Prunus persica
Prunus persica
The peach (Prunus persica) is a deciduous tree native to the region of Northwest China between the Tarim Basin and the north slopes of the Kunlun Shan mountains, where it was first domesticated and cultivated. It bears an edible juicy fruit called a peach or a nectarine.The major phenolic compounds identified in peach are chlorogenic acid, catechins and epicatechins, with other compounds, identified by HPLC, including gallic acid and ellagic acid. Rutin and isoquercetin are the primary flavonols found in clingstone peaches. Red-fleshed peaches are rich in anthocyanins, particularly cyanidin glucosides in six peach and six nectarine cultivars and malvin glycosides in clingstone peaches. As with many other members of the rose family, peach seeds contain cyanogenic glycosides, including amygdalin. These substances are capable of decomposing into a sugar molecule and hydrogen cyanide gas. While peach seeds are not the most toxic within the rose family, large consumption of these chemicals from any source is potentially hazardous to animal and human health.
Products from Prunus persica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5206
Amygdalin 29883-15-6
PDF

-
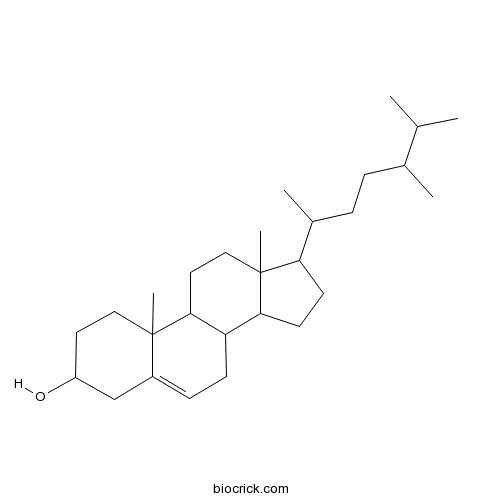
BCN1015
Beta-Sitosterol 83-46-5
PDF
-
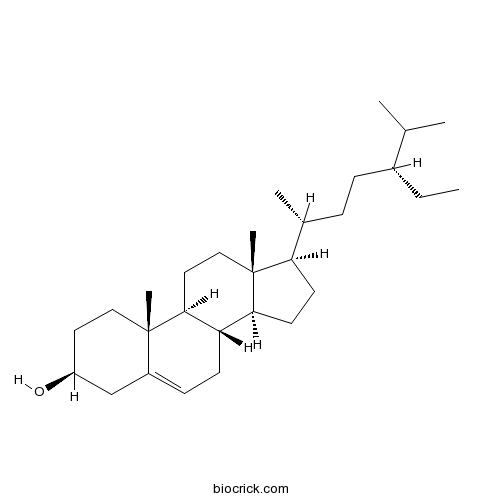
BCN4376
Stigmasterol 83-48-7
PDF
-
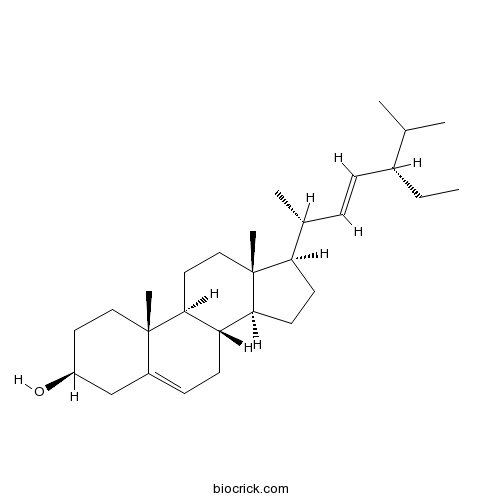
BCN3181
Campesterol 474-62-4
PDF
-
BCN4535
Prunasin 99-18-3
PDF

-
BCN4860
Cycloartanol 4657-58-3
PDF

-
BCN6137
24-Methylenecycloartanol acetate 1259-94-5
PDF

-
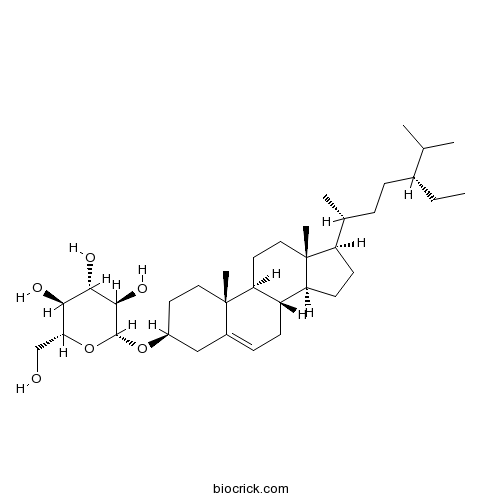
BCN5531
Daucosterol 474-58-8
PDF
-
BCN1259
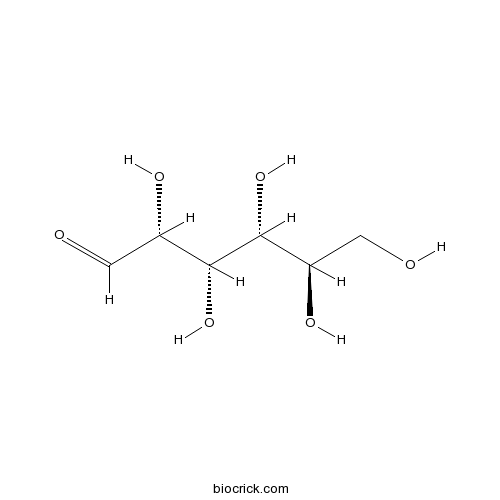
D-(+)-Glucose 50-99-7
PDF
-
BCN5906
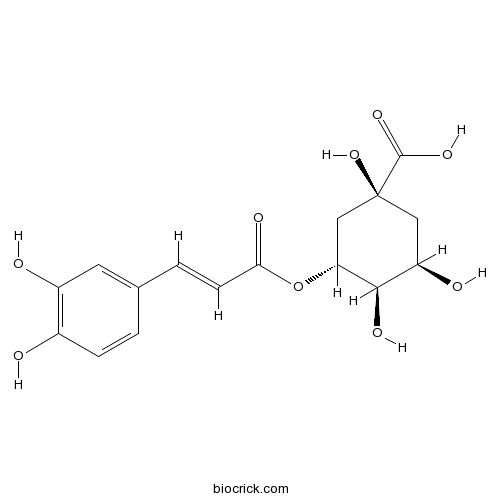
Chlorogenic acid 327-97-9
PDF
-
BCN4450
Neochlorogenic acid 906-33-2
PDF

-
BCN3353
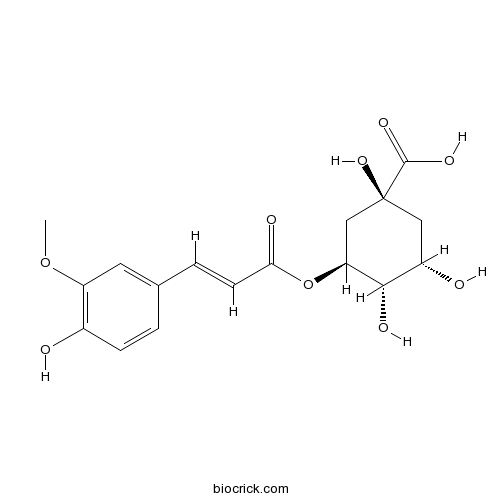
3-O-Feruloylquinic acid 1899-29-2
PDF
-
BCN3821
Linoleic acid 60-33-3
PDF

-
BCN5780
Sucrose 57-50-1
PDF




