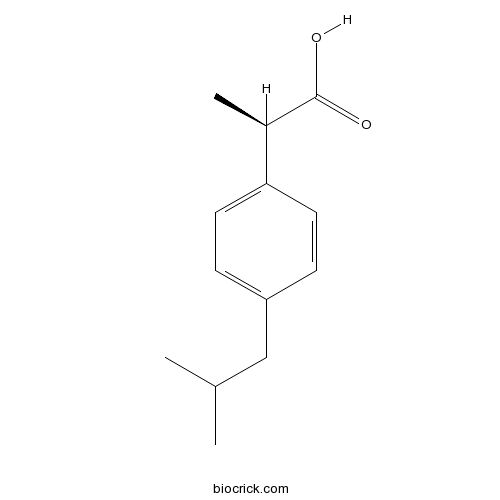
(R)-(-)-IbuprofenCAS# 51146-57-7 |
- Anguizole
Catalog No.:BCC1365
CAS No.:442666-98-0
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Balapiravir
Catalog No.:BCC1396
CAS No.:690270-29-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 51146-57-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 114864 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H18O2 | M.Wt | 206.28 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (R)-Ibuprofen | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (484.78 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(C)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HEFNNWSXXWATRW-SNVBAGLBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H18O2/c1-9(2)8-11-4-6-12(7-5-11)10(3)13(14)15/h4-7,9-10H,8H2,1-3H3,(H,14,15)/t10-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | (R)-(-)-Ibuprofen is the R-enantiomer of Ibuprofen. Ibuprofen is an anti-inflammatory inhibitor targeting COX-1 and COX-2 with IC50 of 13 μM and 370 μM, respectively. | |||||

(R)-(-)-Ibuprofen Dilution Calculator

(R)-(-)-Ibuprofen Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.8478 mL | 24.2389 mL | 48.4778 mL | 96.9556 mL | 121.1945 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9696 mL | 4.8478 mL | 9.6956 mL | 19.3911 mL | 24.2389 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4848 mL | 2.4239 mL | 4.8478 mL | 9.6956 mL | 12.1194 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.097 mL | 0.4848 mL | 0.9696 mL | 1.9391 mL | 2.4239 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0485 mL | 0.2424 mL | 0.4848 mL | 0.9696 mL | 1.2119 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
(R)-Ibuprofen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, is the less active enantiomer of ibuprofen, an inhibitor of Cox-1 and Cox-2.
- (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
Catalog No.:BCC4042
CAS No.:51146-56-6
- (+)-trans-Isolimonene
Catalog No.:BCC9236
CAS No.:5113-87-1
- Cyclic Pifithrin-α hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC2407
CAS No.:511296-88-1
- 8-Bromo-cGMP, sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6935
CAS No.:51116-01-9
- Gitogenin
Catalog No.:BCN3886
CAS No.:511-96-6
- Plumieride
Catalog No.:BCN5631
CAS No.:511-89-7
- Vitamin D4
Catalog No.:BCC2042
CAS No.:511-28-4
- Totarol
Catalog No.:BCN4627
CAS No.:511-15-9
- Sugiol
Catalog No.:BCN3164
CAS No.:511-05-7
- alpha-Onocerol
Catalog No.:BCN5630
CAS No.:511-01-3
- Nicotine 1'-N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN6892
CAS No.:51095-86-4
- 2,7-Dihydrohomoerysotrine
Catalog No.:BCN5629
CAS No.:51095-85-3
- Episyringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7023
CAS No.:51152-20-6
- Boc-D-Asp(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3371
CAS No.:51186-58-4
- Withaferin A
Catalog No.:BCC7495
CAS No.:5119-48-2
- Diosgenin
Catalog No.:BCN6272
CAS No.:512-04-9
- Yamogenin
Catalog No.:BCN8277
CAS No.:512-06-1
- Raffinose
Catalog No.:BCN8427
CAS No.:512-69-6
- Ascaridole
Catalog No.:BCC8121
CAS No.:512-85-6
- Boc-Arg(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3068
CAS No.:51219-18-2
- 6,8-Diprenylgenistein
Catalog No.:BCN4805
CAS No.:51225-28-6
- Wighteone
Catalog No.:BCN5632
CAS No.:51225-30-0
- N-Phthaloyl-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3016
CAS No.:5123-55-7
- Amsacrine
Catalog No.:BCC4309
CAS No.:51264-14-3
An integrated safety analysis of intravenous ibuprofen (Caldolor((R))) in adults.[Pubmed:26604816]
J Pain Res. 2015 Oct 23;8:753-65.
Intravenous (IV) nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as IV ibuprofen are increasingly used as a component of multimodal pain management in the inpatient and outpatient settings. The safety of IV ibuprofen as assessed in ten sponsored clinical studies is presented in this analysis. Overall, 1,752 adult patients have been included in safety and efficacy trials over 11 years; 1,220 of these patients have received IV ibuprofen and 532 received either placebo or comparator medication. The incidence of adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, and changes in vital signs and clinically significant laboratory parameters have been summarized and compared to patients receiving placebo or active comparator drug. Overall, IV ibuprofen has been well tolerated by hospitalized and outpatient patients when administered both prior to surgery and postoperatively as well as for nonsurgical pain or fever. The overall incidence of AEs is lower in patients receiving IV ibuprofen as compared to those receiving placebo in this integrated analysis. Specific analysis of hematological and renal effects showed no increased risk for patients receiving IV ibuprofen. A subset analysis of elderly patients suggests that no dose adjustment is needed in this higher risk population. This integrated safety analysis demonstrates that IV ibuprofen can be safely administered prior to surgery and continued in the postoperative period as a component of multimodal pain management.
