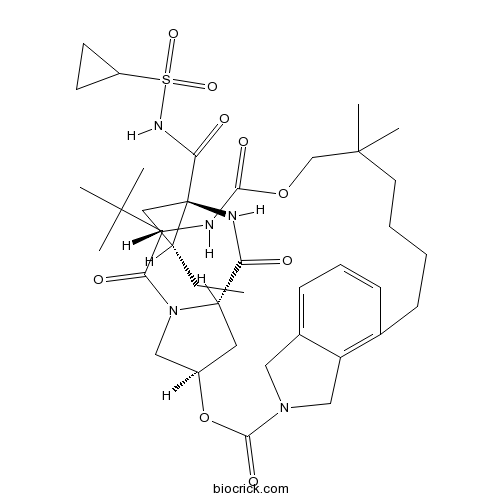
VaniprevirHepatitis C virus NS3/4a protease inhibitor CAS# 923590-37-8 |
- Anguizole
Catalog No.:BCC1365
CAS No.:442666-98-0
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Balapiravir
Catalog No.:BCC1396
CAS No.:690270-29-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 923590-37-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24765256 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C38H55N5O9S | M.Wt | 757.95 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | MK-7009 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | (1R,21S,24S)-21-tert-butyl-N-[(1R,2R)-1-(cyclopropylsulfonylcarbamoyl)-2-ethylcyclopropyl]-16,16-dimethyl-3,19,22-trioxo-2,18-dioxa-4,20,23-triazatetracyclo[21.2.1.14,7.06,11]heptacosa-6(11),7,9-triene-24-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CCC1CC1(C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C2CC2)NC(=O)C3CC4CN3C(=O)C(NC(=O)OCC(CCCCC5=C6CN(CC6=CC=C5)C(=O)O4)(C)C)C(C)(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KUQWGLQLLVFLSM-ONAXAZCASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C38H55N5O9S/c1-7-25-18-38(25,33(46)41-53(49,50)27-14-15-27)40-31(44)29-17-26-20-43(29)32(45)30(36(2,3)4)39-34(47)51-22-37(5,6)16-9-8-11-23-12-10-13-24-19-42(21-28(23)24)35(48)52-26/h10,12-13,25-27,29-30H,7-9,11,14-22H2,1-6H3,(H,39,47)(H,40,44)(H,41,46)/t25-,26-,29+,30-,38-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Vaniprevir (MK-7009) is a non-covalent competitive inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease.
IC50 Value:
Target: HCV NS3/4A Protease; HCV
vaniprevir (MK-7009) is a macrocyclic hepatitis C virus NS3/4a protease inhibitor, is active against both the genotype 1 and genotype 2 NS3/4a protease enzymes. vaniprevir (MK-7009) has good plasma exposure and excellent liver exposure in multiple species. References: | |||||

Vaniprevir Dilution Calculator

Vaniprevir Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3193 mL | 6.5967 mL | 13.1935 mL | 26.387 mL | 32.9837 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2639 mL | 1.3193 mL | 2.6387 mL | 5.2774 mL | 6.5967 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1319 mL | 0.6597 mL | 1.3193 mL | 2.6387 mL | 3.2984 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0264 mL | 0.1319 mL | 0.2639 mL | 0.5277 mL | 0.6597 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0132 mL | 0.066 mL | 0.1319 mL | 0.2639 mL | 0.3298 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
vaniprevir (MK-7009) is a macrocyclic hepatitis C virus NS3/4a protease inhibitor, is active against both the genotype 1 and genotype 2 NS3/4a protease enzymes. vaniprevir (MK-7009) has good plasma exposure and excellent liver exposure in multiple species.
