Scrophularia ningpoensis
Scrophularia ningpoensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
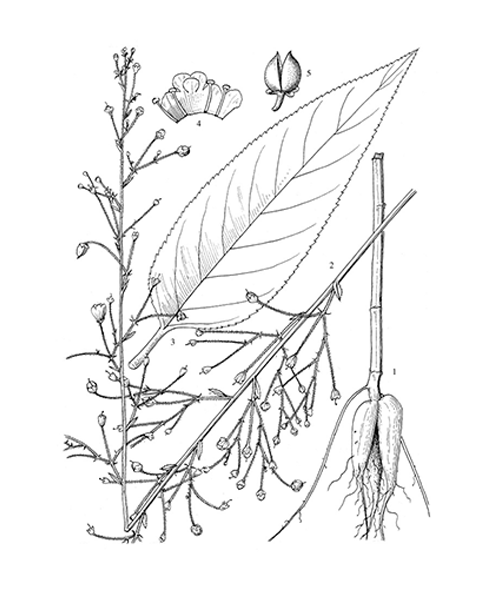
Natural products/compounds from Scrophularia ningpoensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
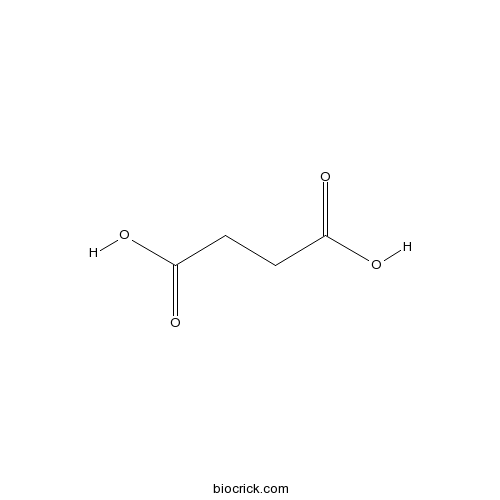
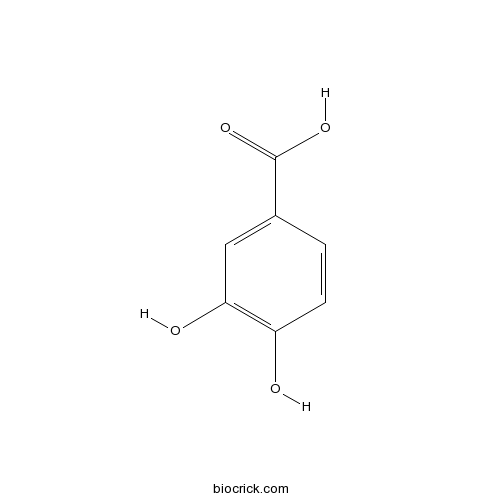
BCN5890
Succinic acid110-15-6
Instructions
-
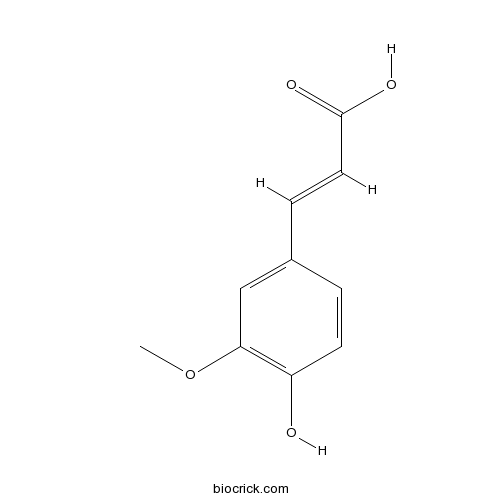
BCN5948
Ferulic acid1135-24-6
Instructions
-
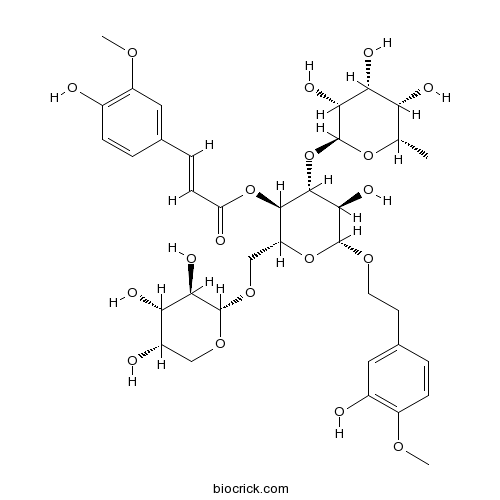
BCN4997
Angoroside C115909-22-3
Instructions
-
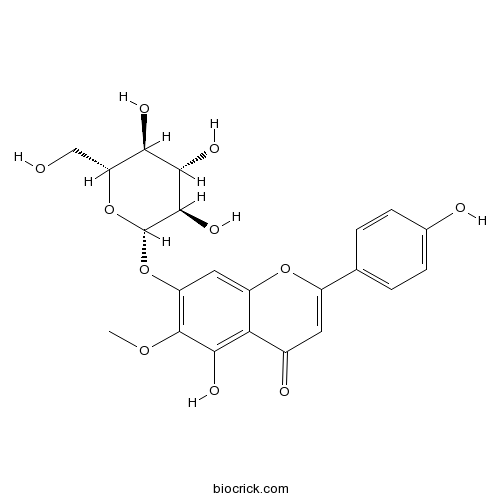
BCN2488
Homoplantaginin17680-84-1
Instructions
-
BCN4995
Harpagoside19210-12-9
Instructions

