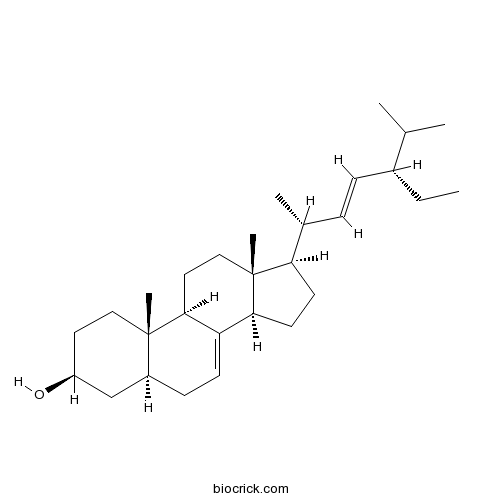
alpha-SpinasterolTRPV1 antagonist; active in vivo CAS# 481-18-5 |
- Dihydroberberine
Catalog No.:BCN2573
CAS No.:483-15-8
- Sesamolin
Catalog No.:BCN1289
CAS No.:526-07-8
- Carnosol
Catalog No.:BCN1055
CAS No.:5957-80-2
- Harpagide
Catalog No.:BCN4996
CAS No.:6926-08-5
- Levistilide A
Catalog No.:BCN1197
CAS No.:88182-33-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 481-18-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281331 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C29H48O | M.Wt | 412.7 |
| Type of Compound | Steroids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Bessisterol; Hitodesterol; 5α-Stigmasta 7,22-dien 3β-ol | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in ethanol with gentle warming | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S,5S,9R,10S,13R,14R,17R)-17-[(E,2R,5S)-5-ethyl-6-methylhept-3-en-2-yl]-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C=CC(C)C1CCC2C1(CCC3C2=CCC4C3(CCC(C4)O)C)C)C(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JZVFJDZBLUFKCA-FXIAWGAOSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Alpha-Spinasterol is a novel efficacious and safe antagonist of the TRPV1 receptor with anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects.Alpha-Spinasterol has a significant therapeutic potential to modulate the development and/or progression of diabetic nephropathy. It also can prevent TP-induced prostatic hyperplasia and may be beneficial in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. |
| Targets | TRPV | HMG-CoA reductase |
| In vivo | α-Spinasterol from Melandrium firmum attenuates benign prostatic hyperplasia in a rat model.[Pubmed: 24682042]Mol Med Rep. 2014 Jun;9(6):2362-6.Spinasterol, a biologically active compound, exhibits a number of pharmacological activities, including antitumor, antiulcerogenic and anticarcinogenic activity, and originates from the aerial parts of Aster scaber Thunb (Asteraceae). The present study investigated whether alpha-Spinasterol isolated from Melandrium firmum Rohrbach could prevent benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) induced by testosterone propionate (TP) in rats. Anti-inflammatory action of hydroalcoholic extract, dichloromethane fraction and steroid α-spinasterol from Polygala sabulosa in LPS-induced peritonitis in mice.[Pubmed: 24161429]J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):144-50.Polygala sabulosa A. W. Bennett is a small herb popularly known as "timutu-pinheirinho" that is widely distributed in southern Brazil and that is used to treat disorders of the bowel and kidney and as a topical anesthetic and expectorant in folk medicine. This study was designed to investigate the anti-inflammatory properties of the hydroalcoholic extract (HEPs), CH2Cl2 fraction and the steroid α-spinasterol obtained from the aerial parts of Polygala sabulosa in a model of acute inflammation induced by intraperitoneal injection of bacterial lipopolysaccharide in mice.
alpha-Spinasterol isolated from the root of Phytolacca americana and its pharmacological property on diabetic nephropathy.[Pubmed: 15326549 ]Planta Med. 2004 Aug;70(8):736-9.
