AT 56L-PGDS inhibitor CAS# 162640-98-4 |
- Sabutoclax
Catalog No.:BCC2236
CAS No.:1228108-65-3
- ABT-199
Catalog No.:BCC3614
CAS No.:1257044-40-8
- WEHI-539
Catalog No.:BCC2055
CAS No.:1431866-33-9
- Obatoclax mesylate (GX15-070)
Catalog No.:BCC2234
CAS No.:803712-79-0
- ABT-737
Catalog No.:BCC3613
CAS No.:852808-04-9
- TW-37
Catalog No.:BCC2257
CAS No.:877877-35-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 162640-98-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11741525 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H27N5 | M.Wt | 397.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO | ||
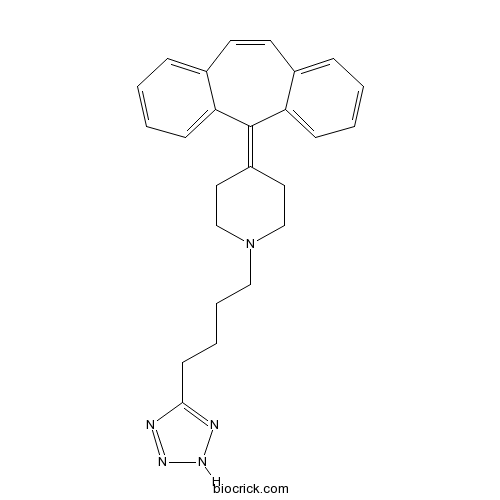
| Chemical Name | 4-(dibenzo[1,2-a:1',2'-e][7]annulen-11-ylidene)-1-[4-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)butyl]piperidine | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CCC1=C2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC4=CC=CC=C42)CCCCC5=NNN=N5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LQNGMDUIRLSESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H27N5/c1-3-9-22-19(7-1)12-13-20-8-2-4-10-23(20)25(22)21-14-17-30(18-15-21)16-6-5-11-24-26-28-29-27-24/h1-4,7-10,12-13H,5-6,11,14-18H2,(H,26,27,28,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Orally active inhibitor of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase (L-PGDS) (Ki = 75 μM, IC50 = 95 μM). Inhibits the production of PGD2 from PGH2 in vitro, with no effect on PGE2 or PGF2α production. |

AT 56 Dilution Calculator

AT 56 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5156 mL | 12.578 mL | 25.156 mL | 50.3119 mL | 62.8899 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5031 mL | 2.5156 mL | 5.0312 mL | 10.0624 mL | 12.578 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2516 mL | 1.2578 mL | 2.5156 mL | 5.0312 mL | 6.289 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0503 mL | 0.2516 mL | 0.5031 mL | 1.0062 mL | 1.2578 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0252 mL | 0.1258 mL | 0.2516 mL | 0.5031 mL | 0.6289 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PGD24 is a lipid mediator involved in sleep and inflammatory responses. PGD2 activates two different types of receptors. PGD2 regulates sleep and pain via DP1 receptors in the central nervous system. This prostanoid also causes contraction of airway smooth muscle via DP1 receptors and mediates chemotaxis of eosinophils and basophils into the lung via DP2 receptors in the periphery. Therefore, PGD2 coordinately regulates allergic reactions, especially airway inflammation, via these two receptors. AT-56 is an orally active and selective inhibitor of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase.
In vitro: AT-56 inhibited human and mouse L-PGDSs in a concentration (3-250 μM)-dependently but did not affect the activities of hematopoietic PGD synthase (H-PGDS), cyclooxygenase-1 and -2, and microsomal PGE synthase-1. AT-56 inhibited L-PGDS activity in a competitive manner against the substrate PGH2 (Km=14 μM) with a Ki value of 75 μM but did not inhibit the binding of 13-cis-retinoic acid, a nonsubstrate lipophilic ligand, to L-PGDS. [2].
In vivo: Orally administered AT-56 (<30 mg>
Clinical trial: Up to now, AT-56 is still in the preclinical development stage.
Reference:
[1] Daisuke Irikura, Kosuke Aritake, Nanae Nagata, Toshihiko Maruyama, Shigeru Shimamoto, and Yoshihiro Urade. Biochemical, Functional, and Pharmacological Characterization of AT-56, an Orally Active and Selective Inhibitor of Lipocalin-type Prostaglandin D Synthase. J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 20;284(12):7623-30.