-
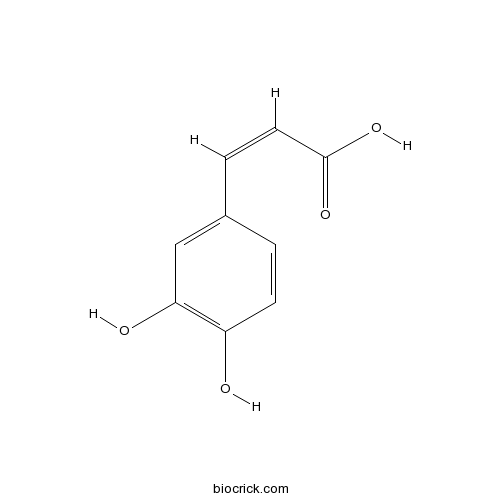
BCN5979
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN5355
Aucubin479-98-1
Instructions

-
BCN5946
Liquiritigenin578-86-9
Instructions

-
BCN4996
Harpagide6926-08-5
Instructions

-
BCN4256
8-O-Acetylharpagide6926-14-3
Instructions

-
BCN8340
Cedrol77-53-2
Instructions

-
BCN4952
Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin80681-45-4
Instructions

-
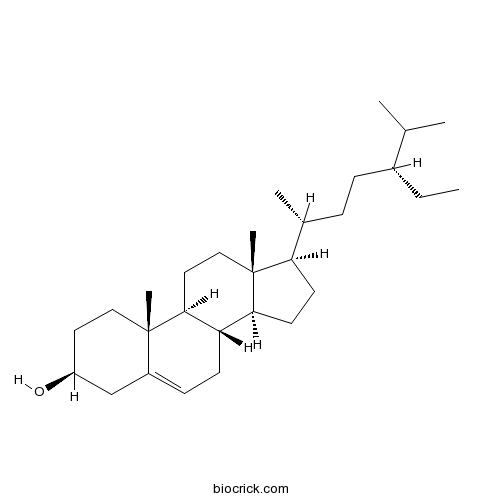
BCN1015
Beta-Sitosterol83-46-5
Instructions
-
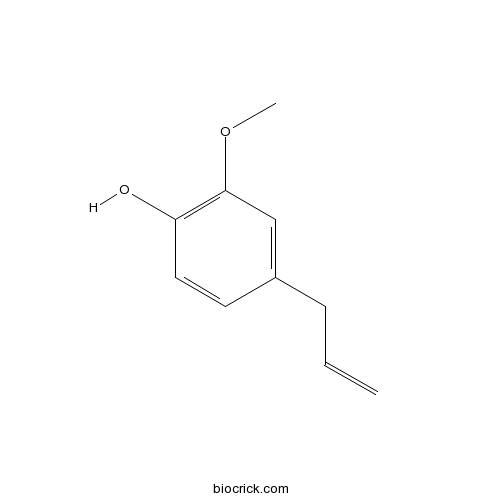
BCN5964
Eugenol97-53-0
Instructions
-
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
[Binding interaction of harpagoside and bovine serum albumin: spectroscopic methodologies and molecular docking].[Pubmed: 29676099]
Scrophularia ningpoensis has exhibited a variety of biological activities and been used as a pharmaceutical product for the treatment of inflammatory ailment, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and so on. Harpagoside (HAR) is considerer as a main bioactive compound in this plant. Serum albumin has important physiological roles in transportation, distribution and metabolism of many endogenous and exogenous substances in body. It is of great significance to study the interaction mechanism between HAR and bovine serum albumin (BSA). The mechanism of interaction between HAR and BSA was investigated using 2D and 3D fluorescence, synchronous florescence, ultraviolet spectroscopy and molecular docking. According to the analysis of fluorescence spectra, HAR could strongly quench the fluorescence of BSA, and the static quenching process indicated that the decrease in the quenching constant was observed with the increase in temperature. The magnitude of binding constants (KA) was more than 1×10⁵ L·mol⁻¹, and the number of binding sites(n) was approximate to 1. The thermodynamic parameters were calculated through analysis of fluorescence data with Stern-Volmer and Van't Hoff equation. The calculated enthalpy change (ΔH) and entropy change (ΔS) implied that the main interaction forces of HAR with BSA were the bonding interaction between van der Waals forces and hydrogen. The negative values of energy (ΔG) demonstrated that the binding of HAR with BSA was a spontaneous and exothermic process. The binding distance(r) between HAR and BSA was calculated to be about 2.80 nm based on the theory of Frster's non-radiation energy transfer, which indicated that energy is likely to be transfer from BSA to HAR. Both synchronous and 3D florescence spectroscopy clearly revealed that the microenvironment and conformation of BSA changed during the binding interaction between HAR and BSA. The molecular docking analysis revealed HAR is more inclined to BSA and human serum albumin (HSA) in subdomain ⅡA (Sudlow's site I). This study will provide valuable information for understanding the action mechanism of HAR.
Harpagoside-induced anaphylactic reaction in an IgE-independent manner both in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 29355053]
Harpagoside (HAR) is an active component of Scrophularia ningpoensis (SN), which has anti-inflammatory and anti-immune effects. SN is used widely in China to treat various diseases. Recently, SN has been used as a traditional Chinese medicine injection and used clinically. However, allergic responses to these injections are frequently reported.
