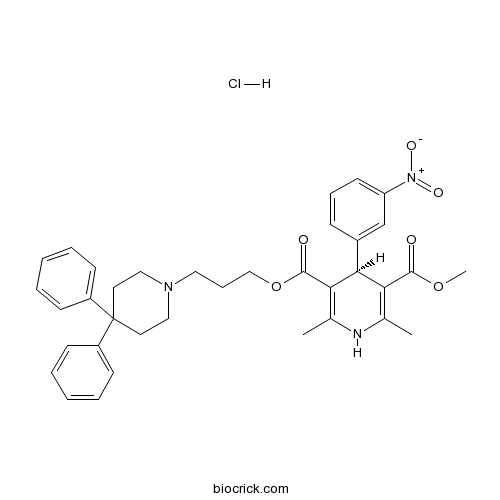
(S)-(+)-Niguldipine hydrochlorideCa2+ channel blocker (L-type) CAS# 113145-69-0 |
- Deuterated Atazanivir-D3-3
Catalog No.:BCC2117
CAS No.:1092540-52-7
- Deuterated Atazanivir-D3-1
Catalog No.:BCC2115
CAS No.:1092540-56-1
- Amprenavir (agenerase)
Catalog No.:BCC3619
CAS No.:161814-49-9
- Atazanavir
Catalog No.:BCC3622
CAS No.:198904-31-3
- BMS-538203
Catalog No.:BCC4136
CAS No.:543730-41-2
- BMS-707035
Catalog No.:BCC2133
CAS No.:729607-74-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 113145-69-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16219720 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C36H40ClN3O6 | M.Wt | 646.18 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-O-[3-(4,4-diphenylpiperidin-1-yl)propyl] 3-O-methyl (4S)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)OCCCN2CCC(CC2)(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4)C5=CC(=CC=C5)[N+](=O)[O-])C(=O)OC.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MHOSUIMBPQVOEU-WAQYZQTGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C36H39N3O6.ClH/c1-25-31(34(40)44-3)33(27-12-10-17-30(24-27)39(42)43)32(26(2)37-25)35(41)45-23-11-20-38-21-18-36(19-22-38,28-13-6-4-7-14-28)29-15-8-5-9-16-29;/h4-10,12-17,24,33,37H,11,18-23H2,1-3H3;1H/t33-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | L-type Ca2+ channel blocker and α1A-adrenoceptor antagonist; more active enantiomer. (R)-(-)-Niguldipine hydrochloride also available. |

(S)-(+)-Niguldipine hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

(S)-(+)-Niguldipine hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5476 mL | 7.7378 mL | 15.4756 mL | 30.9511 mL | 38.6889 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3095 mL | 1.5476 mL | 3.0951 mL | 6.1902 mL | 7.7378 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1548 mL | 0.7738 mL | 1.5476 mL | 3.0951 mL | 3.8689 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.031 mL | 0.1548 mL | 0.3095 mL | 0.619 mL | 0.7738 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0155 mL | 0.0774 mL | 0.1548 mL | 0.3095 mL | 0.3869 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3-Deoxysappanone B
Catalog No.:BCN6012
CAS No.:113122-54-6
- 7-O-Methylrosmanol
Catalog No.:BCN7276
CAS No.:113085-62-4
- VU 0155069
Catalog No.:BCC7715
CAS No.:1130067-06-9
- Potassium benzylpenicillin
Catalog No.:BCC9126
CAS No.:113-98-4
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4526
CAS No.:113-92-8
- Chlorprothixene
Catalog No.:BCC3753
CAS No.:113-59-7
- Estradiol diproppionate
Catalog No.:BCC8960
CAS No.:113-38-2
- IM-12
Catalog No.:BCC5487
CAS No.:1129669-05-1
- Tokinolide B
Catalog No.:BCN2753
CAS No.:112966-16-2
- Calcipotriol
Catalog No.:BCC1444
CAS No.:112965-21-6
- PD128907 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4469
CAS No.:112960-16-4
- HU 211
Catalog No.:BCC5946
CAS No.:112924-45-5
- Physalin L
Catalog No.:BCN2312
CAS No.:113146-74-0
- nor-Binaltorphimine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6614
CAS No.:113158-34-2
- Linopirdine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7231
CAS No.:113168-57-3
- PPPA
Catalog No.:BCC7309
CAS No.:113190-92-4
- H-Phe(4-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3216
CAS No.:1132-68-9
- (3R)-Hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside pentaacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1617
CAS No.:113270-98-7
- (3S)-Hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside pentaacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1616
CAS No.:113270-99-8
- ABT-333
Catalog No.:BCC4129
CAS No.:1132935-63-7
- GDC-0834
Catalog No.:BCC5115
CAS No.:1133432-50-4
- neo-Truxilline
Catalog No.:BCN1949
CAS No.:113350-54-2
- γ-Truxilline
Catalog No.:BCN1948
CAS No.:113350-56-4
- 2-Amino-4-phenylphenol
Catalog No.:BCC8534
CAS No.:1134-36-7
Trophic effects induced by alpha1D-adrenoceptors on endothelial cells are potentiated by hypoxia.[Pubmed:17660397]
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):H2140-7.
