SeselinCAS# 523-59-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 523-59-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 68229 | Appearance | Powder |
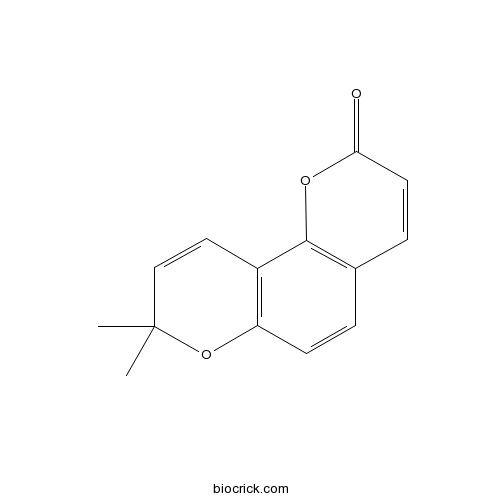
| Formula | C14H12O3 | M.Wt | 228.24 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 8,8-dimethylpyrano[2,3-f]chromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C=CC2=C(O1)C=CC3=C2OC(=O)C=C3)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QUVCQYQEIOLHFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H12O3/c1-14(2)8-7-10-11(17-14)5-3-9-4-6-12(15)16-13(9)10/h3-8H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Seselin Dilution Calculator

Seselin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3814 mL | 21.9068 mL | 43.8135 mL | 87.6271 mL | 109.5338 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8763 mL | 4.3814 mL | 8.7627 mL | 17.5254 mL | 21.9068 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4381 mL | 2.1907 mL | 4.3814 mL | 8.7627 mL | 10.9534 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0876 mL | 0.4381 mL | 0.8763 mL | 1.7525 mL | 2.1907 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0438 mL | 0.2191 mL | 0.4381 mL | 0.8763 mL | 1.0953 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 12-O-Methylinophyllum A
Catalog No.:BCN9449
CAS No.:2131757-10-1
- (-)-Toddalolactone 3′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9448
CAS No.:1176645-57-0
- ent-15α-Acetoxy-11α-hydroxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9447
CAS No.:70324-38-8
- Uncarine F
Catalog No.:BCN9446
CAS No.:14019-66-0
- Angustine
Catalog No.:BCN9445
CAS No.:40041-96-1
- Caloxanthone B
Catalog No.:BCN9444
CAS No.:155233-17-3
- Stipuleanoside R1
Catalog No.:BCN9443
CAS No.:96627-79-1
- Adenostemmoic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN9442
CAS No.:130217-18-4
- Withaphysalin C
Catalog No.:BCN9441
CAS No.:57485-60-6
- ent-Toddalolactone
Catalog No.:BCN9440
CAS No.:1570054-19-1
- 1-Oxohederagenin
Catalog No.:BCN9439
CAS No.:618390-67-3
- 1,5-Epoxy-3-hydroxy-1-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)heptane
Catalog No.:BCN9438
CAS No.:182227-93-6
- 5-Methoxyseselin
Catalog No.:BCN9451
CAS No.:31525-76-5
- 3,6-Dihydroxy-1,2,7-trimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN9452
CAS No.:916210-79-2
- Trigochinin A
Catalog No.:BCN9453
CAS No.:1210299-29-8
- Isozedoarondiol
Catalog No.:BCN9454
CAS No.:108887-68-9
- 1,8-Dihydroxy-p-menth-3-en-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN9455
CAS No.:1392224-56-4
- Toddalolactone 3′-O-ethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN9456
CAS No.:1538607-30-5
- Schisandrolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9457
CAS No.:55511-17-6
- Toddalosin ethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN9458
CAS No.:1538607-31-6
- Toddalolactone 3′-O-methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN9459
CAS No.:143614-35-1
- Phrymarolin B
Catalog No.:BCN9460
CAS No.:1363160-29-5
- Corialin B
Catalog No.:BCN9461
CAS No.:1325717-47-2
- 4α,8β-Dihydroxy-3α-(2-hydroxy-3-acetoxy-2-methylbutyryloxy)eudesm-7(11)-en-12,8α-olide
Catalog No.:BCN9462
CAS No.:1442989-33-4
Advances in the Biosynthesis of Pyranocoumarins: Isolation and (13)C-Incorporation Analysis by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Ultraviolet-Solid-Phase Extraction-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data.[Pubmed:32372647]
J Nat Prod. 2020 May 22;83(5):1409-1415.
