]
Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Sep 15;83:200-4.
Copper is an essential micronutrient involved in fundamental life processes but using a bioluminescence (BL) probe to selectively sense Cu(2+)in vitro or image Cu(2+)in vivo is still unavailable. Herein, a latent BL probe hydrazide D-Luciferin (1) was rationally designed and successfully applied it for selective detection of Cu(2+)in vitro and imaging Cu(2+) in living cells and in tumors. Upon the catalysis of Cu(2+), 1 was converted to D-Luciferin and turned on the BL in the presence of firefly luciferase (fLuc). In vitro tests indicated that 1 could be applied for highly selective sensing Cu(2+) within the range of 0-80muM with a limit of detection (LOD) of 39.0nM. Cell and animal experiments indicated that 1 could be applied for specific BL imaging of Cu(2+) in living cells and tumors and the BL signal of 1 was more stable and longer than that of D-Luciferin. We envision that this unique probe 1 might serve as an elucidative tool for further exploration of the biological roles of Cu(2+) in physiological and pathological processes in the near future.
Intracellular Self-Assembly of Cyclic d-Luciferin Nanoparticles for Persistent Bioluminescence Imaging of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase.[Pubmed:27348334]
ACS Nano. 2016 Jul 26;10(7):7147-53.
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) overexpression induces several disorder symptoms in nerve systems, and therefore long-term tracing of FAAH activity in vivo is of high importance but remains challenging. Current bioluminescence (BL) methods are limited in detecting FAAH activity within 5 h. Herein, by rational design of a latent BL probe (d-Cys-Lys-CBT)2 (1), we developed a "smart" method of intracellular reduction-controlled self-assembly and FAAH-directed disassembly of its cyclic D-Luciferin-based nanoparticles (i.e., 1-NPs) for persistent BL imaging of FAAH activity in vitro, in cells, and in vivo. Using aminoluciferin methyl amide (AMA), Lys-amino-D-Luciferin (Lys-Luc), and amino-D-Luciferin (NH2-Luc) as control BL probes, we validated that the persistent BL of 1 from luciferase-expressing cells or tumors was controlled by the activity of intracellular FAAH. With the property of long-term tracing of FAAH activity in vivo of 1, we envision that our BL precursor 1 could probably be applied for in vivo screening of FAAH inhibitors and the diagnosis of their related diseases (or disorders) in the future.
Label-Free Cell Phenotypic Identification of D-Luciferin as an Agonist for GPR35.[Pubmed:27424891]
Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1461:3-17.
D-Luciferin (also known as beetle or firefly luciferin) is one of the most widely used bioluminescent reporters for monitoring in vitro or in vivo luciferase activity. The identification of several natural phenols and thieno[3,2-b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid derivatives as agonists for GPR35, an orphan G protein-coupled receptor, had motivated us to examine the pharmacological activity of D-Luciferin, given that it also contains phenol and carboxylic acid moieties. Here, we describe label-free cell phenotypic assays that ascertain D-Luciferin as a partial agonist for GPR35. The agonistic activity of D-Luciferin at the GPR35 shall evoke careful interpretation of biological data when D-Luciferin or its analogues are used as probes.