Catecholamines have been shown to be involved in vascular remodeling through the stimulation of alpha(1)-adrenoceptors (alpha(1)-ARs). Recently, it has been demonstrated that catecholamines can stimulate angiogenesis in pathological conditions, even if the mechanisms and the AR subtypes involved still remain unclear. We investigated the influence of hypoxia (3% O(2)) on the ability of picomolar concentrations of phenylephrine (PHE), which are unable to induce any vascular contraction, to induce a trophic effect in human endothelial cells through stimulation of the alpha(1D)-subtype ARs. PHE, at picomolar concentrations, significantly promoted pseudocapillary formation from fragments of human mature vessels in vitro. Exposure to hypoxia significantly potentiated this effect, which was inhibited by the selective alpha(1D)-AR antagonist BMY-7378 and by the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NAME, suggesting that alpha(1D)-ARs were involved in this effect through activation of the nitric oxide pathway. Proliferation and migration of HUVEC were also affected by picomolar PHE concentrations. Again, these effects were significantly potentiated in cells exposed to hypoxia and were inhibited by BMY-7378 and by N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester. Conversely, the alpha(1A)-AR-selective antagonist (S)-(+)-Niguldipine hydrochloride and the alpha(1B)-AR antagonist chloroethylclonidine dihydrochloride did not modify endothelial cell migration and proliferation in response to PHE. These results demonstrate that the stimulation of alpha(1D)-ARs, triggered by picomolar PHE concentrations devoid of any contractile vascular effects, induces a proangiogenic phenotype in human endothelial cells that is enhanced in a hypoxic environment. The role of alpha(1D)-ARs may become more prominent in the adaptive responses to hypoxic vasculature injury.
Stereoisomers of calcium antagonists which differ markedly in their potencies as calcium blockers are equally effective in modulating drug transport by P-glycoprotein.[Pubmed:1352973]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 23;43(12):2601-8.
The (-)-isomer of verapamil is 10-fold more potent as a calcium antagonist than the (+)-isomer. However, both enantiomers are equally effective in increasing cellular accumulation of anticancer drugs [Gruber et al., Int J Cancer 41: 224-226, 1988]. In addition to verapamil, there exists a wide variety of stereoisomers with phenylalkylamines and dihydropyridine structures which markedly differ in their potency as calcium antagonists. We have tested these drugs for their ability to increase intracellular accumulation of [3H]vinblastine ([3H]VBL) in a doxorubicin-resistant cell line (F4-6RADR) derived from the Friend mouse leukemia cell line (F4-6P) and in COS-7 monkey kidney cells. Both cell types express substantial amounts of multidrug resistance gene 1 mRNA and P-glycoprotein as revealed by RNA and immuno blot analysis. The enantiomers with phenylalkylamine structures [(+/-)-verapamil; (+/-)-devapamil; (+/-)-emopamil)] and with dihydropyridine structures [(+/-)-isradipine; (+/-)-nimodipine; (+/-)-felodipine; (+/-)-nitrendipine; (+/-)-niguldipine] increased [3H]VBL accumulation in both cell lines at micromolar concentrations. Although the stereoisomers of these drugs differ markedly in their potency as calcium channel blockers they were about equally effective in increasing VBL levels in the cells. There was no substantial difference in the potencies of the phenylalkylamine drugs in affecting cellular [3H]VBL transport. Major potency differences, however, were observed in the dihydropyridine drug series with the niguldipine isomers as the most effective drugs. Moreover, the niguldipine enantiomers were equally as effective in reversing VBL resistance in F4-6RADR cells as were the verapamil enantiomers. Since (-)-niguldipine (B859-35) displays a 45-fold lower affinity for calcium channel binding sites than (+)-niguldipine, but is equally potent in inhibiting drug transport by P-glycoprotein and in reversing drug resistance, it may be, in addition to (+)-verapamil, another useful candidate drug for the treatment of multidrug resistance in cancer patients.
