Achyranthes bidentata
Achyranthes bidentata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
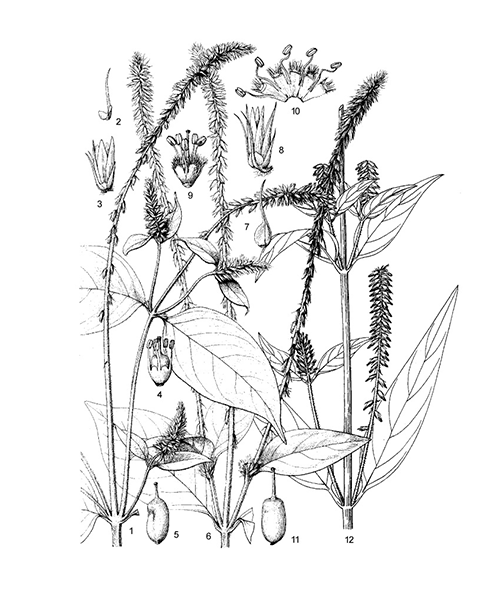

Natural products/compounds from Achyranthes bidentata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
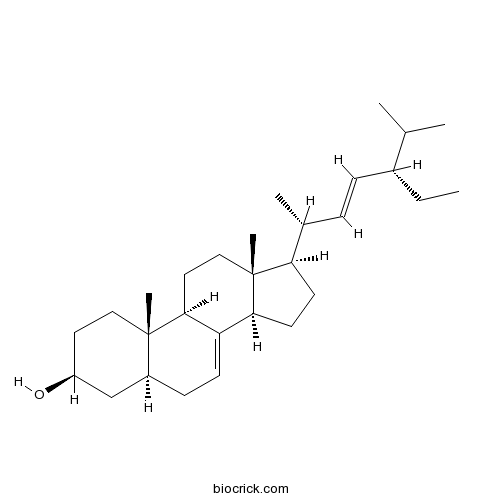
BCN5564
alpha-Spinasterol481-18-5
Instructions
-
BCN5567
Chrysophanol481-74-3
Instructions

-
BCN5616
Oleanolic acid508-02-1
Instructions

-
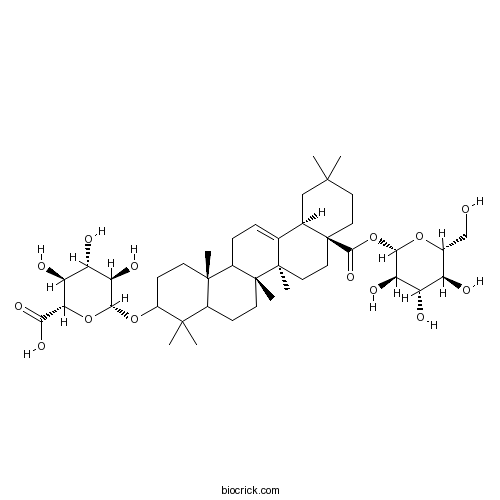
BCN3432
Chikusetsusaponin IVa51415-02-2
Instructions
-
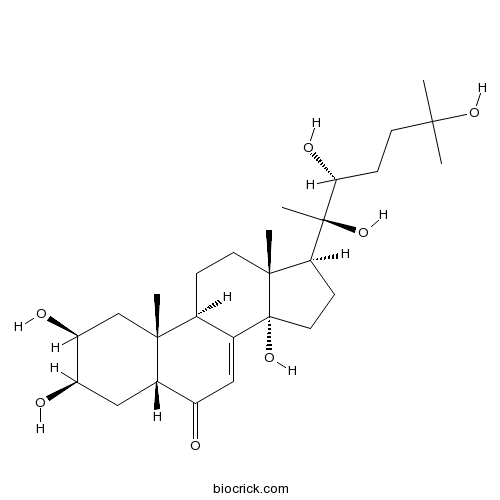
BCN5688
20-Hydroxyecdysone5289-74-7
Instructions
-
BCN1206
Palmitic acid57-10-3
Instructions

