WAY-1006355-HT1A receptor antagonist,potent and selective CAS# 162760-96-5 |
- Granisetron HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1060
CAS No.:107007-99-8
- SB 271046 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1924
CAS No.:209481-24-3
- Adoprazine
Catalog No.:BCC1329
CAS No.:222551-17-9
- SEA0400
Catalog No.:BCC1941
CAS No.:223104-29-8
- Tianeptine
Catalog No.:BCC1999
CAS No.:66981-73-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 162760-96-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5684 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H34N4O2 | M.Wt | 422.56 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO ≥80mg/mL Water ≥16mg/mL Ethanol ≥80mg/mL | ||
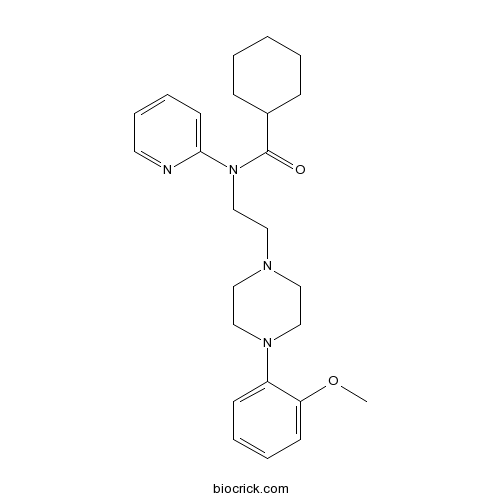
| Chemical Name | N-[2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]-N-pyridin-2-ylcyclohexanecarboxamide | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=CC=C1N2CCN(CC2)CCN(C3=CC=CC=N3)C(=O)C4CCCCC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SBPRIAGPYFYCRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H34N4O2/c1-31-23-12-6-5-11-22(23)28-18-15-27(16-19-28)17-20-29(24-13-7-8-14-26-24)25(30)21-9-3-2-4-10-21/h5-8,11-14,21H,2-4,9-10,15-20H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | WAY-100635 is a potent, silent antagonist of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors with IC50 value of 2.2 nM. | |||||
| Targets | 5-HT1A receptor | |||||
| IC50 | 2.2 nM | |||||

WAY-100635 Dilution Calculator

WAY-100635 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3665 mL | 11.8326 mL | 23.6653 mL | 47.3306 mL | 59.1632 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4733 mL | 2.3665 mL | 4.7331 mL | 9.4661 mL | 11.8326 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2367 mL | 1.1833 mL | 2.3665 mL | 4.7331 mL | 5.9163 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0473 mL | 0.2367 mL | 0.4733 mL | 0.9466 mL | 1.1833 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0237 mL | 0.1183 mL | 0.2367 mL | 0.4733 mL | 0.5916 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
5-HT1A receptors mediate various serotonergic functions and may be implicated in various pathologies including depressive and anxiety disorders, Alzheimer’s disease, and schizophrenia. WAY-100635 is a potential SPECT ligands for the 5-HT1A receptor.
In vitro: WAY-100635 displaced specific binding of the 5-HT1A radioligand, [3H]8-OH-DPAT, to rat hippocampal membranes with a plC50 of 8.87. In functional assays, WAY-100635 was a potent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, with no evidence of any 5-HTIA receptor agonist or partial agonist activity. In the isolated guinea-pig ileum WAY-100635 was a potent and, at high concentrations, an insurmountable antagonist of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist action of 5-carboxamidotryptamine, with an apparent pA 2 value (at 0.3 nM) of 9.71 [2].
In vivo: WAY-100635 blocked the inhibitory action of 8-OH-DPAT on dorsal raphe neuronal firing in the anaesthetised rat at doses which had no inhibitory action per se. In behavioural models, WAY-100635 itself induced no overt behavioural changes but potently antagonised the behavioural syndrome induced by 8-OH-DPAT in the rat and guinea-pig (minimum effective dose = 0.003 mg/kg s.c. and ID50 = 0.01 mg/kg s.c., respectively). WAY-100635 also blocked the hypothermia induced by 8-OH-DPAT in the mouse and rat with ID50 values of 0.01 mg/kg s.c. [2].
Clinical trial: Using the ligand [11C]-WAY100635, an open label, non-randomized positron emission tomography study in healthy male subjects has been conducted to investigate brain 5-HT1A receptor occupancy, pharmacokinetics and safety of single oral doses of GSK163090.
