Paeonia suffruticosa
Paeonia suffruticosa
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
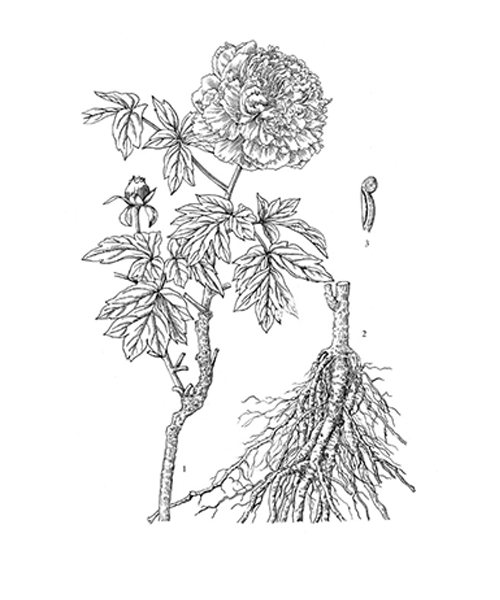

Natural products/compounds from Paeonia suffruticosa
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2801
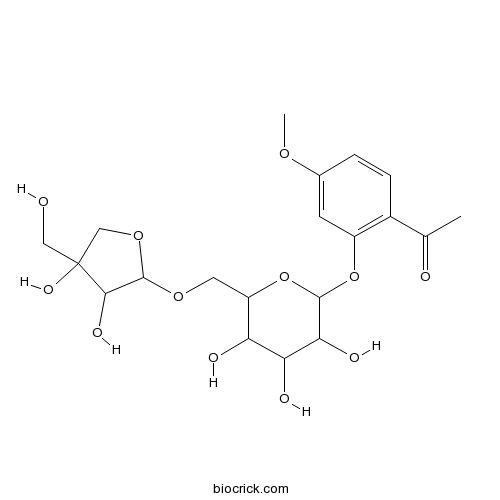
Apiopaeonoside100291-86-9
Instructions
-
BCN7159
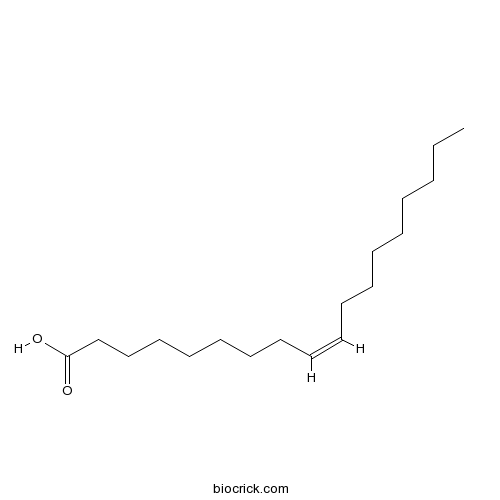
Oleic acid112-80-1
Instructions
-
BCN2941
6'-O-Galloyl paeoniflorin122965-41-7
Instructions

-
BCN1668
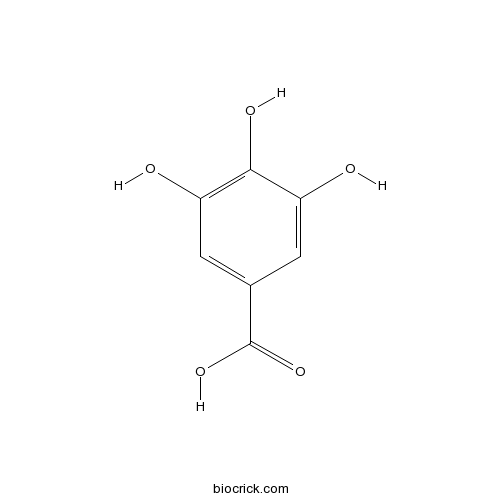
Gallic acid149-91-7
Instructions
-
BCN1688
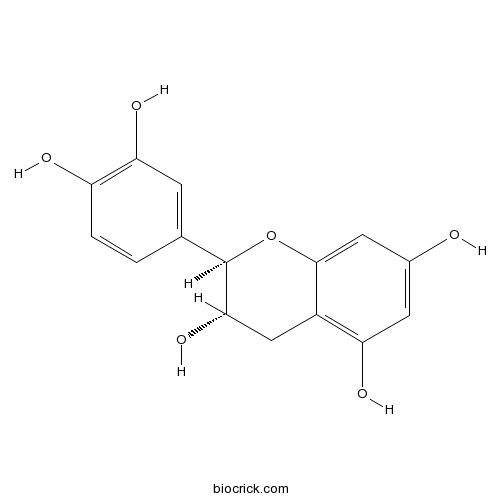
Catechin154-23-4
Instructions
-
BCN2798
Mudanpioside C172760-03-1
Instructions
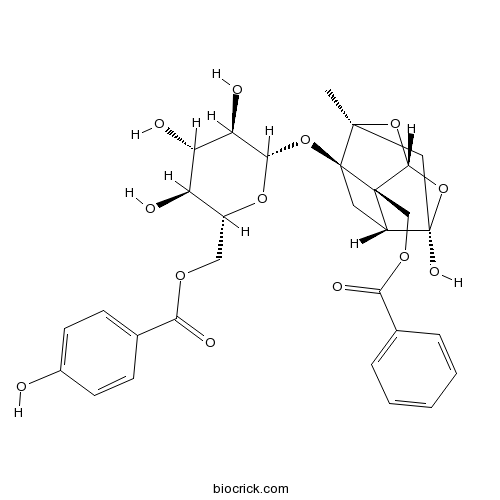
-
BCN6301
Paeoniflorin23180-57-6
Instructions

