Xanthohumol ICAS# 688360-06-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 688360-06-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 12986068 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H22O6 | M.Wt | 370.40 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
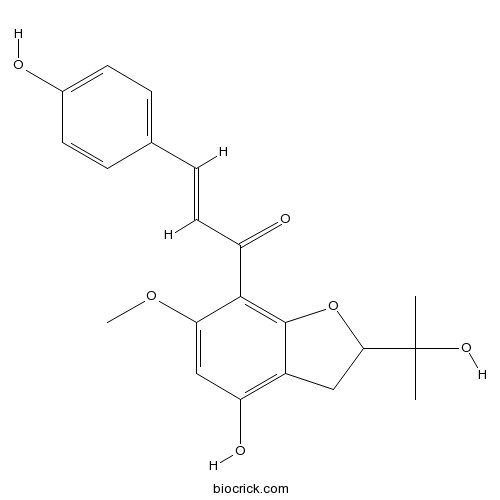
| Chemical Name | (E)-1-[4-hydroxy-2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-6-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-7-yl]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C1CC2=C(C=C(C(=C2O1)C(=O)C=CC3=CC=C(C=C3)O)OC)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PUJSPQKGZNTZCR-RMKNXTFCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H22O6/c1-21(2,25)18-10-14-16(24)11-17(26-3)19(20(14)27-18)15(23)9-6-12-4-7-13(22)8-5-12/h4-9,11,18,22,24-25H,10H2,1-3H3/b9-6+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Xanthohumol I Dilution Calculator

Xanthohumol I Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6998 mL | 13.4989 mL | 26.9978 mL | 53.9957 mL | 67.4946 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.54 mL | 2.6998 mL | 5.3996 mL | 10.7991 mL | 13.4989 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.27 mL | 1.3499 mL | 2.6998 mL | 5.3996 mL | 6.7495 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.054 mL | 0.27 mL | 0.54 mL | 1.0799 mL | 1.3499 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.027 mL | 0.135 mL | 0.27 mL | 0.54 mL | 0.6749 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- IWP 12
Catalog No.:BCC5622
CAS No.:688353-45-9
- 4-Epi-isoinuviscolide
Catalog No.:BCN4251
CAS No.:68832-39-3
- D-Prolinol(oil)
Catalog No.:BCC2708
CAS No.:68832-13-3
- Retusamine
Catalog No.:BCN2122
CAS No.:6883-16-5
- Sempervirine
Catalog No.:BCN4250
CAS No.:6882-99-1
- Sophoridine
Catalog No.:BCN4249
CAS No.:6882-68-4
- Dihydrochelerythrine
Catalog No.:BCN2273
CAS No.:6880-91-7
- Norfluorocurarine
Catalog No.:BCN4811
CAS No.:6880-54-2
- 6-Acetyl-2,2-dimethylchroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN4248
CAS No.:68799-41-7
- 4-Oxobedfordiaic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4247
CAS No.:68799-38-2
- Dipotassium glycyrrhizinate
Catalog No.:BCN8487
CAS No.:68797-35-3
- Dehydroeburicoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3646
CAS No.:6879-05-6
- Xanthohumol L
Catalog No.:BCN8017
CAS No.:688360-15-8
- Astemizole
Catalog No.:BCC7691
CAS No.:68844-77-9
- Boc-D-Tyr(Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2597
CAS No.:68856-96-2
- Fmoc-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3570
CAS No.:68858-20-8
- HMP Linker
Catalog No.:BCC2832
CAS No.:68858-21-9
- 8-O-Methylretusin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN7899
CAS No.:68862-13-5
- Otonecine
Catalog No.:BCN2009
CAS No.:6887-34-9
- Eburicol
Catalog No.:BCN4252
CAS No.:6890-88-6
- Guaiacol salicylate
Catalog No.:BCC8327
CAS No.:87-16-1
- H-D-Glu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2936
CAS No.:6893-26-1
- Kahweol
Catalog No.:BCC9006
CAS No.:6894-43-5
- SKF 91488 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6675
CAS No.:68941-21-9
Xanthohumol ameliorates 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced cellular toxicity in cultured MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells.[Pubmed:29516522]
J Appl Toxicol. 2018 Jul;38(7):1036-1046.