|
| Kinase Assay | Identification of the plant steroid α-spinasterol as a novel transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 antagonist with antinociceptive properties.[Pubmed: 22837009]J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Nov;343(2):258-69.The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor is relevant to the perception of noxious information and has been studied as a therapeutic target for the development of new analgesics. The goal of this study was to perform in vivo and in vitro screens to identify novel, efficacious, and safe TRPV1 antagonists isolated from leaves of the medicinal plant Vernonia tweedieana Baker. |
| Animal Research | α-Spinasterol, a TRPV1 receptor antagonist, elevates the seizure threshold in three acute seizure tests in mice.[Pubmed: 25764210]J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015 Sep;122(9):1239-47.alpha-Spinasterol is a plant-derived compound which was reported to act as a selective antagonist for the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor. Several studies revealed that the TRPV1 receptors might modulate seizure activity in animal models of seizures and epilepsy. |

alpha-Spinasterol Dilution Calculator

alpha-Spinasterol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4231 mL | 12.1153 mL | 24.2307 mL | 48.4614 mL | 60.5767 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4846 mL | 2.4231 mL | 4.8461 mL | 9.6923 mL | 12.1153 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2423 mL | 1.2115 mL | 2.4231 mL | 4.8461 mL | 6.0577 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0485 mL | 0.2423 mL | 0.4846 mL | 0.9692 mL | 1.2115 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0242 mL | 0.1212 mL | 0.2423 mL | 0.4846 mL | 0.6058 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Alpha-Santonin
Catalog No.:BCN7828
CAS No.:481-06-1
- Edoxaban tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC1544
CAS No.:480449-71-6
- Edoxaban
Catalog No.:BCC1543
CAS No.:480449-70-5
- Lucialdehyde B
Catalog No.:BCN2450
CAS No.:480439-84-7
- TFB-TBOA
Catalog No.:BCC5919
CAS No.:480439-73-4
- Carbenicillin, Disodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCC1200
CAS No.:4800-94-6
- Benzofuroxan
Catalog No.:BCC8852
CAS No.:480-96-6
- Dicrotaline
Catalog No.:BCN2079
CAS No.:480-87-5
- Retusine
Catalog No.:BCN2123
CAS No.:480-86-4
- Retronecine
Catalog No.:BCN2034
CAS No.:480-85-3
- Echinatine
Catalog No.:BCN1968
CAS No.:480-83-1
- Indicine
Catalog No.:BCN1995
CAS No.:480-82-0
- Epiandrosterone
Catalog No.:BCC4481
CAS No.:481-29-8
- Ecgonine
Catalog No.:BCN1907
CAS No.:481-37-8
- Juglone
Catalog No.:BCN2639
CAS No.:481-39-0
- Plumbagin
Catalog No.:BCN2586
CAS No.:481-42-5
- Ginkgetin
Catalog No.:BCN2319
CAS No.:481-46-9
- Cepharanthine
Catalog No.:BCN5393
CAS No.:481-49-2
- Tangeretin
Catalog No.:BCN2386
CAS No.:481-53-8
- Aloeemodin
Catalog No.:BCN5565
CAS No.:481-72-1
- Citreorosein
Catalog No.:BCN5566
CAS No.:481-73-2
- Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCN5567
CAS No.:481-74-3
- Estriol 3-sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2236
CAS No.:481-95-8
- Homoferreirin
Catalog No.:BCN4765
CAS No.:482-01-9
alpha-Spinasterol isolated from the root of Phytolacca americana and its pharmacological property on diabetic nephropathy.[Pubmed:15326549]
Planta Med. 2004 Aug;70(8):736-9.