-
BCN6293
Benzoylpaeoniflorin38642-49-8
Instructions
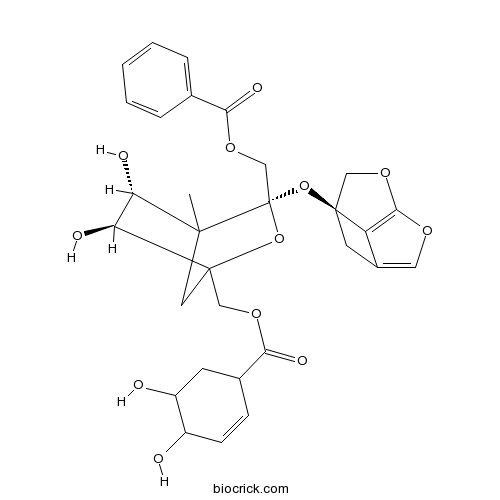
-
BCN6346
Oxypaeoniflorin39011-91-1
Instructions

-
BCN8319
alpha-Linolenic acid463-40-1
Instructions
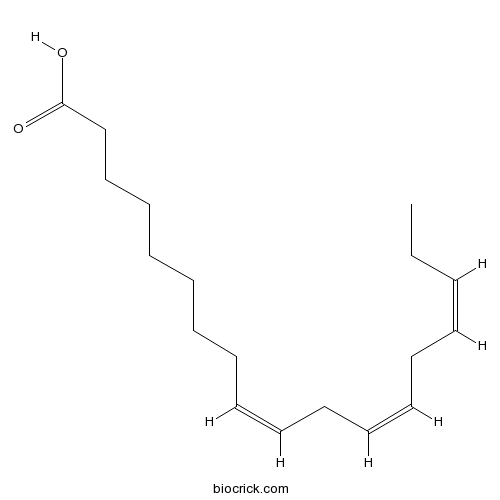
-
BCN5513
Hederagenin465-99-6
Instructions

-
BCN5524
Betulinic acid472-15-1
Instructions
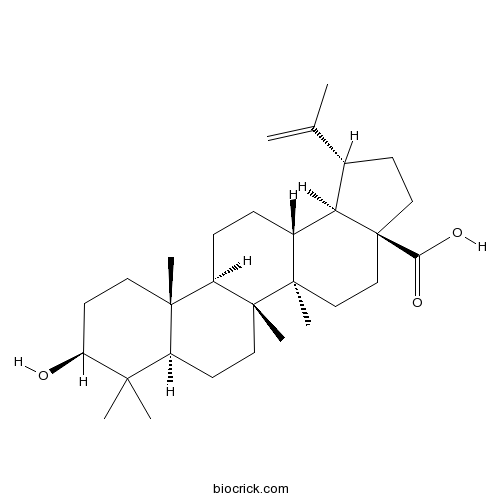
-
BCN5528
Betulin473-98-3
Instructions