Citrus sinensis and Citrus limonia were obtained by germination from seeds, and isotopic-labeling experiments using d-[1-(13)C]glucose were performed with the seedlings. After 60 days, the seedlings were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet-solid-phase extraction-nuclear magnetic resonance, data and the (13)C enrichment patterns of xanthyletin and Seselin indicated that the pyran ring was formed by the methylerythritol phosphate pathway and that the coumarin moiety was derived from the shikimate pathway in both compounds. This information regarding the biosynthetic pathway can be used to increase resistance against phytopathogens, because xanthyletin and Seselin are reported to have antimicrobial activity on the growth of Xylella fastidiosa, which causes citrus variegated chlorosis in orange.
Antiviral activity of seselin from Aegle marmelos against nuclear polyhedrosis virus infection in the larvae of silkworm, Bombyx mori.[Pubmed:31449858]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Dec 5;245:112155.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Traditional Indian medicine has utilized Aeglemarmelos (L.) Corr. commonly called as bael in several indigenous systems against various diseases. Bioactive components isolated from various plant parts of A. marmelos were used in ethno-medicine. More precisely they are known for its antiviral property against various human and animal viruses. AIM OF THE STUDY: The study was conducted to investigate the antiviral activity of A.marmelos against Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV). MATERIALS AND METHODS: Among the various crude extracts tested, hexane extracts of leaves of A. marmelos with promising anti-BmNPV activity was subjected to bioactivity guided fractionation based on column chromatography. Out of 40 fractions obtained from the fractionation, fractions showing similar TLC profiles were pooled into 14 fractions. A fraction with potential activity was used to purify a molecule with anti-BmNPV activity. This molecule was characterized through structural and functional analyses. RESULTS: The functionally and structurally characterized molecule in the fraction with prospective anti-BmNPV activity revealed a single crystal compound 'Seselin' (8, 8-dimethyl pyrido oxazine-2-one). CONCLUSION: It is therefore understood that this Seselin compound could be used as a natural medicine for the management of NPV infection in the silkworm larvae under commercial conditions after suitable field evaluations.
Praeruptorin-B Inhibits 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate-Induced Cell Invasion by Targeting AKT/NF-kappaB via Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 Expression in Human Cervical Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:31026389]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(6):1255-1266.
BACKGROUND/AIMS: Praeruptorins, a Seselin-type coumarin, possess anti-inflammatory and antitumor promoting properties. However, molecular mechanisms through which Praeruptorin-B (Pra-B) exerts an antimetastatic effect on cervical cancer cells remain unclear. METHODS: Cell viability was examined using the MTT assay, whereas cell migration and invasion were examined using the Boyden chamber assay. Western blotting and RT-PCR were performed to investigate the inhibitory effect of Pra-B on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 (MMP-2/-9) expression in HeLa cells. The findings of the luciferase assay confirmed the inhibitory effect of Pra-B on TPA-induced transcriptional activity of MMP2/-9 in HeLa cells. RESULTS: Pra-B inhibited TPA-induced metastatic ability of human cervical cancer cells without any significant toxicity. Pra-B suppressed TPA-induced mRNA and protein expression and transcriptional activity of MMP-2/-9 in HeLa cells. Furthermore, Pra-B inhibited AKT phosphorylation but did not affect the MAPK pathway. Cotreatment of HeLa cells with TPA plus Pra-B or LY294002 (a PI3K inhibitor) reduced cell invasion and MMP-2/-9 expression and transcriptional activity. In addition, Pra-B attenuated TPA-induced nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB-p65/-p50, which reduced Ikk-alpha phosphorylation in HeLa cells. Cotreatment of HeLa cells with TPA plus Pra-B or LY294002 reduced NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. CONCLUSION: These results suggested that Pra-B-mediated inhibition of TPA-induced cell metastasis involved the suppression of p-AKT/NF-kappaB via MMP-2/-9 expression in HeLa cells. Pra-B can be a potential antimetastatic agent against cervical cancer.
