ABT-333Inhibitor of non-nucleoside HCV NS5B CAS# 1132935-63-7 |
- ABT-199
Catalog No.:BCC3614
CAS No.:1257044-40-8
- BM-1074
Catalog No.:BCC2235
CAS No.:1391108-10-3
- HA14-1
Catalog No.:BCC3593
CAS No.:65673-63-4
- Obatoclax mesylate (GX15-070)
Catalog No.:BCC2234
CAS No.:803712-79-0
- ABT-737
Catalog No.:BCC3613
CAS No.:852808-04-9
- TW-37
Catalog No.:BCC2257
CAS No.:877877-35-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1132935-63-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 56640146 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H27N3O5S | M.Wt | 493.57 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Dasabuvir | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 46 mg/mL (93.20 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
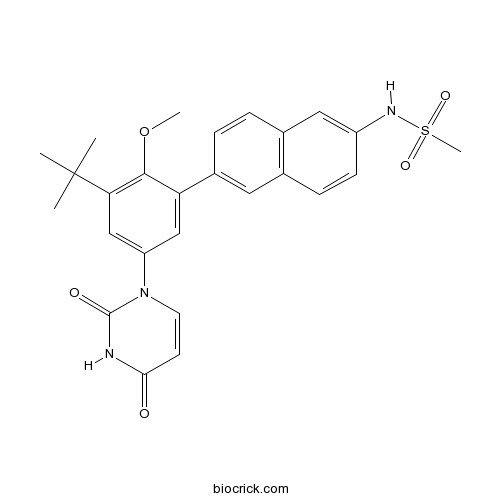
| Chemical Name | N-[6-[3-tert-butyl-5-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)-2-methoxyphenyl]naphthalen-2-yl]methanesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)N2C=CC(=O)NC2=O)C3=CC4=C(C=C3)C=C(C=C4)NS(=O)(=O)C)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NBRBXGKOEOGLOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H27N3O5S/c1-26(2,3)22-15-20(29-11-10-23(30)27-25(29)31)14-21(24(22)34-4)18-7-6-17-13-19(28-35(5,32)33)9-8-16(17)12-18/h6-15,28H,1-5H3,(H,27,30,31) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | ABT-333 is a nonnucleoside inhibitor of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase encoded by the HCV NS5B gene, inhibits recombinant NS5B polymerases derived from HCV genotype 1a and 1b clinical isolates, with IC50 between 2.2 and 10.7 nM.In Vitro:ABT-333 (Dasabuvir) is at least 7,000-fold selective for the inhibition of HCV genotype 1 polymerases over human/mammalian polymerases. ABT-333 (Dasabuvir) inhibits the polymerase enzymatic activity of genotype 1 laboratory strain enzymes (H77, BK, N, and Con1 strains), as well as enzymes produced from polymerase genes from HCV genotype 1-infected subjects, with IC50s between 2.2 and 10.7 nM. ABT-333 inhibits replication of HCV subgenomic replicons in cell culture assays, with EC50 values of 7.7 and 1.8 nM against genotype 1a (H77) and 1b (Con1), respectively. In the presence of 40% human plasma, there is a 12- to 13-fold decrease in inhibitory potency, yielding EC50s of 99 and 21 nM for HCV genotype 1a (H77) and 1b (Con1) replicons, respectively[1]. References: | |||||

ABT-333 Dilution Calculator

ABT-333 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0261 mL | 10.1303 mL | 20.2606 mL | 40.5211 mL | 50.6514 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4052 mL | 2.0261 mL | 4.0521 mL | 8.1042 mL | 10.1303 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2026 mL | 1.013 mL | 2.0261 mL | 4.0521 mL | 5.0651 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0405 mL | 0.2026 mL | 0.4052 mL | 0.8104 mL | 1.013 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0203 mL | 0.1013 mL | 0.2026 mL | 0.4052 mL | 0.5065 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
ABT-333 is an inhibitor of non-nucleoside HCV NS5B polymerase.
12 weeks of treatment with ABT-450/r, ABT-333 and ribavirin has been shown the rates of sustained virologic response of 93% to 95% among previously untreated patients and 47% among patients who had not had a response or who had had only a partial response to prior therapy with peginterferon and ribavirin [1]. In addition, in most cases, the studies have been reported that virologic failure was associated with the emergence of variants with substitutions in NS5B, at positions known to confer resistance in vitro to ABT-333 [2].