-
BCN8528
D-Galactose59-23-4
Instructions

-
BCN4213
N-trans-Feruloyltyramine66648-43-9
Instructions

-
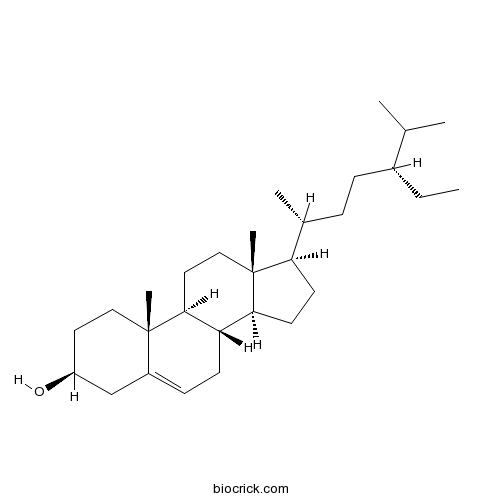
BCN1015
Beta-Sitosterol83-46-5
Instructions
-
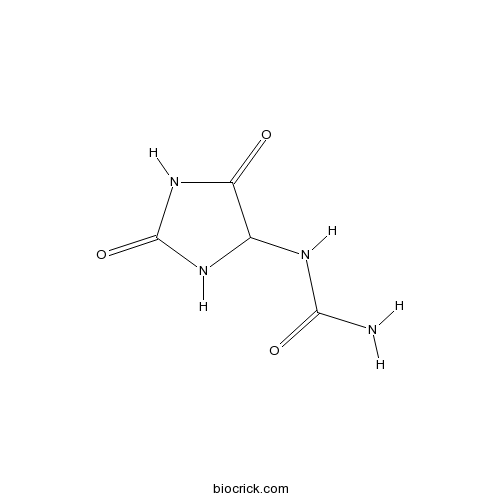
BCN4527
Allantoin97-59-6
Instructions
Intervention and effect analysis of Achyranthes bidentata blume combined with aerobic exercise to interfere with type 2 diabetes.[Pubmed: 29737299]
With the continuous progress of traditional Chinese medicine extraction technology in recent years, the active components of traditional Chinese medicine have been continuously extracted and analyzed. In this paper, the authors studied the effect of aerobic exercise combined with the extract of the Achyranthes bidentata on the serum indexes of T2DM rats. Through systematic analysis of measurement indexes of Chinese medicine treatment group, we found that all indexes of FPG, INS, NOXs, ROS and SOD all showed a marked improvement, which fully proved the effect of Achyranthes bidentata extract on improving the condition of rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this experiment, we can see that aerobic exercise can relieve diabetic patients' condition by comparing and analyzing various indexes of type II diabetes in experimental rats. At the same time, the effect of the combination of aerobic exercise and the extract of Achyranthes bidentata is obviously better than that of the extract of pure Achyranthes bidentata.
Intervention and effect analysis of Achyranthes bidentata blume combined with aerobic exercise to interfere with type 2 diabetes.[Pubmed: 29735466]
With the continuous progress of traditional Chinese medicine extraction technology in recent years, the active components of traditional Chinese medicine have been continuously extracted and analyzed. In this paper, the authors studied the effect of aerobic exercise combined with the extract of the Achyranthes bidentata on the serum indexes of T2DM rats. Through systematic analysis of measurement indexes of Chinese medicine treatment group, we found that all indexes of FPG, INS, NOXs, ROS and SOD all showed a marked improvement, which fully proved the effect of Achyranthes bidentata extract on improving the condition of rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this experiment, we can see that aerobic exercise can relieve diabetic patients' condition by comparing and analyzing various indexes of type II diabetes in experimental rats. At the same time, the effect of the combination of aerobic exercise and the extract of Achyranthes bidentata is obviously better than that of the extract of pure Achyranthes bidentata.
[Allele-specific PCR to identification of Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix and Cyathulae Radix formula granules].[Pubmed: 29676092]
To establish a robust and accuracy molecular method to identify Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix and Cyathulae Radix formula granules. ITS sequences of Achyranthes bidentata and Cyathula officinalis were aligned, specific SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) were excavated, specific primers were designed and allele-specific PCR method was established. The genomic DNA was successfully extracted from the herbal medicine and its formula granules by using an improved CTAB (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide) method and then performed PCR with the designed primers. The 187 bp specific band could be amplified only in the presentation of C. officinalis and its granules when use of C. officinalis specific primers, whereas the 162 bp band could be amplified only in the presentation of A. bidentata and its granules when use of A. bidentata specific primers. This method was also successfully applied in the identification of commercial formula granules.
Quantitative Analysis of Multi-components by Single Marker and Fingerprint Analysis of Achyranthes bidentata Blume.[Pubmed: 29659734]