Employing Pressurized Hot Water Extraction (PHWE) to Explore Natural Products Chemistry in the Undergraduate Laboratory.[Pubmed:30474625]
J Vis Exp. 2018 Nov 7;(141).
A recently developed pressurized hot water extraction (PHWE) method which utilizes an unmodified household espresso machine to facilitate natural products research has also found applications as an effective teaching tool. Specifically, this technique has been used to introduce second- and third-year undergraduates to aspects of natural products chemistry in the laboratory. In this report, two experiments are presented: the PHWE of eugenol and acetyleugenol from cloves and the PHWE of Seselin and (+)-epoxysuberosin from the endemic Australian plant species Correa reflexa. By employing PHWE in these experiments, the crude clove extract, enriched in eugenol and acetyleugenol, was obtained in 4-9% w/w from cloves by second-year undergraduates and Seselin and (+)-epoxysuberosin were isolated in yields of up to 1.1% w/w and 0.9% w/w from C. reflexa by third-year students. The former exercise was developed as a replacement for the traditional steam distillation experiment providing an introduction to extraction and separation techniques, while the latter activity featured guided-inquiry teaching methods in an effort to simulate natural products bioprospecting. This primarily derives from the rapid nature of this PHWE technique relative to traditional extraction methods that are often incompatible with the time constraints associated with undergraduate laboratory experiments. This rapid and practical PHWE method can be used to efficiently isolate various classes of organic molecules from a range of plant species. The complementary nature of this technique relative to more traditional methods has also been demonstrated previously.
Seselin ameliorates inflammation via targeting Jak2 to suppress the proinflammatory phenotype of macrophages.[Pubmed:30338847]
Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;176(2):317-333.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Sepsis is a serious clinical condition with a high mortality rate. Anti inflammatory agents have been found to be beneficial for the treatment of sepsis. Here, we have evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of Seselin in models of sepsis and investigated the underlying molecular mechanism(s). EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: In vivo therapeutic effects of Seselin was evaluated in two models of sepsis, caecal ligation and puncture or injection of LPS, in C57BL/6 mice. In vitro, anti-inflammatory activity of Seselin was assessed with macrophages stimulated with LPS and IFN-gamma. Anti inflammatory actions were analysed with immunohistochemical methods, ELISA and Western blotting. Flow cytometry was used to assess markers of macrophage phenotype (pro- or anti-inflammatory). Other methods used included co-immunoprecipitation, cellular thermal shift assay and molecular docking. KEY RESULTS: In vivo, Seselin clearly ameliorated sepsis induced by caecal ligation and puncture. In lung tissue from septic mice and in cultured macrophages, Seselin down-regulated levels of proinflammatory factors and activity of STAT1 and p65, the master signal pathway molecules for polarization of macrophages into the proinflammatory phenotype. Importantly, adoptive transfer of bone marrow-derived macrophages, pretreated with Seselin, lowered systemic proinflammatory factors in mice challenged with LPS. The underlying mechanism was that Seselin targeted Jak2 to block interaction with IFNgamma receptors and downstream STAT1. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: Seselin exhibited anti-inflammatory activity through its action on Jak2. These results indicated a possible application of Seselin to the treatment of inflammatory disease via blocking the development of the proinflammatory phenotype of macrophages.
Assessment of Antihyperlipidemic and Antitumor Effect of Isolated Active Phytoconstituents from Apium graveolens L. through Bioassay-Guided Procedures.[Pubmed:29624455]
J Diet Suppl. 2019;16(2):193-206.