References:
[1] Kowdley KV1, Lawitz E, Poordad F, Cohen DE, Nelson DR, Zeuzem S, Everson GT, Kwo P, Foster GR, Sulkowski MS, Xie W, Pilot-Matias T, Liossis G, Larsen L, Khatri A, Podsadecki T, Bernstein B.Phase 2b trial of interferon-free therapy for hepatitis C virus genotype 1. N Engl J Med. 2014 Jan 16;370(3):222-32.
[2] Poordad F1, Lawitz E, Kowdley KV, Cohen DE, Podsadecki T, Siggelkow S, Heckaman M, Larsen L, Menon R, Koev G, Tripathi R, Pilot-Matias T, Bernstein B. Exploratory study of oral combination antiviral therapy for hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2013 Jan 3;368 (1):45-53.
- (3S)-Hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside pentaacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1616
CAS No.:113270-99-8
- (3R)-Hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside pentaacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1617
CAS No.:113270-98-7
- H-Phe(4-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3216
CAS No.:1132-68-9
- PPPA
Catalog No.:BCC7309
CAS No.:113190-92-4
- Linopirdine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7231
CAS No.:113168-57-3
- nor-Binaltorphimine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6614
CAS No.:113158-34-2
- Physalin L
Catalog No.:BCN2312
CAS No.:113146-74-0
- (S)-(+)-Niguldipine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6947
CAS No.:113145-69-0
- 3-Deoxysappanone B
Catalog No.:BCN6012
CAS No.:113122-54-6
- 7-O-Methylrosmanol
Catalog No.:BCN7276
CAS No.:113085-62-4
- VU 0155069
Catalog No.:BCC7715
CAS No.:1130067-06-9
- Potassium benzylpenicillin
Catalog No.:BCC9126
CAS No.:113-98-4
- GDC-0834
Catalog No.:BCC5115
CAS No.:1133432-50-4
- neo-Truxilline
Catalog No.:BCN1949
CAS No.:113350-54-2
- γ-Truxilline
Catalog No.:BCN1948
CAS No.:113350-56-4
- 2-Amino-4-phenylphenol
Catalog No.:BCC8534
CAS No.:1134-36-7
- Baclofen
Catalog No.:BCC8839
CAS No.:1134-47-0
- 2-Aminophenyl phenyl sulfide
Catalog No.:BCC8553
CAS No.:1134-94-7
- Jatamanvaltrate B
Catalog No.:BCN7128
CAS No.:1134138-66-1
- VER 155008
Catalog No.:BCC2338
CAS No.:1134156-31-2
- Rhein-8-glucoside calcium salt
Catalog No.:BCN6349
CAS No.:113443-70-2
- Epidanshenspiroketallactone
Catalog No.:BCN3142
CAS No.:113472-19-8
- Ivacaftor hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1664
CAS No.:1134822-07-3
- Ivacaftor benzenesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC1663
CAS No.:1134822-09-5
ABT-450/ ritonavir and ABT-267 in combination with ABT-333 for the treatment of hepatitis C virus.[Pubmed:25800085]
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015 Apr;16(6):929-37.
INTRODUCTION: The global prevalence of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) is estimated to be 80 - 115 million and currently viremic infections account for 350,000 deaths annually. As the knowledge about HCV evolves, new anti-viral treatments have been developed. The primary goal of antiviral therapies has been to eradicate HCV virus from serum and achieve sustained virologic response (SVR). Historically, interferon has been a staple of nearly all HCV treatment regimens, despite significant toxic effects. AREAS COVERED: In recent years, HCV treatment has changed rapidly and significantly. All-oral treatment regimens show promise for treatment with shorter duration and more manageable side effects. New antivirals aimed at improving SVR may provide a cure to nearly all HCV-infected patients. The unique combination of ABT-450 (paritaprevir) and ABT-267 (ombitasvir) provides highly effective treatment for patients with genotype 1 HCV. This review will examine the antiviral properties, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and side effects of these agents. EXPERT OPINION: The combination of ABT-450/r and ABT-267 has improved potency, favorable side effect profile, and low risk of resistance compared to the first-generation protease inhibitors. This combination is likely to be a major part of novel upcoming HCV treatment regimens and is likely to be widely used by clinicians. Additional data is awaited in additional patient populations, and with possible shorter treatment durations.