A simple and effective method of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with diode array detection was established to identify the origin of Achyranthes bidentata Blume and evaluate its quality, based on chromatographic fingerprint combined with the similarity analysis, hierarchical cluster analysis and the quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker (QAMS). In the chromatographic fingerprint, 16 peaks were selected as the common model to evaluate the similarities among 18 batches (S1-S18) of A. bidentata Blume samples collected from different origins in China. The similarities values for 18 batches of samples were more than 0.75, which compared with control fingerprint. Furthermore, 18 batches of A. bidentata Blume samples were categorized into two groups for quantitative analysis, the quantification of three bioactive constituents (β-ecdysterone, cyasterone and 5-hydroxymethyl furfural) between QAMS and external standard method proved the consistency of the two methods, the three constituents showed good regression (R > 0.9995) within linear ranges, and their recoveries were within the range of 97.6-101.5%. This study demonstrated that the quality of A. bidentata Blume can be successfully evaluated by means of a combination of HPLC chromatographic fingerprint and QAMS approach.
Anti-osteoporosis activity of a novel Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide via stimulating bone formation.[Pubmed: 29352921]
Achyranthes bidentata is an important Traditional Chinese Medicine for the treatment of osteoporosis. In this study, A. bidentata polysaccharide (ABPB), which was extracted with alkali from the root of A. bidentata at room temperature, significantly increased the bone mineral density, bone mineral content, trabecular thickness, trabecular number and biomechanical properties of ovariectomized (OVX) rats, indicating that ABPB had prominent curative effects on osteoporosis in OVX rats. A novel polysaccharide (ABPB-3) was purified from ABPB, and its structure was characterized as a repeating unit consisting of →4)-α-d-GalpA-(1→, →2,4)-α-l-Rhap-(1→, →5)-α-l-Araf-(1→, →2,3,5)-α-l-Araf-(1→, →3)-β-d-Galp-(1→, →3,4,6)-β-d-Galp-(1→, terminated with α-l-Araf, α-l-Rhap and β-d-Galp. Up to now, there were no literature reports relevant to the structure of ABPB-3. In the zebrafish model of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIOP), ABPB-3 significantly increased the relative fluorescence intensity of the skull bone mass in a concentration-dependent manner, indicating that it stimulated bone formation activity. Thus, ABPB and ABPB-3 have the potential to be used for the anti-osteoporosis medicine.
Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide suppresses osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via inhibiting RANKL signaling.[Pubmed: 29345352]
Osteoclasts are highly differentiated multinucleated giant cells that play fundamental roles in bone resorption and in the pathogenesis of osteolytic conditions, such as osteoporosis and cancer-induced bone loss. Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide (ABP) is a hydrophilic compound with anti-oxidation and anti-aging characteristics. The impact of ABP on RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption has not been assessed, hence, in this study we investigated the effect of ABP on osteoclast formation and resorption in murine bone marrow derived osteoclasts. We found that ABP was able to suppress RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity at concentrations above 6.5 µM, while demonstrating no cytotoxicity at concentrations up to 10 µM. The actions of ABP were mediated through inhibition of RANKL-induced c-Fos and NFATc1 gene and protein expression. Furthermore, we found that ABP suppressed NFATc1 transcriptional activity, and the phosphorylation of MAPK pathways induced by RANKL. Collectively, ABP attenuates RANKL-mediated osteoclast activity and signaling, and might serve as a potential therapeutic candidate for preventing bone loss related diseases.