The seeds of A. graveolens yielded coumarin derivatives such as Seselin, methoxsalen, and 3H-isobenzofuran-1-one through chromatographic separation techniques. The structure of the components has been established on the basis of spectral data analysis. The present study was undertaken to explore the antihyperlipidemic and antitumor effects of ethanolic extract and phytoconstituents of A. graveolens in rodents. Albino rats were administered intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of Triton WR 1339 for the induction of hyperlipidemia at a dose of 400 mg/kg body weight. After 24 h of Triton administration, the test drugs were administered orally at dose of 50 mg/kg body weight in rats. The extract and isolated components were further investigated for the tumor take inhibitory activity in hybrid mice (of C57BL strain + Swiss albino strain). Preventive group animals were injected daily with the extract and isolated components at a dose of 50 mg/kg body weight i.p. for 10 consecutive days. The animals were observed for the growth of tumor after injection of B16F10 melanoma cells into the dorsal skin of mice. The study showed significant reduction in total cholesterol (p < .001), triglycerides (p < .001) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) level ((b)p < .01) and significantly increased high density lipoprotein (HDL) level (p < .01) after the treatment. Pretreatment showed delay in tumor growth by increasing the volume-doubling time (p < .01), growth delay (p < .01), and mean survival time (p < .001). Acute treatment caused stimulatory effect on HDL level and inhibition in total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) elevation induced by Triton. Tumor regression studies showed a regression response for tumor growth in vivo of murine mouse melanoma tumor cell lines.
Anticancer effects of O-aminoalkyl derivatives of alloxanthoxyletin and seselin.[Pubmed:28946189]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Nov;95:1412-1424.
Seselin and alloxanthoxyletin, naturally occurring pyranocoumarins, were recently isolated from a number of plant sources, such as family of Rutaceae. It was previously reported that their natural and synthetic derivatives show cytotoxic and antitumor activity. In the present study new series of O-aminoalkyl substituted alloxanthoxyletins and Seselins were synthesized and evaluated for their anticancer toxicity. Microwave assisted synthesis was used, and the structures of the compounds were confirmed by (1)H NMR, (13)C NMR and MS spectroscopic data. The molecular and crystal structure of 3a was analyzed by single crystal X-ray diffraction. Alloxanthoxyletin derivatives 2a, 2b, and 2d showed the highest cytotoxic potential against HTB-140 cells with IC50 of 2.48, 2.80 and 2.98muM, respectively. In vitro drug sensitivity testing in HaCaT, A549 and HTB-140 cells were also performed. Tumor cells showed a higher sensitivity to tested compounds than normal cells. Compounds 2a, 2b and 2d inhibited cell migration and exerted stronger effect on A549 and HTB-140 cells than on HaCaT cells. In order to explain the basic mechanism of cell death induction we have investigated the effect of derivatives 2a, 2b and 2d on early and late apoptosis using annexin V-FITC/7-AAD flow cytometry analysis. Derivatives 2a and 2b were much more potent inducers of early apoptosis in HTB-140 cells compared to HaCaT and A549 cells.
Crystal structure of tetra-hydro-seselin, an angular pyran-ocoumarin.[Pubmed:28932418]
Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017 Jul 4;73(Pt 8):1117-1120.
In the title compound, tetra-hydro-Seselin, C14H16O3, a pyran-ocoumarin [systematic name: 8,8-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-tetra-hydro-2H,8H-pyrano[2,3-f]chromen-2-one] obtained from the hydrogenation of Seselin in the presence of Pd/C in MeOH at room temperature, the dihedral angle between the central benzene ring and the best planes of the outer fused ring systems are 6.20 (7) and 10.02 (8) degrees . In the crystal, mol-ecules show only very weak inter-molecular C-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO inter-actions.
Crystal structure of di-bromo-meth-oxy-seselin (DBMS), a photobiologically active pyran-ocoumarin.[Pubmed:28529796]
Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017 Apr 28;73(Pt 5):774-776.