References:
[1] Al Hussainy R, Verbeek J, van der Born D, Braker AH, Leysen JE, Knol RJ, Booij J, Herscheid JK.
Design, synthesis, radiolabeling, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of bridgehead iodinated analogues of N-{2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl}-N-(pyridin-2-yl)cyclohexanecarboxamide (WAY-100635) as potential SPECT ligands for the 5-HT1A receptor. J Med Chem. 2011;54(10):3480-91.
[2] Forster EA, Cliffe IA, Bill DJ, Dover GM, Jones D, Reilly Y, Fletcher A. A pharmacological profile of the selective silent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, WAY-100635. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;281(1):81-8.
- Anemarrhena B
Catalog No.:BCN7592
CAS No.:1627521-95-2
- LDN-214117
Catalog No.:BCC5528
CAS No.:1627503-67-6
- AZD8186
Catalog No.:BCC6470
CAS No.:1627494-13-6
- 1-Hydroxy-2-prenylnaphthalene
Catalog No.:BCN1722
CAS No.:16274-34-3
- 3,4-Dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-2H-naphtho[1,2-b]pyran
Catalog No.:BCN1539
CAS No.:16274-33-2
- Kaempferol tetraacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1721
CAS No.:16274-11-6
- 6-Deoxyjacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN6573
CAS No.:16265-56-8
- HQL 79
Catalog No.:BCC7703
CAS No.:162641-16-9
- AT 56
Catalog No.:BCC6036
CAS No.:162640-98-4
- AZD3759
Catalog No.:BCC6475
CAS No.:1626387-80-1
- Temsirolimus
Catalog No.:BCC3678
CAS No.:162635-04-3
- Sorokinianin
Catalog No.:BCN6978
CAS No.:162616-73-1
- Yunnancoronarin A
Catalog No.:BCN1723
CAS No.:162762-93-8
- PFI-2
Catalog No.:BCC5561
CAS No.:1627676-59-8
- LJI308
Catalog No.:BCC6538
CAS No.:1627709-94-7
- 7-Epi-10-oxo-docetaxel
Catalog No.:BCC5410
CAS No.:162784-72-7
- IEM 1754 dihydrobroMide
Catalog No.:BCC5049
CAS No.:162831-31-4
- 2,3,9,10-Tetrahydroxyberberine
Catalog No.:BCN3550
CAS No.:162854-37-7
- Polygalasaponin V
Catalog No.:BCN2790
CAS No.:162857-65-0
- Polygalaxanthone III
Catalog No.:BCN2354
CAS No.:162857-78-5
- Antibiotic AB 4015B
Catalog No.:BCN1826
CAS No.:162857-79-6
- (S)-3,5-DHPG
Catalog No.:BCC6802
CAS No.:162870-29-3
- Kaempferol-7-O-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN2296
CAS No.:16290-07-6
- 3,4-Dihydroxybenzylamine Hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC8280
CAS No.:16290-26-9
Verbal memory and 5-HT1A receptors in healthy volunteers--A PET study with [carbonyl-(11)C]WAY-100635.[Pubmed:26775837]
Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Mar;26(3):570-7.
The serotonin 5-HT1A receptor is a putative drug development target in disorders with cognitive and in particular memory deficits. However, previous human positron emission tomography (PET) studies on 5-HT1A receptor binding and memory functions have yielded discrepant results. We explored the association between verbal memory and 5-HT1A receptor binding in 24 healthy subjects (14 male, 10 female, aged 18-41 years). The cognitive tests included the Wechsler Memory Scale-Revised (WMS-R), Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised (WAIS-R) and Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST). 5-HT1A receptor binding was measured with PET and the radioligand [carbonyl-(11)C]WAY-100635, which was quantified with the gold standard method based on kinetic modeling using arterial blood samples. We found that global 5-HT1A receptor binding was positively correlated with measures of verbal memory, such that subjects who had higher receptor binding tended to have better verbal memory than subjects who had lower receptor binding. Regional analyses suggested significant correlations in multiple neocortical brain regions and the raphe nuclei. We did not find significant correlations between 5-HT1A receptor binding and executive functions as measured with WCST. We conclude that neocortical as well as raphe 5-HT1A receptors are involved in verbal memory function in man.
Effects of hormone replacement therapy on cerebral serotonin-1A receptor binding in postmenopausal women examined with [carbonyl-(1)(1)C]WAY-100635.[Pubmed:24845171]
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014 Jul;45:1-10.