-
BCN5607
Resveratrol501-36-0
Instructions

-
BCN5738
Paeonol552-41-0
Instructions

-
BCN3821
Linoleic acid60-33-3
Instructions

-
BCN2805
Paeonolide72520-92-4
Instructions

-
BCN2799
Benzoyloxypeoniflorin72896-40-3
Instructions
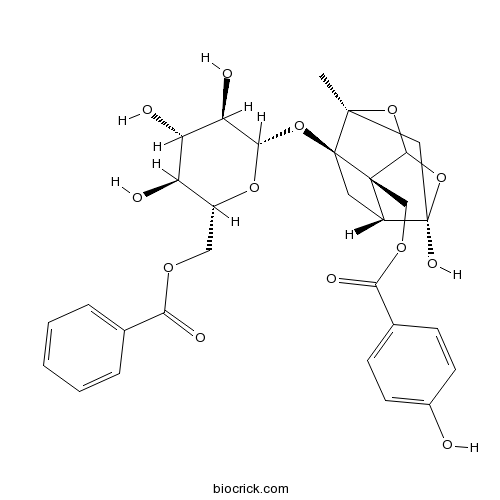
-
BCN6309
Coumarin91-64-5
Instructions

-
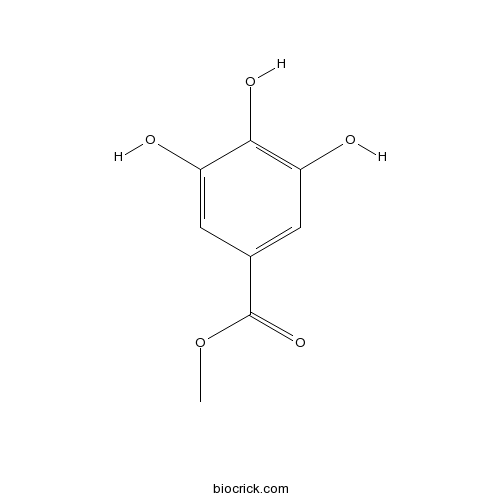
BCN3823
Methyl gallate99-24-1
Instructions
[Morphological, microscopic, multiple-component assay and fingerprinting based systematic research on quality evaluation of Moutan Cortex(Paeonia suffruticosa)].[Pubmed: 30111048]
None
Aqueous extracts of Paeonia suffruticosa modulates mitochondrial proteostasis by reactive oxygen species-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic cancer cells.[Pubmed: 30097117]
Pancreatic cancer (PC) remains the leading cause of cancer mortality, with limited therapeutic targets, and alterations in endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-related proteostasis may be a potential target for therapy. The root bark of Paeonia suffruticosa has been shown to inhibit cancer growth and metastasis, although its impact on PC is unknown.
Fatty acid desaturase 3 (PsFAD3) from Paeonia suffruticosa reveals high α-linolenic acid accumulation.[Pubmed: 30080606]
α-linolenic acid (ALA) deficiency and a skewed ω6: ω3 fatty acid ratio in the diet are thought to be a major cause for the high incidence of cardiovascular, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases. Recent years, tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.) with the high proportion of ALA (more than 45% in seed oil) is widely concerned. However, the underlying accumulation mechanism of the ALA in tree peony seeds remains unknown. In this study, comparative transcriptome analysis was performed between two cultivars ('Saiguifei' and 'Jingshenhuanfa') with different ALA contents. The analysis of the metabolic enzymes associated with ALA biosynthesis and temporal accumulation patterns of unsaturated fatty acids demonstrated the importance of microsomal ω-3 fatty acid desaturase 3 (FAD3). Moreover, PsFAD3 gene was identified from tree peony seeds, which was located in endoplasmic reticulum and the expression levels of PsFAD3 were consistent with ALA accumulation patterns in seeds. Heterologous expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Arabidopsis thaliana confirmed that the isolated PsFAD3 protein could catalyze ALA synthesis. These results indicated that PsFAD3 was involved in the synthesis of ALA in seeds and could be exploited by the genetic breeding of new cultivars with high ALA content in tree peony as well as other potential crops.
Paeonol attenuates acute lung injury by inhibiting HMGB1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced shock rats.[Pubmed: 29883962]
High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a highly conserved DNA-binding nuclear protein that facilitates gene transcription and the DNA repair response. However, HMGB1 may be released by necrotic cells as well as activated monocytes and macrophages following stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), or tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Extracellular HMGB1 plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury (ALI) through activating the nuclear transcription factor κB (NF-κB) P65 pathway, thus, it may be a promising therapeutic target in shock-induced ALI. Paeonol (Pae) is the main active component of Paeonia suffruticosa, which has been used to inhibit the inflammatory response in traditional Chinese medicine. We have proven that Pae inhibits the expression, relocation and secretion of HMGB1 in vitro. However, the role of Pae in the HMGB1-NF-κB pathway remains unknown. We herein investigated the role of Pae in LPS-induced ALI rats. In this study, LPS induced a marked decrease in the mean arterial pressure (MAP) and survival rate (only 25% after 72 h), and induced severe pathological changes in the lung tissue of rats, which was accompanied by elevated expression of HMGB1 and its downstream protein NF-κB P65. Treatment with Pae significantly improved the survival rate (>60%) and MAP, and attenuated the pathological damage to the lung tissue in ALI rats. Western blotting revealed that Pae also inhibited the total expression of HMGB1, NF-κB P65 and TNF-α in the lung tissue of ALI rats. Moreover, Pae increased the expression of HMGB1 in the nucleus, inhibited the production of HMGB1 in the cytoplasm, and decreased the expression of P65 both in the nucleus and cytoplasm of lung tissue cells in LPS-induced ALI rats. The results were in agreement with those observed in the in vitro experiment. These findings indicate that Pae may be a potential treatment for ALI through its repression of the HMGB1-NF-κB P65 signaling pathway.