- AZD3759
Catalog No.:BCC6475
CAS No.:1626387-80-1
- Temsirolimus
Catalog No.:BCC3678
CAS No.:162635-04-3
- Sorokinianin
Catalog No.:BCN6978
CAS No.:162616-73-1
- Eriosemation
Catalog No.:BCN3738
CAS No.:162616-72-0
- Isolupalbigenin
Catalog No.:BCN6835
CAS No.:162616-70-8
- 3-Hydroxy-5,7-dimethoxy-3',4'-methylenedioxyflavan
Catalog No.:BCN1540
CAS No.:162602-04-2
- Broussoflavonol F
Catalog No.:BCN3571
CAS No.:162558-94-3
- Fmoc-Dap(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3188
CAS No.:162558-25-0
- CDP 840 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7814
CAS No.:162542-90-7
- Salirasib
Catalog No.:BCC1918
CAS No.:162520-00-5
- Subelliptenone G
Catalog No.:BCN1720
CAS No.:162473-22-5
- VR23
Catalog No.:BCC6523
CAS No.:1624602-30-7
- HQL 79
Catalog No.:BCC7703
CAS No.:162641-16-9
- 6-Deoxyjacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN6573
CAS No.:16265-56-8
- Kaempferol tetraacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1721
CAS No.:16274-11-6
- 3,4-Dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-2H-naphtho[1,2-b]pyran
Catalog No.:BCN1539
CAS No.:16274-33-2
- 1-Hydroxy-2-prenylnaphthalene
Catalog No.:BCN1722
CAS No.:16274-34-3
- AZD8186
Catalog No.:BCC6470
CAS No.:1627494-13-6
- LDN-214117
Catalog No.:BCC5528
CAS No.:1627503-67-6
- Anemarrhena B
Catalog No.:BCN7592
CAS No.:1627521-95-2
- WAY-100635
Catalog No.:BCC2053
CAS No.:162760-96-5
- Yunnancoronarin A
Catalog No.:BCN1723
CAS No.:162762-93-8
- PFI-2
Catalog No.:BCC5561
CAS No.:1627676-59-8
- LJI308
Catalog No.:BCC6538
CAS No.:1627709-94-7
The G-protein coupled receptor 56, expressed in colonic stem and cancer cells, binds progastrin to promote proliferation and carcinogenesis.[Pubmed:28380450]
Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):40606-40619.
Overexpression of human progastrin increases colonic mucosal proliferation and colorectal cancer progression in mice. The G-protein coupled receptor 56 (GPR56) is known to regulate cell adhesion, migration, proliferation and stem cell biology, but its expression in the gut has not been studied. We hypothesized that the promotion of colorectal cancer by progastrin may be mediated in part through GPR56. Here, we found that GPR56 expresses in rare colonic crypt cells that lineage trace colonic glands consistent with GPR56 marking long-lived colonic stem-progenitor cells. GPR56 was upregulated in transgenic mice overexpressing human progastrin. While recombinant human progastrin promoted the growth and survival of wild-type colonic organoids in vitro, colonic organoids cultured from GPR56-/- mice were resistant to progastrin. We found that progastrin directly bound to, and increased the proliferation of, GPR56-expressing colon cancer cells in vitro, and proliferation was increased in cells that expressed both GPR56 and the cholecystokinin-2 receptor (CCK2R). In vivo, deletion of GPR56 in the mouse germline abrogated progastrin-dependent colonic mucosal proliferation and increased apoptosis. Loss of GPR56 also inhibited progastrin-dependent colonic crypt fission and colorectal carcinogenesis in the azoxymethane (AOM) mouse model of colorectal cancer. Overall, we found that progastrin binds to GPR56 expressing colonic stem cells, which in turn promotes their expansion, and that this GPR56-dependent pathway is an important driver and potential new target in colorectal carcinogenesis.
Biochemical, functional, and pharmacological characterization of AT-56, an orally active and selective inhibitor of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase.[Pubmed:19131342]
J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 20;284(12):7623-30.
We report here that 4-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene-1-[4-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-butyl]-piperidine (AT-56) is an orally active and selective inhibitor of lipocalin-type prostaglandin (PG) D synthase (L-PGDS). AT-56 inhibited human and mouse L-PGDSs in a concentration (3-250 microm)-dependent manner but did not affect the activities of hematopoietic PGD synthase (H-PGDS), cyclooxygenase-1 and -2, and microsomal PGE synthase-1. AT-56 inhibited the L-PGDS activity in a competitive manner against the substrate PGH(2) (K(m) = 14 microm) with a K(i) value of 75 microm but did not inhibit the binding of 13-cis-retinoic acid, a nonsubstrate lipophilic ligand, to L-PGDS. NMR titration analysis revealed that AT-56 occupied the catalytic pocket, but not the retinoid-binding pocket, of L-PGDS. AT-56 inhibited the production of PGD(2) by L-PGDS-expressing human TE-671 cells after stimulation with Ca(2+) ionophore (5 microm A23187) with an IC(50) value of about 3 microm without affecting their production of PGE(2) and PGF(2alpha) but had no effect on the PGD(2) production by H-PGDS-expressing human megakaryocytes. Orally administered AT-56 (<30 mg/kg body weight) decreased the PGD(2) production to 40% in the brain of H-PGDS-deficient mice after a stab wound injury in a dose-dependent manner without affecting the production of PGE(2) and PGF(2alpha) and also suppressed the accumulation of eosinophils and monocytes in the bronco-alveolar lavage fluid from the antigen-induced lung inflammation model of human L-PGDS-transgenic mice.