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is an environmental contaminant. Xanthohumol Is a prenylated flavonoid found in hops (Humulus lupulus) and beer. The aim of the current study was to explore the role of Xanthohumol In modulating the toxicity of TCDD in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. In cells treated with TCDD alone, intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations, mitochondrial membrane potential disruption, reactive oxygen species production, cardiolipin peroxidation, nitric oxide release and cytochrome P450 1A1 expression were significantly increased. TCDD treatment increased the mRNA levels of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and nuclear factor kappa B, and significantly decreased the level of protein kinase B (AKT) in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. However, the presence of xanthohumol alleviated the pathological effects of TCDD. In addition, xanthohumol treatment significantly increased the expression of genes associated with osteoblast differentiation (alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin, osteoprotegerin and osterix). We conclude that xanthohumol has a beneficial influence and may antagonize TCDD toxicity in osteoblastic cells.
Xanthohumol exerts protective effects in liver alterations associated with aging.[Pubmed:29536163]
Eur J Nutr. 2019 Mar;58(2):653-663.
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: Aging is associated with a deregulation of biological systems that lead to an increase in oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, among other effects. Xanthohumol Is the main preylated chalcone present in hops (Humulus lupulus L.) whose antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and chemopreventive properties have been shown in recent years. In the present study, the possible protective effects of xanthohumol on liver alterations associated with aging were evaluated. METHODS: Male young and old senescence-accelerated prone mice (SAMP8), aged 2 and 10 months, respectively, were divided into four groups: non-treated young, non-treated old, old treated with 1 mg/kg/day xanthohumol, and old treated with 5 mg/kg/day xanthohumol. Male senescence-accelerated resistant mice (SAMR1) were used as controls. After 30 days of treatment, animals were sacrificed and livers were collected. mRNA (AIF, BAD, BAX, Bcl-2, eNOS, HO-1, IL-1beta, NF-kappaB2, PCNA, sirtuin 1 and TNF-alpha) and protein expressions (BAD, BAX, AIF, caspase-3, Blc-2, eNOS, iNOS, TNF-alpha, IL1beta, NF-kappaB2, and IL10) were measured by RT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively. Mean values were analyzed using ANOVA. RESULTS: A significant increase in mRNA and protein levels of oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory and proliferative markers, as well as pro-apoptotic parameters was shown in old non-treated SAMP8 mice compared to the young SAMP8 group and SAMR1 mice. In general, age-related oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis were significantly decreased (p < 0.05) after XN treatment. In most cases, this effect was dose-dependent. CONCLUSIONS: XN was shown to modulate inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in aged livers, exerting a protective effect in hepatic alterations.
Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity of Minor Hops Prenylflavonoids and New Insights on Prenyl Group Cyclization.[Pubmed:29597299]
Molecules. 2018 Mar 28;23(4). pii: molecules23040776.
Synthesis of minor prenylflavonoids found in hops and their non-natural derivatives were performed. The antiproliferative activity of the obtained compounds against some human cancer cell lines was investigated. Using Xanthohumol Isolated from spent hops as a lead compound, a series of minor hop prenylflavonoids and synthetic derivatives were obtained by isomerization, cyclisation, oxidative-cyclisation, oxidation, reduction and demethylation reactions. Three human cancer cell lines-breast (MCF-7), prostate (PC-3) and colon (HT-29)-were used in antiproliferative assays, with cisplatin as a control compound. Five minor hop prenyl flavonoids and nine non-natural derivatives of xanthohumol have been synthetized. Syntheses of xanthohumol K, its dihydro- and tetrahydro-derivatives and 1'',2'',alpha,beta-tetrahydroxanthohumol C were described for the first time. All of the minor hops prenyl flavonoids exhibited strong to moderate antiproliferative activity in vitro. The minor hops flavonoids xanthohumol C and 1'',2''-dihydroxanthohumol K and non-natural 2,3-dehydroisoxanthohumol exhibited the activity comparable to cisplatin. Results described in the article suggest that flavonoids containing chromane- and chromene-like moieties, especially chalcones, are potent antiproliferative agents. The developed new efficient, regioselective cyclisation reaction of the xanthohumol prenyl group to 1'',2''-dihydroxantohumol K may be used in the synthesis of other compounds with the chromane moiety.