[Antifungal effects of three medicinal crops on Phytophthora nicotianae].[Pubmed: 29218935]
Tobacco black shank is one of the most harmful soil-borne diseases infected by Phytophthora parasitica. In order to probe the control method to this disease, in this study, the mycelial growth rate method was employed to investigate the antifungal effects of extracts from stem-leaf and root, root exudates, and their combination of Scrophularia ningpoensis, Chuanmingshen violaceum and Pinellia ternata The results showed that: ①Stem-leaf and root extracts of S. ningpoensis, C. violaceum and P. ternata exhibited different antifungal activities, and the inhibition increased with the increase of extract concentration. The antifungal effect of S. ningpoensis extracts at 0.5 g•mL⁻¹ was the strongest than other medicinal plants, the inhibition rate of steam-leaf and root extracts reached 74.88%, 69.27%, respectively. The inhibitory effect of C. violaceum and P. ternata was relatively lower, however, there is a significant gain effect after combination of steam-leaf and root extracts of C. violaceum. ②The root exudates of S. ningpoensis, C. violaceum and P. ternata showed fungistasis to Phytophthora nicotianae, and fungistasis was enhanced with the increase of root exudate concentration. The antifungal effect in the order of C. violaceum > S. ningpoensis > P. ternata. ③The antifungal activity of combination of extract and root exudate from S. ningpoensis was similar with the effect of C. violaceum, they were both stronger than P. ternata, and the antifungal activity for three combination were located between the antifungal activity of their extracts and root exudates. S. ningpoensis and C. violaceum can be potentially applied to prevent and control the tobacco black shank.
[A quantitative method for simultaneous assay of seven active ingredients with one marker in Scrophularia ningpoensis root].[Pubmed: 29098827]
To establish a new quantitative method for simultaneous determination of multi-components in Scrophularia root by using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and validate its feasibilities.Meanwhile,using catalpol as one chemical reference substance to establish the relative correct factors and relative retention values of aucubin,harpagide,acteoside,angoroside C,harpagoside and cinnamic acid.Then using the quantitative analysis of multi-components by single-marker (QAMS)model,the six analytes can be quantitatively determined in Scrophularia root.The method was evaluated by comparison of the quantitative results to external standard method.No significant differences were observed between the quantitative results of the two methods.The obtained RCFs were credible.It is feasible and suitable to evaluate the quality of Scrophularia root.
[Identification and phylogenetic analysis of endophytic fungi isolated from Scrophularia ningpoensis].[Pubmed: 28994533]