- GSK962040 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4152
CAS No.:923565-22-4
- GSK962040
Catalog No.:BCC4163
CAS No.:923565-21-3
- ABT-263 (Navitoclax)
Catalog No.:BCC1272
CAS No.:923564-51-6
- SAR407899
Catalog No.:BCC5593
CAS No.:923359-38-0
- Nilotinib monohydrochloride monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1801
CAS No.:923288-90-8
- Opicapone
Catalog No.:BCC6545
CAS No.:923287-50-7
- SAR407899 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5592
CAS No.:923262-96-8
- Refametinib R enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC4055
CAS No.:923032-38-6
- Refametinib
Catalog No.:BCC4276
CAS No.:923032-37-5
- 3-O-Methyl-3-methoxymaxterone
Catalog No.:BCC8639
CAS No.:92282-70-7
- Sanggenon N
Catalog No.:BCN4846
CAS No.:92280-12-1
- (±)-MDMA hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5965
CAS No.:92279-84-0
- Simeprevir
Catalog No.:BCC1949
CAS No.:923604-59-5
- 3-Acetoxy-4-cadinen-8-one
Catalog No.:BCN4461
CAS No.:923950-05-4
- DUBs-IN-3
Catalog No.:BCC5258
CAS No.:924296-17-3
- DUBs-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5256
CAS No.:924296-18-4
- DUBs-IN-2
Catalog No.:BCC5257
CAS No.:924296-19-5
- HBX 41108
Catalog No.:BCC6137
CAS No.:924296-39-9
- AdipoRon
Catalog No.:BCC4756
CAS No.:924416-43-3
- T 5601640
Catalog No.:BCC5617
CAS No.:924473-59-6
- AZD-5597
Catalog No.:BCC6453
CAS No.:924641-59-8
- 4,5-Epoxyartemisinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4462
CAS No.:92466-31-4
- Rupesin E
Catalog No.:BCN7009
CAS No.:924901-58-6
- 21-Deoxyneridienone B
Catalog No.:BCN4463
CAS No.:924910-83-8
HCV evolutionary genetics of SVR versus virologic failure assessed from the vaniprevir phase III registration trials.[Pubmed:26947564]
Antiviral Res. 2016 Jun;130:118-29.
UNLABELLED: In the phase III registration studies conducted in Japan, Japanese HCV gt1 patients administered Vaniprevir 300 mg twice daily plus pegylated interferon/ribavirin for 12 or 24 weeks achieved SVR24 rates of 83.7-84.5% among treatment-naive patients, and 92.0-96.2% and 61.9% among breakthrough/relapsers or null-responders to prior interferon based therapy. As evidenced by direct sequencing, patients who did not achieve SVR24 principally failed due to treatment-emerging mutations at D168 or in a few cases R155. In this work, additional sequence analysis was conducted to address whether there were baseline polymorphisms associated with failure, evaluate the persistence of resistant virus among treatment failures, and assess for evidence of second site co-evolution with R155 or D168 mutations. To accomplish this, clonal sequencing (up to 40 clones per sample) was conducted on baseline, failure, and follow-up samples from all 38 patients among the Vaniprevir treatment arms who met virologic failure criteria (37 gt1b, 1 gt1a, herein referred to as virologic failures) and baseline samples from 41 Vaniprevir-treated SVR24 patients (all gt1b) selected among the three studies. SVR24 and virologic failure patients showed similar distributions of baseline polymorphisms previously associated with failure to one or more protease inhibitors. Furthermore, there was no evidence for baseline polymorphisms or a genetic signature across the NS3 protease domain specific to virologic failure patients, and which distinguishes them from baseline SVR24 sequences beyond a chance distribution. 24 of 32 virologic failures for whom baseline, failure, and follow-up samples were available showed reduced prevalence of the resistant virus first observed at the time of failure during the protocol-defined follow-up period of 24 weeks. Finally, pairwise analysis using either alignment or phylogenetic based methodologies provided no evidence for second site evolution with either the R155 or D168 mutations attributed to failure. This work supports and extends earlier findings based upon direct sequencing that attributed virologic failure to Vaniprevir in the Phase III studies solely to the emergence of R155 or D168 mutations, with no apparent influence by other residues within the NS3 protease domain on treatment outcome. CLINICALTRIALS. GOVIDENTIFIERS: NCT01370642, NCT01405937, NCT01405560.