Based on an inhibitory activity-guided fractionation for the high glucose-induced proliferation of glomerular mesangial cells (GMCs), chloroform extracts of the roots of Phytolacca americana were found to contain alpha-Spinasterol (C (29)H (48)O), a delta (7)-sterol. This phytosterol proved to be a potent inhibitor (IC (50) = 3.9 x 10 (-12) g/mL, 9.5 pmol/L) of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation caused by high-ambient glucose (5.6 mM vs. 25 mM), and its inhibitory potency was about 1,000 times higher than that of simvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor used as a positive control. alpha-Spinasterol also significantly reduced the increases of serum triglycerides, renal weight and urinary protein excretion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, and these were comparable to the results observed in insulin-treated diabetic mice. Therefore, the results obtained in this study suggest that alpha-Spinasterol has a significant therapeutic potential to modulate the development and/or progression of diabetic nephropathy.
Anti-inflammatory action of hydroalcoholic extract, dichloromethane fraction and steroid alpha-spinasterol from Polygala sabulosa in LPS-induced peritonitis in mice.[Pubmed:24161429]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):144-50.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Polygala sabulosa A. W. Bennett is a small herb popularly known as "timutu-pinheirinho" that is widely distributed in southern Brazil and that is used to treat disorders of the bowel and kidney and as a topical anesthetic and expectorant in folk medicine. This study was designed to investigate the anti-inflammatory properties of the hydroalcoholic extract (HEPs), CH2Cl2 fraction and the steroid alpha-Spinasterol obtained from the aerial parts of Polygala sabulosa in a model of acute inflammation induced by intraperitoneal injection of bacterial lipopolysaccharide in mice. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The anti-inflammatory effect of HEPs (3-300 mg/kg, i.g.), CH2Cl2 fraction (0.003-30 mg/kg, i.g.) and steroid alpha-Spinasterol (0.001-1mg/kg, i.p. or 1-10mg/kg, i.g.), were evaluated in mice subjected to the acute inflammation caused by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 0.02 microg/kg). The anti-inflammatory activity of the HEPs, CH2Cl2 fraction and steroid were assessed by determining the total numbers of leukocytes and differential cell counts (neutrophils and mononuclear cells) and levels of pro-inflammatory (IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6) or anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines in peritoneal fluid. RESULTS: The administration of HEPs (3-300 mg/kg, i.g.) completely inhibited inflammatory cell infiltration (300 mg/kg, i.g.) and it reduced TNF-alpha (100-300 mg/kg) and IL-1beta (100mg/kg) levels in LPS-injected mice. Furthermore, the administration of CH2Cl2 fraction (0.003-30 mg/kg, i.g.) or alpha-Spinasterol (0.001-10mg/kg, by i.p. or i.g.) significantly reduces inflammatory cell infiltration in LPS-injected mice. Moreover, dexamethasone (0.5mg/kg, i.p., used as a positive control) inhibited inflammatory cell infiltration and reduced the levels of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 in LPS-injected mice. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together, these results provide the first experimental evidence demonstrating that HEPs have significant anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced inflammation. These effects appear to be, at least in part, due to the presence of alpha-Spinasterol. These findings support the widespread use of Polygala sabulosa in popular medicine and demonstrate that this plant has therapeutic potential for the development of phytomedicines with anti-inflammatory properties.
alpha-Spinasterol, a TRPV1 receptor antagonist, elevates the seizure threshold in three acute seizure tests in mice.[Pubmed:25764210]
J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015 Sep;122(9):1239-47.