Significant solubility of carbon dioxide in Soluplus((R)) facilitates impregnation of ibuprofen using supercritical fluid technology.[Pubmed:28375669]
Pharm Dev Technol. 2018 Sep;23(7):697-705.
Treatment of Soluplus((R)) with supercritical carbon dioxide allows promising applications in preparing dispersions of amorphous solids. Several characterization techniques were employed to reveal this effect, including CO2 gas sorption under high pressure and physicochemical characterizations techniques. A gravimetric method was used to determine the solubility of carbon dioxide in the polymer at elevated pressure. The following physicochemical characterizations were used: thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform, infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Drug loading of the polymer with ibuprofen as a model drug was also investigated. The proposed treatment with supercritical carbon dioxide allows to prepare solid solutions of Soluplus((R)) in less than two hours at temperatures that do not exceed 45 degrees C, which is a great advantage to be used for thermolabile drugs. The advantages of using this technology for Soluplus((R)) formulations lies behind the high sorption capability of carbon dioxide inside the polymer. This will ensure rapid diffusion of the dissolved/dispersed drug inside the polymer under process conditions and rapid precipitation of the drug in the amorphous form during depressurization accompanied by foaming of the polymer.
Parmacokinetic evaluation of ibuprofen controlled release matrix tablets using hydrophilic Eudragit(R) polymer and co-excipients.[Pubmed:26408874]
Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015 Sep;28(5):1745-55.
The present study was conducted to formulate controlled release dosage forms containing Ibuprofen with Eudragit(R) S 100 polymer. The tablets were formulated at three different ratios with the polymer to investigate the effect of different concentrations of polymer on in vitro drug release patterns/kinetics and in vivo absorption/pharmacokinetics. Pre-formulation studies were conducted including bulk density, tapped density, compressibility index, Hausner ratio and angle of repose. In vitro studies were conducted using phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) as dissolution medium. In vivo performance was evaluated using albino rabbits. Physico-chemical characteristics (i.e. dimensional tests, weight variation, hardness, friability and drug content determination) fell in the USP acceptable limits. The compressibility index was found to range between 12.02 +/- 0.01% and 18.66 +/- 0.03%, the Hausner ratio varied between 1.02 +/- 0.01 and 1.19 +/- 0.10 and the angle of repose ranged from 15.19 +/- 0.01 to 24.52 +/- 0.10, all indicating better flow properties than the bulk-reference standard. Both bulk and tapped densities also fell in the USP acceptable range. Ibuprofen market tablets showed Tmax of 2.1 +/- 0.4h, which was significantly (P-value <0.05) lower compared to that of the reference standard (i.e. 4.09 +/- 1.3h). Ibuprofen test formulation has a half-life (t1/2) of 16.9 +/- 2.5h, which was significantly (P-value<0.001) higher compared to that of the reference standard (i.e. 9.23 +/- 2.9h). Eudragit(R) S 100 polymers can be used efficiently to develop directly compressed prolonged release tablets.
A clinical trial comparing Lanconone(R) with ibuprofen for rapid relief in acute joint pain.[Pubmed:27052991]
Trials. 2016 Apr 6;17:189.
BACKGROUND: To study the effect of Lanconone(R) (1000 mg) on acute pain on exertion as compared to the standard of care, Ibuprofen (400 mg). METHOD: The study recruited 72 subjects diagnosed with mild to moderate knee joint pain on exertion. Subjects with Pain Visual Analogue Scale of more than 40 mm were included. Uphill walking was provided as the stressor using Naughton's protocol on a treadmill. The subjects walked for 10 minutes continuously followed by a rest period and baseline pain score for index knee joint was recorded. Subjects were administered a single dose of Lanconone(R) (1000 mg)/Ibuprofen (400 mg). Thereafter the same stressor was provided at 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6 hours, subsequently, pain scores were recorded on a visual analogue scale. Double stopwatch method was used to evaluate the onset of pain relief and time taken to meaningful pain relief. RESULT: Both Lanconone(R) and Ibuprofen showed the first perceived pain relief at 65.31 +/- 35.57 mins as compared to 60.82 +/- 32.56 mins respectively. The mean time taken to experience meaningful pain relief in Lanconone(R) group was 196.59 +/- 70.85 mins compared to 167.13 +/- 71.41 mins amongst Ibuprofen group. The meaningful pain relief continued for 6 hours. CONCLUSION: The current study successfully demonstrated rapid pain-relieving potential of Lanconone(R) which was comparable to Ibuprofen. No adverse event related to the interventions was reported in the study. TRIAL REGISTRATION: Clinical trials.gov NCT02417506 . 21 January 2015.


