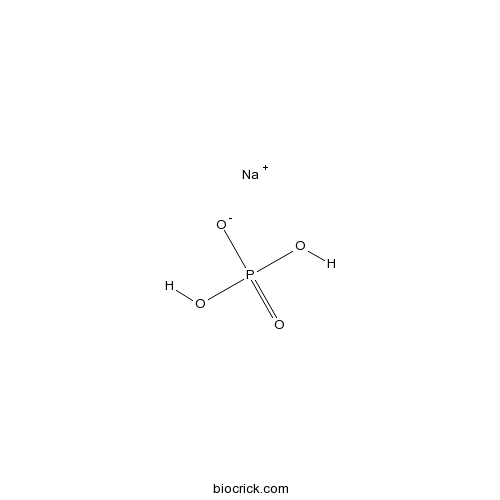
Sodium phosphate monobasicCAS# 7558-80-7 |
- Resminostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1888
CAS No.:1187075-34-8
- RG2833
Catalog No.:BCC1893
CAS No.:1215493-56-3
- Daminozide
Catalog No.:BCC1514
CAS No.:1596-84-5
- Tasquinimod
Catalog No.:BCC1987
CAS No.:254964-60-8
- CHAPS
Catalog No.:BCC1476
CAS No.:75621-03-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 7558-80-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23672064 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | NaH2PO4 | M.Wt | 119.98 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 800 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;dihydrogen phosphate | ||
| SMILES | OP(=O)(O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AJPJDKMHJJGVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/Na.H3O4P/c;1-5(2,3)4/h;(H3,1,2,3,4)/q+1;/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Commonly used in biological assay buffers. |

Sodium phosphate monobasic Dilution Calculator

Sodium phosphate monobasic Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 8.3347 mL | 41.6736 mL | 83.3472 mL | 166.6944 mL | 208.3681 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.6669 mL | 8.3347 mL | 16.6694 mL | 33.3389 mL | 41.6736 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.8335 mL | 4.1674 mL | 8.3347 mL | 16.6694 mL | 20.8368 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1667 mL | 0.8335 mL | 1.6669 mL | 3.3339 mL | 4.1674 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0833 mL | 0.4167 mL | 0.8335 mL | 1.6669 mL | 2.0837 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Sodium phosphate dibasic
Catalog No.:BCC7585
CAS No.:7558-79-4
- 20-Deoxyingenol 3-angelate
Catalog No.:BCN6642
CAS No.:75567-38-3
- Ingenol 3-Angelate
Catalog No.:BCN2961
CAS No.:75567-37-2
- Dencichin
Catalog No.:BCN2555
CAS No.:7554-90-7
- Moxonidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5163
CAS No.:75536-04-8
- Nilvadipine
Catalog No.:BCC3799
CAS No.:75530-68-6
- Cedrin
Catalog No.:BCN4748
CAS No.:75513-81-4
- Flupirtine maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4456
CAS No.:75507-68-5
- BI6727 (Volasertib)
Catalog No.:BCC3886
CAS No.:755038-65-4
- BI 2536
Catalog No.:BCC2081
CAS No.:755038-02-9
- Regorafenib
Catalog No.:BCC3646
CAS No.:755037-03-7
- N-Methylnuciferine
Catalog No.:BCN3971
CAS No.:754919-24-9
- alpha-Tocopherolquinone
Catalog No.:BCN4305
CAS No.:7559-04-8
- Kaerophyllin
Catalog No.:BCN4304
CAS No.:75590-33-9
- Methyl 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN4589
CAS No.:7560-49-8
- Fludarabine Phosphate (Fludara)
Catalog No.:BCC3681
CAS No.:75607-67-9
- (S)-(+)-α-Methylhistamine dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6700
CAS No.:75614-93-6
- (-)-Usnic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4306
CAS No.:7562-61-0
- CHAPS
Catalog No.:BCC1476
CAS No.:75621-03-3
- Moracenin B
Catalog No.:BCC8341
CAS No.:75629-19-5
- Gomisin K1
Catalog No.:BCN7030
CAS No.:75629-20-8
- Oncrasin 1
Catalog No.:BCC2390
CAS No.:75629-57-1
- Knightolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1912
CAS No.:75638-70-9
- Chalcostrobamine
Catalog No.:BCN1900
CAS No.:75638-72-1
The effect of monobasic sodium phosphate on statolith synthesis in aurelia.[Pubmed:6120564]
Scan Electron Microsc. 1981;(Pt 3):355-62.
The effect of monobasic sodium phosphate on statolith synthesis in Aurelia metamorphosing in artificial sea water (ASW) and in low sulfate ASW was determined. Phosphate enhances statolith synthesis in organisms metamorphosing in ASW and restores statolith numbers to normal or above in organisms developing in low sulfate ASW. A small amount of sulfate must be present in the medium along with phosphate during the time period of statolith synthesis for normal statolith formation. Apparently, neither sulfate nor phosphate is stored in the organisms during early strobilation for later use in statolith synthesis because pre-treatment of either ion in early strobilation followed by treatment with the other ion does not result in statolith formation. Calcifying vesicles of the rhopalia of organisms from low sulfate ASW are normal in number, acid phosphatase activity, and in ability to initiate mineralization (by forming minute statoliths). While phosphate is not incorporated directly into the statoliths, it contributes to an efficient uptake of calcium and sulfur into the cells and/or calcifying vesicles, stimulating growth of calcium sulfate dihydrate statoliths. The high efficiency of the phosphate effect in enhancing statolith synthesis intracellularly demonstrates that phosphate acts at the cellular level in the jellyfish calcification process and emphasizes that phosphate probably plays multiple roles in the calcification of higher organisms.