Preclinical research points to a strong modulatory influence of gonadal hormones on the serotonin system. However, human data corroborating this association remains scarce. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of hormone replacement therapy on 5-HT(1)A receptor binding in postmenopausal women using positron emission tomography (PET) and the radioligand [carbonyl-(11)C]WAY-100635. In this randomized, double-blind, longitudinal study, 30 postmenopausal women underwent treatment with either a combination of oral 17beta-estradiol valerate and micronized progesterone (group 1, n=10), oral 17beta-estradiol valerate (group 2, n=10), or placebo (group 3, n=10). Two PET measurements were performed, one the day before treatment start and the second after at least eight weeks of treatment. Plasma levels of estradiol (E(2)), progesterone (P(4)), sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) were collected prior to PET measurements. As expected, hormone replacement therapy led to a significant increase in E(2) and P4 plasma levels in group 1 and to a significant increase in E(2) levels in group 2. The 5-HT(1)A receptor binding did not change significantly after estrogen, combined estrogen/progesterone treatment or placebo in any of the investigated brain regions. There were no significant correlations between changes in E(2) or P4 values and changes in 5-HT(1)A receptor binding. Although we were not able to confirm effects of gonadal hormone treatment on 5-HT(1)A receptor binding, our data do not preclude associations between sex steroid levels and serotonin, the neurotransmitter implicated most strongly in the pathogenesis of affective and anxiety disorders. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00755963.
Structural Insights into 5-HT1A/D4 Selectivity of WAY-100635 Analogues: Molecular Modeling, Synthesis, and in Vitro Binding.[Pubmed:27331407]
J Chem Inf Model. 2016 Jul 25;56(7):1324-31.
The resurgence of interest in 5-HT1A receptors as a therapeutic target requires the existence of highly selective 5-HT1A ligands. To date, WAY-100635 has been the prototypical antagonist of these receptors. However, this compound also has significant affinity for and activity at D4 dopamine receptors. In this context, this work was aimed at better understanding the 5-HT1A/D4 selectivity of WAY-100635 and analogues from a structural point of view. In silico investigations revealed two key interactions for the 5-HT1A/D4 selectivity of WAY-100635 and analogues. First, a hydrogen bond only found with the Ser 7.36 of D4 receptor appeared to be the key for a higher D4 affinity for newly synthesized aza analogues. The role of Ser 7.36 was confirmed as the affinity of aza analogues for the mutant D4 receptor S7.36A was reduced. Then, the formation of another hydrogen bond with the conserved Ser 5.42 residue appeared to be also critical for D4 binding.
Neuroprotective effects of HTR1A antagonist WAY-100635 on scopolamine-induced delirium in rats and underlying molecular mechanisms.[Pubmed:27760517]
BMC Neurosci. 2016 Oct 19;17(1):66.
BACKGROUND: Limited surveys have assessed the performance of 5-hydroxytreptamine receptor 1A and its antagonist WAY-100635 in pharmacological manipulations targeting delirium therapies. The purpose of this paper was to assess the central pharmacological activity of WAY-100635 in a rat model of scopolamine-induced delirium and its underlying mechanism. RESULTS: A delirium rat model was established by intraperitoneal injection of scopolamine and behavioral changes evaluated through open field and elevated plus maze experiments. Concentrations of monoamines in the hippocampus and amygdalae were detected by high performance liquid chromatography. The effect of WAY-100635 on the recovery of rats from delirium was assessed by stereotactic injection of WAY-100635 and its mechanism of action determined by measuring mRNA and protein expression via real time PCR and western blotting methods. The total distance and the number of crossing and rearing in the elevated plus maze test and the time spent in the light compartment in the dark/light test of scopolamine-treated rats were significantly increased while the percentage of time spent in the open arms was decreased, showing the validity of the established delirium rat model. The measurement of the concentrations of noradrenaline, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, the homovanillic acid, 5-hydroxy-3-indoleacetic acid and serotonin concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of scopolamine-induced delirium rats were significantly increased. The intra-hippocampus and intra-BLA injections of WAY-100635 improved the delirium-like behavior of rats by significantly reducing the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome and the release of IL1-beta and IL8 into CSF. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together, these findings indicate that WAY-100635 may exert a therapeutic effect on post-operative delirium by controlling neurotransmission as well as suppressing neuroinflammation in the central nervous system.