The title compound, C15H14Br2O4 [systematic name: rac-(9S,10R)-3,9-dibromo-10-methoxy-8,8-dimethyl-9,10-dihydropyrano[2,3-h]chromen -2(8H)-one], is a pyran-ocoumarin derivative formed by the bromination of Seselin, which is a naturally occurring angular pyran-ocoumarin isolated from the Indian herb Trachyspermum stictocarpum. In the mol-ecule, the benzo-pyran ring system is essentially planar, with a maximum deviation of 0.044 (2) A for the O atom. The di-hydro-pyran ring is in a half-chair conformation and the four essentially planar atoms of this ring form a dihedral angle of 4.6 (2) degrees with the benzo-pyran ring system. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked by weak C-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along [010]. In addition, pi-pi stacking inter-actions, with centroid-centroid distances of 3.902 (2) and 3.908 (2) A, link the hydrogen-bonded chains into layers parallel to (001).
Crystal structure of a photobiologically active brominated angular pyran-ocoumarin: bromo-hy-droxy-seselin.[Pubmed:28316830]
Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017 Feb 28;73(Pt 3):453-455.
The title compound, C14H13BrO3 [systematic name: rac-(9S,10R)-9-bromo-10-hy-droxy-8,8-dimethyl-9,10-di-hydro-2H,8H-pyrano[2,3-f]ch romen-2-one], is a substituted pyran-ocoumarin, obtained by bromination of Seselin [8,8-dimethyl-2H,8H-pyrano[2,3-f]chromen-2-one], which was isolated from the Indian herb Trachyspermum stictocarpum (Aajmod). The pyrano ring has a distorted half-chair conformation and its mean plane is inclined to the coumarin mean plane by 1.6 (2) degrees . In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked by pairs of O-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO hydrogen bonds, forming inversion dimers with an R(2)2(16) ring motif. The dimers stack along the a-axis direction and are linked by offset pi-pi inter-actions, forming columns [inter-centroid distance = 3.514 (4) A].
Structure elucidation and DNA binding specificity of natural compounds from Cassia siamea leaves: A biophysical approach.[Pubmed:27085054]
J Photochem Photobiol B. 2016 Jun;159:218-28.
A novel isoflavone, 5,6,7-trimethoxy-3-(3',4',5'-trimethoxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one (1) along with a known pyranocoumarin, Seselin (2) have been isolated from the ethanolic extract of the leaves of Cassia siamea (Family: Fabaceae). Compound 1 has been reported for the first time from any natural source and has not been synthesized so far. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of chemical and physical evidences viz. elemental analysis, UV, FT-IR, (1)H-NMR, (13)C-NMR and mass spectral analysis. Structure of compound (1) was further authenticated by single-crystal X-ray analysis and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. A multi-technique approach employing UV-Visible spectroscopy, fluorescence, KI quenching studies, competitive displacement assay, circular dichroism and viscosity studies have been utilized to probe the extent of interaction and possible binding modes of isolated compounds (1-2) with calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA). Both the compounds were found to interact with DNA via non-intercalative binding mode with moderate proficiencies. Groove binding was the major interaction mode in the case of compound 2 while compound 1 probably interacts with DNA through electrostatic interactions. These studies provide deeper insight in understanding of DNA-drug (natural products) interaction which could be helpful to improve their bioavailability for therapeutic purposes.
Cp*Co(III)-Catalyzed Annulations of 2-Alkenylphenols with CO: Mild Access to Coumarin Derivatives.[Pubmed:26451846]
Org Lett. 2015 Nov 6;17(21):5404-7.
Cp*Co(III)-catalyzed annulations of 2-alkenylphenols with CO for the synthesis of coumarin derivatives have been developed. The reaction features mild reaction conditions, broad substrate scope, and good functional group tolerance. Preliminary mechanistic studies were conducted, suggesting that C-H activation is the turnover limiting step. Furthermore, the efficiency of this reaction was demonstrated by the rapid total synthesis of three natural products herniarin, xanthyletin, and Seselin.