(+)-Niguldipine binds with very high affinity to Ca2+ channels and to a subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptors.[Pubmed:2548881]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):131-45.
The enantiomers of the 1,4-dihydropyridine (DHP) niguldipine (3-methyl-5-[3-(4,4-diphenyl-1-piperidinyl)-propyl]- 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate- hydrochloride) were investigated with respect to their interaction with 1,4-DHP receptors on L-type Ca2+ channels and alpha-adrenoceptors. The Ki values for niguldipine were dependent on the membrane protein concentrations in the radioligand binding assay. 'True' Ki values (at extrapolated 'zero' membrane protein) were determined with guinea-pig membranes for (+)-niguldipine and were found to be 85 pmol/l for the 1,4-DHP receptor of skeletal muscle, 140 pmol/l for that of brain and 45 pmol/l for that of heart. (-)-Niguldipine was approximately 40 times less potent. (+)-Niguldipine (Ki: 78 nmol/l) and (-)-niguldipine (Ki: 58 nmol/l) bound with approximately equal affinity to the alpha 1-adrenoceptors ('alpha 1B') in liver cell membranes. The (+)-niguldipine alpha 1-adrenoceptor inhibition data for rat brain cortex membranes were better fitted by a two-site model. The high-affinity component ('alpha 1A') had a Ki value of 52 pmol/l in competition experiments with [3H]prazosin. The low-affinity site (alpha 1B) had 200- to 600-fold less affinity. (-)-Niguldipine was greater than 40-fold less potent at alpha 1A- but was nearly equipotent to the (+)enantiomer at alpha 1B-sites. (+)-Niguldipine was the most selective compound for discriminating alpha 1A- from alpha 1B-adrenoceptors and is a novel prototype for 1,4-DHPs which bind with nearly equal affinity to skeletal muscle and brain or heart 1,4-DHP receptors.
Stereoselective binding of niguldipine enantiomers to alpha 1A-adrenoceptors labeled with [3H]5-methyl-urapidil.[Pubmed:2555206]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 17;172(4-5):329-37.
[3H]5-Methyl-urapidil, a potent antihypertensive derivative of urapidil, binds to alpha 1A-adrenoceptors in rat brain cortex membranes with a dissociation constant (KD) of 0.89 nM and a Bmax of 116 fmol/mg protein. The ligand does not bind to purified liver cell membranes (alpha 1B-adrenoceptors). [3H]5-Methyl-urapidil also labels 5-HT1A receptors in brain membranes (KD: 0.84 nM and Bmax: 235 fmol/mg protein). (+/-)-Niguldipine, a novel 1,4-dihydropyridine with Ca2+-antagonistic as well as alpha 1A-adrenoceptor blocking properties, is a competitive inhibitor of [3H]5-methyl-urapidil binding to alpha 1A-adrenoceptors. In contrast to those for prazosin, the Ki values for niguldipine were highly dependent on the membrane protein concentration, indicating partitioning of niguldipine into hydrophobic compartments unavailable for alpha-adrenoceptor interaction. The extrapolated, 'true' Ki values were as follows: (+/-)-niguldipine: 0.298 nM, (-)-niguldipine: 3.12 nM, (+)-niguldipine: 0.145 nM.