alpha-Spinasterol is a plant-derived compound which was reported to act as a selective antagonist for the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor. Several studies revealed that the TRPV1 receptors might modulate seizure activity in animal models of seizures and epilepsy. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of alpha-Spinasterol on the seizure threshold in three acute models of seizures, i.e., in the intravenous (i.v.) pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) seizure test, in the maximal electroshock seizure threshold (MEST) test and in the model of psychomotor seizures induced by 6 Hz stimulation in mice. Our results revealed significant anticonvulsant effect of alpha-Spinasterol in all the used seizure tests. In the i.v. PTZ test, statistically significant elevation was noted in case of the threshold for myoclonic twitches (doses of 0.1-1 mg/kg) and generalized clonus seizures (doses of 0.5 and 1 mg/kg) but not for tonic seizures. The studied TRPV1 antagonist also increased the threshold for tonic hindlimb extension in the MEST (doses of 0.5 and 1 mg/kg) and 6 Hz psychomotor seizure (doses of 0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg) tests in mice. Furthermore, alpha-Spinasterol did not produce any significant impairment of motor coordination (assessed in the chimney test) and muscular strength (investigated in the grip-strength test) and it did not provoke significant changes in body temperature in mice. Based on the results of our study and the fact that alpha-Spinasterol is characterized by good blood-brain permeability, we postulate further investigation of this compound to precisely evaluate mechanism of its anticonvulsant action and opportunity of its usage in clinical practice.
alpha-Spinasterol from Melandrium firmum attenuates benign prostatic hyperplasia in a rat model.[Pubmed:24682042]
Mol Med Rep. 2014 Jun;9(6):2362-6.
Spinasterol, a biologically active compound, exhibits a number of pharmacological activities, including antitumor, antiulcerogenic and anticarcinogenic activity, and originates from the aerial parts of Aster scaber Thunb (Asteraceae). The present study investigated whether alpha-Spinasterol isolated from Melandrium firmum Rohrbach could prevent benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) induced by testosterone propionate (TP) in rats. Male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups of eight rats following castration. A negative control group received subcutaneous injections of corn oil. Treatments were administered orally 1 h prior to TP injection. All the rats were sacrificed at the scheduled termination time and their prostates were removed, cleaned and weighed. The prostate size ratio (prostate weight/rat body weight) was then calculated. Additional histopathological examinations were conducted, and the levels of TP and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the serum and prostate were measured. TP significantly increased the prostate size ratio (P<0.01), and DHT and testosterone levels in the serum and prostate. The TP-induced increase was significantly inhibited in alpha-Spinasterol-treated rats when compared with the negative controls (P<0.05). In addition, histopathological examination demonstrated that alpha-Spinasterol treatment suppressed TP-induced prostatic hyperplasia. It is concluded that alpha-Spinasterol can prevent TP-induced prostatic hyperplasia and may be beneficial in the management of BPH.
Identification of the plant steroid alpha-spinasterol as a novel transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 antagonist with antinociceptive properties.[Pubmed:22837009]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Nov;343(2):258-69.
The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor is relevant to the perception of noxious information and has been studied as a therapeutic target for the development of new analgesics. The goal of this study was to perform in vivo and in vitro screens to identify novel, efficacious, and safe TRPV1 antagonists isolated from leaves of the medicinal plant Vernonia tweedieana Baker. All of the fractions and the hydroalcoholic extract produced antinociception in mice during the capsaicin test, but the dichloromethane fraction also had antioedematogenic effect. Among the compounds isolated from the dichloromethane fraction, only alpha-Spinasterol reduced the nociception and edema induced by capsaicin injection. Moreover, alpha-Spinasterol demonstrated good oral absorption and high penetration into the brain and spinal cord of mice. alpha-Spinasterol was able to displace [3H]resiniferatoxin binding and diminish calcium influx mediated by capsaicin. Oral administration of the dichloromethane fraction and alpha-Spinasterol also produced antinociceptive effect in the noxious heat-induced nociception test; however, they did not change the mechanical threshold of naive mice. The treatment with alpha-Spinasterol did not produce antinociceptive effect in mice systemically pretreated with resiniferatoxin. In addition, alpha-Spinasterol and the dichloromethane fraction reduced the edema, mechanical, and heat hyperalgesia elicited by complete Freund's adjuvant paw injection. The dichloromethane fraction and alpha-Spinasterol did not affect body temperature or locomotor activity. In conclusion, alpha-Spinasterol is a novel efficacious and safe antagonist of the TRPV1 receptor with antinociceptive effect.


