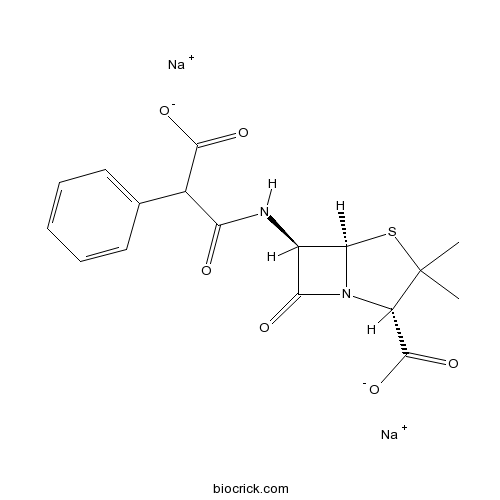
Carbenicillin, Disodium SaltInhibits the cell-wall synthesis,antibiotic CAS# 4800-94-6 |
- Baicalein
Catalog No.:BCN5599
CAS No.:491-67-8
- Luteolin
Catalog No.:BCN5600
CAS No.:491-70-3
- Chloroquine diphosphate
Catalog No.:BCC3915
CAS No.:50-63-5
- Apigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5658
CAS No.:520-36-5
- Vitamin D3
Catalog No.:BCN2186
CAS No.:67-97-0
- D-64131
Catalog No.:BCC1510
CAS No.:74588-78-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 4800-94-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 20933 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H16N2O6SNa2 | M.Wt | 422.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Sodium carbenicillin | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 125 mg/mL (295.96 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 62.5 mg/mL (147.98 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | disodium;(2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2-carboxylato-2-phenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C(N2C(S1)C(C2=O)NC(=O)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)[O-])C(=O)[O-])C.[Na+].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RTYJTGSCYUUYAL-YCAHSCEMSA-L | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H18N2O6S.2Na/c1-17(2)11(16(24)25)19-13(21)10(14(19)26-17)18-12(20)9(15(22)23)8-6-4-3-5-7-8;;/h3-7,9-11,14H,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23)(H,24,25);;/q;2*+1/p-2/t9?,10-,11+,14-;;/m1../s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Antibiotic. Selection reagent for AMPR transformed cells. |

Carbenicillin, Disodium Salt Dilution Calculator

Carbenicillin, Disodium Salt Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3674 mL | 11.8371 mL | 23.6742 mL | 47.3485 mL | 59.1856 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4735 mL | 2.3674 mL | 4.7348 mL | 9.4697 mL | 11.8371 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2367 mL | 1.1837 mL | 2.3674 mL | 4.7348 mL | 5.9186 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0473 mL | 0.2367 mL | 0.4735 mL | 0.947 mL | 1.1837 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0237 mL | 0.1184 mL | 0.2367 mL | 0.4735 mL | 0.5919 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Carbenicillin inhibits the cell-wall synthesis (peptidoglycan cross-linking) by inactivating transpeptidase on the inner surface of the bacterial cell membrane. Carbenicillin is a white to slightly yellow, hygroscopic powder soluble in water and in alcohol. Carbenicillin is most effective against gram-negative bacteria but may also have some effect against gram-positive bacteria. Aqueous solutions of Carbenicillin are stable for 24 hours at room temperature and up to 72 hours when stored at 0-5°C. Carbenicillin is recommended for use in place of ampicillin to maintain the selective marker bla (b-lactamase or ampicillin resistance) Carbenicillin is soluble in water and alcohol at 50mg/ml. Recommended working concentrations up to 500µg/ml antibiotic keep dry store at 4°C, warm to room temperature before opening Carbenicillin is a white to slightly yellow, hygroscopic powder soluble in water and in alcohol. Carbenicillin is most effective against gram-negative bacteria but may also have some effect against gram-positive bacteria. Aqueous solutions of Carbenicillin are stable for 24 hours at room temperature and up to 72 hours when stored at 0-5°C. Carbenicillin is recommended for use in place of ampicillin to maintain the selective marker bla (b-lactamase or ampicillin resistance) Carbenicillin is soluble in water and alcohol at 50mg/ml. Recommended working concentrations up to 500µg/ml antibiotic keep dry store at 4°C, warm to room temperature before opening
