p-Coumaric acid ethyl esterCAS# 7362-39-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 7362-39-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 676946 | Appearance | Powder |
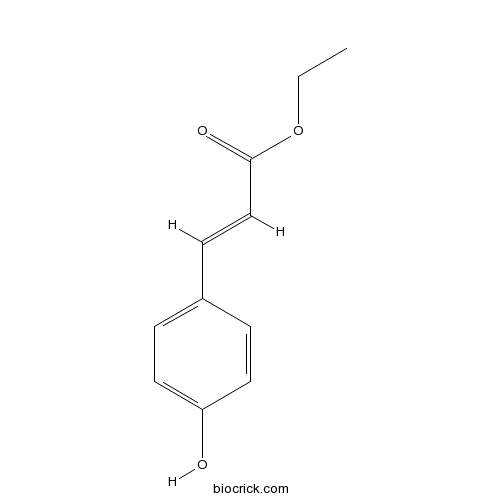
| Formula | C11H12O3 | M.Wt | 192.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | ethyl (E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C=CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZOQCEVXVQCPESC-VMPITWQZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H12O3/c1-2-14-11(13)8-5-9-3-6-10(12)7-4-9/h3-8,12H,2H2,1H3/b8-5+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | p-Coumaric acid ester has moderate free radical scavenging ability. |
| Targets | Carbonic Anhydrase |
| In vitro | P -Coumaric Acid Ester with Potential Antioxidant Activity from the Genus Salvia[Reference: WebLink]Free Radicals & Antioxidants, 2011, 1(1):23-7.A phytochemical analysis of the acetone extract of the aerial parts of the plants Salvia splendens and Salvia lanigra yielded a long chain alkyl p-coumaric acid ester; eicosanyl-cis-p-coumarate (1), which has not previously been isolated from Salvia genus, together with two triterpenoids; oleanolic acid (2) and echinocystic acid (3) and two flavonoids; 7-methoxyapigenin (4) and luteolin-7-O-glucoside (5).
|
| Structure Identification | J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Apr 8;63(13):3402-18.Sensomics analysis of key bitter compounds in the hard resin of hops (Humulus lupulus L.) and their contribution to the bitter profile of Pilsner-type beer.[Pubmed: 25793563]Recent brewing trials indicated the occurrence of valuable bitter compounds in the hard resin fraction of hop.
|

p-Coumaric acid ethyl ester Dilution Calculator

p-Coumaric acid ethyl ester Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2029 mL | 26.0146 mL | 52.0291 mL | 104.0583 mL | 130.0728 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0406 mL | 5.2029 mL | 10.4058 mL | 20.8117 mL | 26.0146 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5203 mL | 2.6015 mL | 5.2029 mL | 10.4058 mL | 13.0073 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1041 mL | 0.5203 mL | 1.0406 mL | 2.0812 mL | 2.6015 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.052 mL | 0.2601 mL | 0.5203 mL | 1.0406 mL | 1.3007 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 5-Amino-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)pyrazole
Catalog No.:BCC8727
CAS No.:73616-27-0
- 1-(4-Methoxycinnamoyl)pyrrole
Catalog No.:BCN4027
CAS No.:736140-70-8
- Xylazine
Catalog No.:BCC5167
CAS No.:7361-61-7
- 3-Hydroxybenzylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1804
CAS No.:73604-31-6
- (-)-Bicuculline methobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6555
CAS No.:73604-30-5
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
- 27-p-Coumaroyloxyursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4288
CAS No.:73584-67-5
- Mevastatin
Catalog No.:BCN2568
CAS No.:73573-88-3
- cis-ACBD
Catalog No.:BCC6587
CAS No.:73550-55-7
- 7-Acetyllycopsamine
Catalog No.:BCN2000
CAS No.:73544-48-6
- Tetrachyrin
Catalog No.:BCN4776
CAS No.:73483-88-2
- 1-Deoxymannojirimycin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6995
CAS No.:73465-43-7
- H-Asp-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC2882
CAS No.:7362-93-8
- HEPES
Catalog No.:BCC7590
CAS No.:7365-45-9
- Naringenin 5-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN2747
CAS No.:
- Onysilin
Catalog No.:BCN3379
CAS No.:73695-94-0
- Oxypeucedanin
Catalog No.:BCN2494
CAS No.:737-52-0
- Acetylursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4290
CAS No.:7372-30-7
- Fmoc-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3541
CAS No.:73724-45-5
- Fmoc-Thr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3549
CAS No.:73731-37-0
- Broussonin B
Catalog No.:BCN4593
CAS No.:73731-86-9
- Broussonin A
Catalog No.:BCN4592
CAS No.:73731-87-0
- Acanthoside B
Catalog No.:BCN4291
CAS No.:7374-79-0
- N-(4-Aminobenzoyl)-β-alanine
Catalog No.:BCC9056
CAS No.:7377-08-4
Sensomics analysis of key bitter compounds in the hard resin of hops (Humulus lupulus L.) and their contribution to the bitter profile of Pilsner-type beer.[Pubmed:25793563]
J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Apr 8;63(13):3402-18.
Recent brewing trials indicated the occurrence of valuable bitter compounds in the hard resin fraction of hop. Aiming at the discovery of these compounds, hop's epsilon-resin was separated by means of a sensory guided fractionation approach and the key taste molecules were identified by means of UV/vis, LC-TOF-MS, and 1D/2D-NMR studies as well as synthetic experiments. Besides a series of literature known xanthohumol derivatives, multifidol glucosides, flavon-3-on glycosides, and p-coumaric acid esters, a total of 11 bitter tastants are reported for the first time, namely, 1",2"-dihydroxanthohumol F, 4'-hydroxytunicatachalcone, isoxantholupon, 1-methoxy-4-prenylphloroglucinol, dihydrocyclohumulohydrochinone, xanthohumols M, N, and P, and isoxanthohumols M, N, and P, respectively. Human sensory analysis revealed low bitter recognition threshold concentrations ranging from 5 (co-multifidol glucopyranoside) to 198 mumol/L (trans-p-Coumaric acid ethyl ester) depending on their chemical structure. For the first time, LC-MS/MS quantitation of these taste compounds in Pilsner-type beer, followed by taste re-engineering experiments, revealed the additive contribution of iso-alpha-acids and the identified hard resin components to be truly necessary and sufficient for constructing the authentic bitter percept of beer. Finally, brewing trails using the epsilon-resin as the only hop source impressively demonstrated the possibility to produce beverages strongly enriched with prenylated hop flavonoids.


