MLN8054Aurora A inhibitor CAS# 869363-13-3 |
- MLN8237 (Alisertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2166
CAS No.:1028486-01-2
- CCT137690
Catalog No.:BCC2188
CAS No.:1095382-05-0
- ENMD-2076
Catalog No.:BCC2186
CAS No.:934353-76-1
- TAK-901
Catalog No.:BCC2180
CAS No.:934541-31-8
- PF-03814735
Catalog No.:BCC2184
CAS No.:942487-16-3
- AMG-900
Catalog No.:BCC2175
CAS No.:945595-80-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 869363-13-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11712649 | Appearance | Powder |
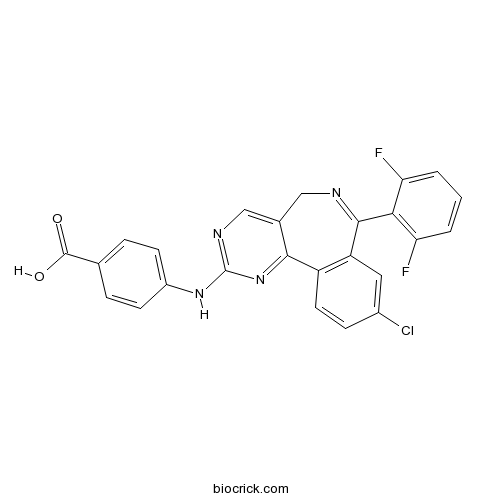
| Formula | C25H15ClF2N4O2 | M.Wt | 476.86 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 30 mg/mL (62.91 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[[9-chloro-7-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-5H-pyrimido[5,4-d][2]benzazepin-2-yl]amino]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C2=CN=C(N=C2C3=C(C=C(C=C3)Cl)C(=N1)C4=C(C=CC=C4F)F)NC5=CC=C(C=C5)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HHFBDROWDBDFBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H15ClF2N4O2/c26-15-6-9-17-18(10-15)23(21-19(27)2-1-3-20(21)28)29-11-14-12-30-25(32-22(14)17)31-16-7-4-13(5-8-16)24(33)34/h1-10,12H,11H2,(H,33,34)(H,30,31,32) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | MLN8054 is an oral, ATP-competitive, selective small-molecule inhibitor of Aurora A with IC50 value of 4 nM. | |||||
| Targets | Aurora A | |||||
| IC50 | 4 nM | |||||

MLN8054 Dilution Calculator

MLN8054 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0971 mL | 10.4853 mL | 20.9705 mL | 41.941 mL | 52.4263 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4194 mL | 2.0971 mL | 4.1941 mL | 8.3882 mL | 10.4853 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2097 mL | 1.0485 mL | 2.0971 mL | 4.1941 mL | 5.2426 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0419 mL | 0.2097 mL | 0.4194 mL | 0.8388 mL | 1.0485 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.021 mL | 0.1049 mL | 0.2097 mL | 0.4194 mL | 0.5243 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
MLN8054 is a potent of Aurora A kinase (AAK) inhibitor consisting of a benzazepine core scaffold with a fused amino pyrimidine and an aryl carboxylic acid which represents an unprecedented kinase inhibitor framework. The inhibition of MLN8054 towards AAK is ATP-competitive, reversible and selective with an IC50 value of 4nM, which is more than 40-fold and 100-fold selective comparing to Aurora B kinase (IC50 = 175 nM) and a range of other kinases respectively. MLN8054 exerts antitumor activity against human tumor xenografts through AAK inhibition, which results in deactivation of Pt288, spindle defects, accumulation of G2/M, and apoptosis-induced cell death in tumor cells.