- Benzofuroxan
Catalog No.:BCC8852
CAS No.:480-96-6
- Dicrotaline
Catalog No.:BCN2079
CAS No.:480-87-5
- Retusine
Catalog No.:BCN2123
CAS No.:480-86-4
- Retronecine
Catalog No.:BCN2034
CAS No.:480-85-3
- Echinatine
Catalog No.:BCN1968
CAS No.:480-83-1
- Indicine
Catalog No.:BCN1995
CAS No.:480-82-0
- Seneciphylline
Catalog No.:BCN5563
CAS No.:480-81-9
- Integerrimine
Catalog No.:BCN2131
CAS No.:480-79-5
- Platyphylline
Catalog No.:BCN2115
CAS No.:480-78-4
- Jacoline
Catalog No.:BCN2088
CAS No.:480-76-2
- Jaconine
Catalog No.:BCN2089
CAS No.:480-75-1
- 2',4',6'-Trihydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3996
CAS No.:480-66-0
- TFB-TBOA
Catalog No.:BCC5919
CAS No.:480439-73-4
- Lucialdehyde B
Catalog No.:BCN2450
CAS No.:480439-84-7
- Edoxaban
Catalog No.:BCC1543
CAS No.:480449-70-5
- Edoxaban tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC1544
CAS No.:480449-71-6
- Alpha-Santonin
Catalog No.:BCN7828
CAS No.:481-06-1
- alpha-Spinasterol
Catalog No.:BCN5564
CAS No.:481-18-5
- Epiandrosterone
Catalog No.:BCC4481
CAS No.:481-29-8
- Ecgonine
Catalog No.:BCN1907
CAS No.:481-37-8
- Juglone
Catalog No.:BCN2639
CAS No.:481-39-0
- Plumbagin
Catalog No.:BCN2586
CAS No.:481-42-5
- Ginkgetin
Catalog No.:BCN2319
CAS No.:481-46-9
- Cepharanthine
Catalog No.:BCN5393
CAS No.:481-49-2
The behavior of carbenicillin as a nonreabsorbable anion.[Pubmed:239076]
J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Aug;86(2):183-94.
In order to study the mechanism of hypokalemic alkalosis which occurs in some patients being treated with disodium carbenicillin, renal clearance experiments were carried out in rats and observations were made on electrical changes in isolated toad bladders. In rats maintained on a sodium-free diet, intravenous infusion of carbenicillin at 40 mg. per hour resuited in an immediate diuresis characterized by a striking increase in K and NH4 excretion, and progressive acidification of the urine. In a control group of rats, also prepared with a sodium free diet, intravenous infusion of mannitol resulted in a comparable diuresis, but no significant changes in K and NH4 excretion, and no acidification of the urine. The urinary changes in the carbenicillin-treated rats could not be accounted for by any alterations in blood electrolytes, acid-base values, or glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Isonatric, isohydric substitution of carbenicillin for chloride in the mucosal bathing media of toad bladders mounted in Ussing chambers resulted in a reversible increase in electrical potential (PD) and resistance (R) without a comparable change in short-circuit current (SCC). Substitution in the serosal medium resulted in a reversal of polarity of PD and SCC in 4 of 9 experiments, a finding best explained by more rapid movement of chloride from M leads to S than carbenicillin movement from S leads to M (a chloride diffusion potential). The observations in both the rat and toad bladder experiments are consistent with the view that carbenicillin behaves as a nonreabsorbable anion. Hypokalemic alkalosis in patients receiving this drug can thus be attributed to increased electrical negativity of the distal nephron with subsequent enhancement of K and H secretion.
Compatibility of verapamil hydrochloride with penicillin admixtures during simulated Y-site injection.[Pubmed:3348228]
Am J Hosp Pharm. 1988 Jan;45(1):142-5.