Isolation of seselin from Clausena anisata (Rutaceae) leaves and its effects on the feeding and development of Lucilia cuprina larvae may explain its use in ethnoveterinary medicine.[Pubmed:24095830]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):886-91.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: The leaves of Clausena anisata are used traditionally to expel maggots from wounds of animals in Zimbabwe. We have previously proved in the laboratory that the plant certainly affects the behaviour and growth of blowfly larvae. The objective of this study was to isolate and identify the active compounds responsible for this activity. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The acetone extract of Clausena anisata leaf powder was separated by solvent-solvent partition into five fractions. The n-hexane fraction was the most active in the larvicidal assay and therefore subjected to open column chromatography on silica gel. RESULTS: The isolated compound was identified by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectroscopy (MS) as the pyranocoumarin, Seselin, chemically known as 2',2'-dimethylpyranocoumarin. It inhibited feed intake in the first and second instars of blowfly larvae at the minimum concentration tested of 1 ppm resulting in significant lower mass pupae (13.5+/-0.5 mg and 22.4+/-0.4 mg for the first and second instar larvae respectively) compared to the solvent control group (26.19+/-0.8 mg) (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: This is the first report of the isolation of Seselin from the leaves of Clausena anisata and the first report of the compound having an effect against blowfly larvae.
Antithrombotic activity of a newly synthesized coumarin derivative 3-(5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-chroman-6-yl)-N-{2-[3-(5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-chroman-6 -yl)-propionylamino]-ethyl}-propionamide.[Pubmed:23534412]
Chem Biol Drug Des. 2013 Apr;81(4):499-508.
Anti-platelet therapy is a useful strategy to prevent acute thromboembolic artery occlusions. This study was designed to assess the efficacy of Seselin derivatives against murine pulmonary thromboembolism, bleeding time, platelet activation and thrombosis. Administration of C3 (16 mg/kg) offered 70% protection against collagen- and epinephrine-induced pulmonary thromboembolism and 30% protection against arachidonic acid-induced death in mice, without adversely affecting bleeding time. No significant difference was observed by C3 in ferric chloride-induced arterial thrombosis in rats. Significant reduction in thrombus weight was observed in arteriovenous shunt model. In rat PRP, C3 reduced ADP and collagen-induced platelet aggregation. In chronic hamster model of dyslipidemia, administration of C3 (16 mg/kg p.o. for 90 days) had no effect on plasma lipids, vasoreactivity and platelet adhesion. C3 fed hamsters showed reduced whole-blood aggregation response to ADP and collagen compared to HC-fed hamsters. In addition, C3 augmented thrombin time; however, time to occlusion was not increased. These results convincingly demonstrated that C3 is a novel molecule that reduces the risk of thrombosis and alleviates prothrombotic state associated with hyperlipidemia without any adverse effect on bleeding time. The high benefit/risk ratio of this compound makes it a suitable candidate for future valid studies.
Biological activities of Indian celery, Seseli diffusum (Roxb. ex Sm.) Sant. & Wagh.[Pubmed:22095902]
Phytother Res. 2012 May;26(5):783-6.
In continuation of our work on Indian celery (Seseli diffusum (Roxb. ex Sm.) Santapau & Wagh; Umbelliferae), the fractionation of the 80% MeOH-H(2) O extract of the seeds was performed to identify the principles responsible for its folk use as an antispasmodic and diuretic. Several compounds were isolated as active components: Seselin (1) and anthriscinol methyl ether (4) showed a selective cytotoxicity to some yeast strains. Compound 1 also showed spasmolytic activity. On the other hand, isopimpinellin (3) and isorutarin (5) exhibited a spasmogenic effect on the smooth muscle preparations. Compound 5 was also found to have antioxidant activity. Among them, compound 4 was isolated for the first time from this plant.