The endophytic fungi from root, main stem, branch and leaf of Scrophularia ningpoensis were isolated and identified from Wulong and Chongqing, and the population diversity analysis and phylogenetic analysis were followed. The result indicated that, as to population diversity index, S. ningpoensis from Wulong: leaf>main stem=branch>root, branch from Chongqing>branch from Wulong. Fifty-eight endophytic fungi were obtained, most of which were the pathogens of the plant. Colletotrichum was the prevailing genus, of which C. gloeosporioides and C. boninense were the prevailing strains. Leaf and seedlings might be the main path of infection. Endophytic fungi and pathogen might convert to each other, influenced by such factors as environment, genotype et al.
New Iridoids from Scrophularia ningpoensis.[Pubmed: 28867715]
Five new compounds including five iridoids (1-5) and six known compounds were isolated from the rhizomes of Scrophularia ningpoensis. Their structures were determined by extensive NMR and IR, MS spectroscopic data analyses. The anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal, and cytotoxic activities of the isolated compounds were evaluated. Compound 11 exhibited significant inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 macrophage cells.
[Transcriptome characterization for Scrophularia ningpoensis based on high-throughput sequencing technology and related genes for synthesis of terpenoid compounds].[Pubmed: 28840684]
To investigate the profile of gene function and search for SSR, a new technology of high-throughput Solexa/Illumina sequencing was used to generate the root transcriptome of Scrophularia ningpoensis, and 65 602 036 raw reads were obtained. Based on the bioinformatics analysis and Trinity, 73 983 unigenes were obtained with an average length of 823 bp. The comparison of sequence homology in database showed that 56 389 unigenes had different degrees of homology. A total of 520 metabolic pathways related genes and 191 relDODO transcription factors were identified by the Swiss-Prot, GO, KEGG and COG.The 11 659 SSRs were found by MISA and the highest frequency was AG/CT. In this study, we obtained numerous SSRs to provide references for the study of functional gene cloning and genetic diversity of S. ningpoensis. The key genes involved in the secondary metabolism are the basis for the study of biosynthesis and regulatory mechanism of the secondary metabolites.
Two pairs of unusual melibiose and raffinose esters from Scrophularia ningpoensis.[Pubmed: 28537094]
A pair of unusual melibiose esters (1α/1β) and a pair of unusual raffinose esters (2α/2β), were isolated from Scrophularia ningpoensis. Structures of them were established by detailed spectroscopic analyses to be 6-O-(E)-cinnamoyl-α-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→6)-α(β)-d-glucopyranose (1α/1β) and 6-O-(E)/(Z)-cinnamoyl-α-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→6)-α-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-d-fructofuranose (2α/2β), respectively. All these compounds were evaluated for antifouling activity against the settlement of Balanus amphitrite larvae, along with the cytotoxic effect against the proliferation of HeLa cell lines.
A new iridoid glycoside and a new cinnamoyl glycoside from Scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl.[Pubmed: 28326841]
None
[Species, Damage and Community Structure of Weeds in Scrophularia ningpoensis Fields in Nanchuan, Chongqing].[Pubmed: 27254914]
To investigate the damage and community structure of weeds in Scrophularia ningpoensis fields in Nanchuan, Chongqing.