Elimination of HCV via a non-ISG-mediated mechanism by vaniprevir and BMS-788329 combination therapy in human hepatocyte chimeric mice.[Pubmed:26569595]
Virus Res. 2016 Feb 2;213:62-68.
We previously reported that interferon (IFN)-free direct-acting antiviral combination treatment succeeded in eradicating genotype 1b hepatitis C virus (HCV) in human hepatocyte chimeric mice. In this study, we examined the effect of Vaniprevir (MK7009, NS3/4A protease inhibitor) and BMS-788329 (NS5A inhibitor) combination treatment on HCV genotype 1b and the expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) using a subgenomic replicon system and the same animal model. Combination treatment with Vaniprevir and BMS-788329 significantly reduced HCV replication compared to Vaniprevir monotherapy in HCV replicon cells (Huh7/Rep-Feo cells). HCV genotype 1b-infected human hepatocyte chimeric mice were treated with Vaniprevir alone or in combination with BMS-788329 for four weeks. Vaniprevir monotherapy reduced serum HCV RNA titers in mice, but viral breakthrough was observed in mice with high HCV titers. Ultra-deep sequence analysis revealed a predominant replacement by drug-resistant substitutions at 168 in HCV NS3 region in these mice. Conversely, in mice with low HCV titers, HCV was eradicated by Vaniprevir monotherapy without viral breakthrough. In contrast to monotherapy, combination treatment with Vaniprevir and BMS-788329 succeeded in completely eradicating HCV regardless of serum viral titer. IFN-alpha treatment significantly increased ISG expression; however, Vaniprevir and BMS-788329 combination treatment caused no increase in ISG expression both in cultured cells and in mouse livers. Therefore, combination treatment with Vaniprevir and BMS-788329 eliminated HCV via a non-ISG-mediated mechanism. This oral treatment might offer an alternative DAA combination therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Vaniprevir plus peginterferon alfa-2b and ribavirin in treatment-experienced Japanese patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 (GT1b) infection: Phase 3 studies.[Pubmed:26936417]
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Oct;31(10):1674-1683.
BACKGROUND AND AIM: Vaniprevir is a macrocyclic hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural (NS)3/4A protease inhibitor. The objective of these phase 3 multicenter, open-label trials was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Vaniprevir + peginterferon alfa-2b + ribavirin (PR) in Japanese patients with HCV genotype (GT)1 infection who had previously failed treatment with interferon-based regimens. METHODS: Japanese patients with chronic HCV GT1 were enrolled. In PN044, patients with previous relapse or virologic breakthrough were randomized to Vaniprevir (300 mg twice daily) + PR for 12 weeks followed by PR for another 12 weeks (12-week arm) or Vaniprevir + PR for 24 weeks (24-week arm). In PN045, patients with previous partial/null response received Vaniprevir + PR for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was sustained virologic response at 24 weeks after completing treatment (SVR24 ). RESULTS: In PN044 (n = 51), SVR24 was 92.0% and 96.2% in the 12- and 24-week arms, respectively. In PN045 (n = 42), SVR24 was 61.9% in all patients and 55.2% in previous null responders. In both studies, Vaniprevir + PR was generally safe and well tolerated; the majority of adverse events were mild/moderate and included pyrexia, decreased hemoglobin, headache, nausea, pruritus, and decreased platelet count. Polymorphisms in the HCV NS3 gene at baseline (Y56, Q80, and V170) did not impact treatment outcome. Virologic failure was principally associated with the on-treatment emergence of R155 or D168 mutations. CONCLUSIONS: Vaniprevir + PR is an effective, well-tolerated treatment for Japanese patients with HCV GT1 infection who failed previous interferon-based treatment. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01405937 and NCT01405560 (Protocols PN044 and PN045).