The compatibility of verapamil hydrochloride during simulated Y-site injection with i.v. admixtures containing 11 different penicillins was studied. Admixtures of penicillin G potassium (62.5 mg/mL), nafcillin sodium (40 mg/mL), oxacillin sodium (40 mg/mL), ampicillin sodium (40 mg/mL), carbenicillin disodium (40 mg/mL), methicillin sodium (40 mg/mL), ticarcillin sodium (40 mg/mL), azlocillin sodium (40 mg/mL), mezlocillin sodium (40 mg/mL), piperacillin sodium (40 mg/mL), and amdinocillin (20 mg/mL) were prepared in both 5% dextrose injection and 0.9% sodium chloride injection in minibags. Verapamil hydrochloride injection 4 mL (10 mg) was then added to each admixture, and the admixtures were examined macroscopically and microscopically for precipitate immediately and at 15 minutes and 24 hours after mixing. To simulate Y-site injection of verapamil, verapamil hydrochloride injection 1 mL (2.5 mg) was added to 1 mL of each penicillin admixture in a test tube. For admixtures in which precipitates formed, the pH was recorded before and after verapamil was added to the admixtures. Loss of verapamil hydrochloride when mixed with the penicillin admixtures was determined using reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Addition of verapamil hydrochloride to admixtures containing nafcillin sodium, oxacillin sodium, ampicillin sodium, and mezlocillin sodium resulted in substantial loss of verapamil hydrochloride. The results for the Y-site injection study showed visible precipitation with the same penicillin admixtures. Because a precipitate formed when verapamil hydrochloride was added to nafcillin sodium, oxacillin sodium, ampicillin sodium, or mezlocillin sodium in the diluents studied, we recommended that verapamil hydrochloride be administered separately or that the i.v. tubing be flushed thoroughly before and after this drug is administered through a Y-injection site with these penicillin admixtures.
Model of the deposition of aerosol particles in the respiratory tract of the rat. II. Hygroscopic particle deposition.[Pubmed:23550602]
J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2013 Apr;26(2):101-19.
BACKGROUND: Rats are frequently used to study the pharmacological and toxicological effects of inhaled aerosol particles. The deposition behavior of aerosol particles in airways is affected by their hygroscopic properties, which accordingly influence the results of such studies. METHOD: A recently published nonhygroscopic aerosol particle deposition model for rat airways was extended with equations for hygroscopic particle growth in humid air and with a model to mimic the temperature and relative humidity conditions in the rat airways transformed from the upper human airways. As there are no experimental data available for hygroscopic deposition in rat lungs, several model assumptions were made for the humidity distribution in the upper rat airways. RESULTS: The total and regional deposition probability of salt particles in the diameter range 0.02 to 5 mum in rat lung was significantly changed by the hygroscopic properties. The maximum ratios of the total deposition of inhaled initially dry sodium chloride, cobalt chloride, and zinc sulfate particles compared with nonhygroscopic particles were 3.28, 2.44, and 2.13, respectively, and the minimum ratios 0.57, 0.63, and 0.70, respectively. The corresponding maximum (and minimum) ratios for the hygroscopic drugs histamine dihydrochloride, carbenicillin disodium, and atropine sulfate were 1.86 (0.65), 1.53 (0.70), and 1.35 (0.76), respectively. Total deposition was about 20% higher in human airways than in rat airways. The flow regime in the rat upper airways influenced total and regional deposition much less than it did in human airways. CONCLUSION: The hygroscopicity of salt and drug aerosol particles is an important factor in rat lung deposition.
Hypokalemic, metabolic alkalosis induced by high-dose ampicillin sodium.[Pubmed:326044]
Am J Hosp Pharm. 1977 May;34(5):528-31.
A case of hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis precipitated by high-dose intravenous ampicillin sodium is discussed. Cases of hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis attributable to ampicillin sodium have not been reported previously. There have been reports of this phenomenon associated with high doses of penicillin sodium and carbenicillin disodium. The possible mechanism of antibiotic-induced hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis is discussed. It is suggested that most cases of antibiotic-induced hypokalemia respond to oral or intravenous potassium chloride.
Hypokalemia associated with antibiotic treatment. Evidence in children with malignant neoplasms.[Pubmed:1067752]
Am J Dis Child. 1976 Oct;130(10):1104-8.
A patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia developed hypokalemia during two separate courses of antibiotic therapy. In a review of 33 children from our institution with various malignant neoplasms, 24 of 48 antibiotic courses were associated with hypokalemia that could not be explained by gastrointestinal fluid losses. Carbenicillin disodium, gentamicin sulfate, and methicillin sodium or nafcillin sodium combination therapy was associated with hypokalemia in 23 of 35 courses in which serum electrolytes were monitored. No correlation between hypokalemia and the stage of the basic disease or the use of antineoplastic agents was found with this antibiotic combination. Our data and a review of the literature suggest that carbenicillin produces hypokalemia through an impermeant anion effect on the renal tubule. Children receiving carbenicillin should be monitored with frequent serum potassium determinations.