Reference
Mark G. Manfredi, Jeffery A. Ecsedy, Kristan A. Meetze, Suresh K. Balani, Olga Burenkova. Wei Chen, Katherine M. Galvin, Kara M. Hoar, Jessica J. Huck, Patrick J. LeRoy, Emily T. Ray, Todd B. Sells, Bradley Stringer, Stephen G. Stroud, Tricia J. Vos, Gabriel S. Weatherhead, Deborah R. Wysong, Mengkun Zhang, Joseph B. Bolen, and Christopher F. Claiborne. Antitumor activity of MLN8054, an orally active small-molecule inhibitor of aurora A kinase. PNAS 2007; 104(10): 4106-4111
- AZD8330
Catalog No.:BCC3733
CAS No.:869357-68-6
- Neurokinin B (human, porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC7119
CAS No.:86933-75-7
- Neurokinin A (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC6955
CAS No.:86933-74-6
- PF-573228
Catalog No.:BCC4496
CAS No.:869288-64-2
- SB 203580 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4293
CAS No.:869185-85-3
- Eudesma-3,11-dien-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN7607
CAS No.:86917-79-5
- Umeclidinium bromide
Catalog No.:BCC2022
CAS No.:869113-09-7
- (R)-(-)-α-Methylhistamine dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC5665
CAS No.:868698-49-1
- 3',5'-Dimethoxybiphenyl-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN7529
CAS No.:868666-20-0
- Carfilzomib (PR-171)
Catalog No.:BCC1145
CAS No.:868540-17-4
- Iristectorigenin B
Catalog No.:BCN8391
CAS No.:39012-01-6
- (+)-Puerol B 2''-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4561
CAS No.:868409-19-2
- 14-Deoxy-17-hydroxyandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN4560
CAS No.:869384-82-7
- Praeroside II
Catalog No.:BCN7001
CAS No.:86940-46-7
- JNJ 10191584 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC7362
CAS No.:869497-75-6
- Tecovirimat
Catalog No.:BCC5518
CAS No.:869572-92-9
- Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2572
CAS No.:86967-51-3
- Obestatin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5912
CAS No.:869705-22-6
- A-770041
Catalog No.:BCC1323
CAS No.:869748-10-7
- threo-Guaiacylglycerol beta-coniferyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN1323
CAS No.:869799-76-8
- A 841720
Catalog No.:BCC7550
CAS No.:869802-58-4
- Andropanolide
Catalog No.:BCN4559
CAS No.:869807-57-8
- Formoxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN6451
CAS No.:869880-32-0
- Radezolid
Catalog No.:BCC1882
CAS No.:869884-78-6
MLN8054 and Alisertib (MLN8237): Discovery of Selective Oral Aurora A Inhibitors.[Pubmed:26101564]
ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015 Apr 22;6(6):630-4.
The Aurora kinases are essential for cell mitosis, and the dysregulation of Aurora A and B have been linked to the etiology of human cancers. Investigational agents MLN8054 (8) and alisertib (MLN8237, 10) have been identified as high affinity, selective, orally bioavailable inhibitors of Aurora A that have advanced into human clinical trials. Alisertib (10) is currently being evaluated in multiple Phase II and III clinical trials in hematological malignancies and solid tumors.
Molecular dynamics and free energy studies on Aurora kinase A and its mutant bound with MLN8054: insight into molecular mechanism of subtype selectivity.[Pubmed:22990663]
Mol Biosyst. 2012 Nov;8(11):3049-60.
Because of the high conservation of ATP-binding sites in kinases, the quest for selective kinase inhibitors has been increasingly urgent in recent years. The Aurora kinase family represents attractive targets in cancer therapy and several small molecule inhibitors targeting Aurora kinases are undergoing clinical trials. Among them, MLN8054 has been proved to be a selective Aurora-A inhibitor, and is currently being evaluated in a phase I trial for patients with advanced solid tumors. But the detailed selectivity mechanism of MLN8054 towards Aurora-A over Aurora-B is still not resolved. In the present work, this selectivity mechanism was investigated using molecular dynamics simulations and binding free energy calculations. The predicted binding conformations and binding affinities of MLN8054 to Aurora-A and its mutant that mimics Aurora-B suggest that there exists stronger interaction between MLN8054 and Aurora-A through an induced DFG-up conformation. Further analyses can provide some information about the structural basis for the selectivity mechanism. Binding of MLN8054 to Aurora-A induces the conformation of the activation loop to adopt an unusual DFG-up conformation and opens the hydrophobic pocket of the active site, thus increasing the interaction between MLN8054 and the residue Val279. The residue Glu177 in Aurora-B displays electrostatic repulsion with MLN8054, while the corresponding Thr217 in Aurora-A has favorable interactions with MLN8054. The conformation change and the difference between the binding pockets for Aurora-A and B are key factors responsible for the selectivity. The results could be helpful for the rational design of selective inhibitors of Aurora-A kinase.