Paeonol extracted from Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. ameliorated UVB-induced skin photoaging via DLD/Nrf2/ARE and MAPK/AP-1 pathway.[Pubmed: 29748977]
Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. (PS) has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for a long time. However, there are no studies that investigate the preventive effects of PS on ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced photoaging. In this study, paeonol (PA) was detected the main compound in PS root. In vitro, PS and PA significantly inhibited UVB-induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and activator protein 1 in keratinocytes, which consequently led to degradation of procollagen type I. On the other hand, PS and PA increased NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 and heme oxygenase-1 expression, confirmed by greater nuclear accumulation of nuclear factor E2-releated factor 2 (Nrf2). Furthermore, this study proved that the endogenous antioxidant system Nrf2/antioxidant response element was regulated by dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, a tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle-associated protein whose level was decreased after UVB exposure. PS and PA promoted the production of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, as well as the activation of Nrf2 and antioxidant response element, resulting in preventing procollagen type I ruined caused by UVB. In vivo, topical application of PS and PA attenuated UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 production and promoted procollagen type I in hairless mice. These results suggested PA a promising botanical in protecting skin from UVB-induced photoaging.
Paeonol Reduces the Nucleocytoplasmic Transportation of HMGB1 by Upregulating HDAC3 in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells.[Pubmed: 29736733]
Extracellular high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a lethal pro-inflammatory mediator in endotoxin shock. Hyperacetylation of HMGB1, regulated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs), changes its subcellular localization and secretion to the extracellular matrix. Paeonol (2'-hydroxy-4'-methoxyacetophenone), one of the main active components of Paeonia suffruticosa, exerts anti-inflammatory effects. Our previous study demonstrated that Paeonol inhibited the relocation and secretion of HMGB1 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW264.7 cells. However, it is still unclear whether Paeonol can regulate HATs/HDACs, which are responsible for the translocation of HMGB1 from nucleus to cytoplasm. To answer this question, P300 (a transcriptional coactivator with HATs) and HDAC3 were investigated using RT-qPCR and western blotting. The results showed that HMGB1 translocated from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, accompanied by upregulation of P300 and downregulation of HDAC3 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Paeonol, however, reversed the expression of P300 and HDAC3 significantly, suggesting that Paeonol may be involved in the acetylation of HMGB1 by regulating P300/HDAC3. Then, the effect of HDAC3 on the nucleocytoplasmic transportation of HMGB1 by HDAC3-SiRNA was evaluated. The results demonstrated that the inhibition of HDAC3 resulted in the nucleocytoplasmic translocation of HMGB1, with or without LPS stimulation. Moreover, Paeonol had no effect on the translocation of HMGB1 following ablation of HDAC3. These findings support the hypothesis that Paeonol can inhibit the translocation and secretion of HMGB1 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells by upregulating the expression of HDAC3. Paeonol may therefore be a valuable candidate as an HMGB1-targeting drug for inflammatory diseases via upregulation of HDAC3.