Phase I assessment of new mechanism-based pharmacodynamic biomarkers for MLN8054, a small-molecule inhibitor of Aurora A kinase.[Pubmed:21148750]
Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 1;71(3):675-85.
The mitotic kinase Aurora A is an important therapeutic target for cancer therapy. This study evaluated new mechanism-based pharmacodynamic biomarkers in cancer patients in two phase I studies of MLN8054, a small-molecule inhibitor of Aurora A kinase. Patients with advanced solid tumors received MLN8054 orally for 7 consecutive days in escalating dose cohorts, with skin and tumor biopsies obtained before and after dosing. Skin biopsies were evaluated for increased mitotic cells within the basal epithelium. Tumor biopsies were assessed for accumulation of mitotic cells within proliferative tumor regions. Several patients in the highest dose cohorts showed marked increases in the skin mitotic index after dosing. Although some tumors exhibited increases in mitotic cells after dosing, others displayed decreases, a variable outcome consistent with dual mechanisms of mitotic arrest and mitotic slippage induced by antimitotics in tumors. To provide a clearer picture, mitotic cell chromosome alignment and spindle bipolarity, new biomarkers of Aurora A inhibition that act independently of mitotic arrest or slippage, were assessed in the tumor biopsies. Several patients, primarily in the highest dose cohorts, had marked decreases in the percentage of mitotic cells with aligned chromosomes and bipolar spindles after dosing. Evidence existed for an exposure-effect relationship for mitotic cells with defects in chromosome alignment and spindle bipolarity that indicated a biologically active dose range. Outcomes of pharmacodynamic assays from skin and tumor biopsies were concordant in several patients. Together, these new pharmacodynamic assays provide evidence for Aurora A inhibition by MLN8054 in patient skin and tumor tissues.
MLN8054, a small molecule inhibitor of aurora kinase a, sensitizes androgen-resistant prostate cancer to radiation.[Pubmed:21514073]
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Jul 15;80(4):1189-97.
PURPOSE: To determine whether MLN8054, an Aurora kinase A (Aurora-A) inhibitor causes radiosensitization in androgen-insensitive prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. METHODS AND MATERIALS: In vitro studies consisted of culturing PC3 and DU145 prostate cancer cells and then immunoblotting Aurora A and phospho-Aurora A after radiation and/or nocodazole with MLN8054. Phases of the cell cycle were measured with flow cytometry. PC3 and DU145 cell lines were measured for survival after treatment with MLN8054 and radiation. Immunofluorescence measured gamma-H2AX in the PC3 and DU145 cells after treatment. In vivo studies looked at growth delay of PC3 tumor cells in athymic nude mice. PC3 cells grew for 6 to 8 days in mice treated with radiation, MLN8054, or combined for 7 more days. Tumors were resected and fixed on paraffin and stained for von Willebrand factor, Ki67, and caspase-3. RESULTS: In vitro inhibition of Aurora-A by MLN8054 sensitized prostate cancer cells, as determined by dose enhancement ratios in clonogenic assays. These effects were associated with sustained DNA double-strand breaks, as evidenced by increased immunofluorescence for gamma-H2AX and significant G2/M accumulation and polyploidy. In vivo, the addition of MLN8054 (30 mg/kg/day) to radiation in mouse prostate cancer xenografts (PC3 cells) significantly increased tumor growth delay and apoptosis (caspase-3 staining), with reduction in cell proliferation (Ki67 staining) and vascular density (von Willebrand factor staining). CONCLUSION: MLN8054, a novel small molecule Aurora-A inhibitor showed radiation sensitization in androgen-insensitive prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo. This warrants the clinical development of MLN8054 with radiation for prostate cancer patients.


