11-O-SyringylbergeninCAS# 126485-47-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 126485-47-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 195481.0 | Appearance | Powder |
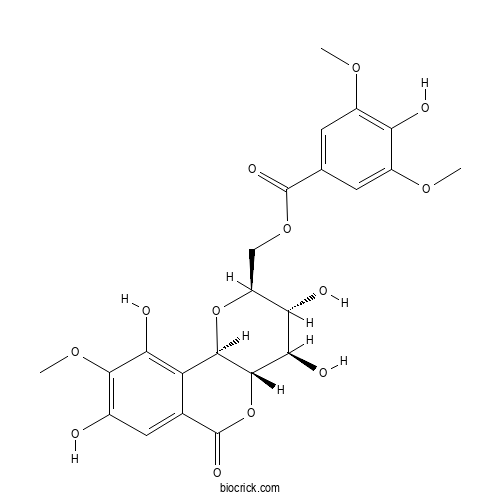
| Formula | C23H24O13 | M.Wt | 508.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(2S,3R,4R,4aS,10bR)-3,4,8,10-tetrahydroxy-9-methoxy-6-oxo-3,4,4a,10b-tetrahydro-2H-pyrano[3,2-c]isochromen-2-yl]methyl 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1O)OC)C(=O)OCC2C(C(C3C(O2)C4=C(C(=C(C=C4C(=O)O3)O)OC)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GXCBETDJJWPGAQ-PCOXRIKQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H24O13/c1-31-11-4-8(5-12(32-2)15(11)25)22(29)34-7-13-16(26)18(28)21-20(35-13)14-9(23(30)36-21)6-10(24)19(33-3)17(14)27/h4-6,13,16,18,20-21,24-28H,7H2,1-3H3/t13-,16-,18+,20+,21-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

11-O-Syringylbergenin Dilution Calculator

11-O-Syringylbergenin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9668 mL | 9.8342 mL | 19.6684 mL | 39.3368 mL | 49.171 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3934 mL | 1.9668 mL | 3.9337 mL | 7.8674 mL | 9.8342 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1967 mL | 0.9834 mL | 1.9668 mL | 3.9337 mL | 4.9171 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0393 mL | 0.1967 mL | 0.3934 mL | 0.7867 mL | 0.9834 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0197 mL | 0.0983 mL | 0.1967 mL | 0.3934 mL | 0.4917 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 7,4'-Di-O-methyltectorigenin
Catalog No.:BCX1493
CAS No.:13186-08-8
- Ginsenoside CY
Catalog No.:BCX1492
CAS No.:83480-65-3
- ent-kauran-16β,17-diol
Catalog No.:BCX1491
CAS No.:16836-31-0
- Erucic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1490
CAS No.:112-86-7
- Dihydrohelenalin
Catalog No.:BCX1489
CAS No.:34257-95-9
- 12-Hydroxyganoderenic acid B
Catalog No.:BCX1488
CAS No.:1309931-84-7
- Paroxetine Impurity A Hydrochloride salt
Catalog No.:BCX1487
CAS No.:1394842-91-1
- Fluvoxamine Impurity D
Catalog No.:BCX1486
CAS No.:61718-80-7
- Aceclofenac impurity I
Catalog No.:BCX1485
CAS No.:15362-40-0
- Monbarbatain A
Catalog No.:BCX1484
CAS No.:138711-55-4
- Gymconopin C
Catalog No.:BCX1483
CAS No.:844493-85-2
- (±)-Taxifolin
Catalog No.:BCX1482
CAS No.:24198-97-8
- 12β-Acetoxycoccinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1495
CAS No.:125247-74-7
- 9-epi-6-Methoxygeniposidic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1496
CAS No.:1215178-87-2
- Denthyrsinin
Catalog No.:BCX1497
CAS No.:118169-17-8
- Confusarin
Catalog No.:BCX1498
CAS No.:108909-02-0
- Swertiaside
Catalog No.:BCX1499
CAS No.:96087-14-8
- Potentillanoside A
Catalog No.:BCX1500
CAS No.:1309589-79-4
- Homocapsaicin II
Catalog No.:BCX1501
CAS No.:71240-51-2
- Regaloside E
Catalog No.:BCX1502
CAS No.:123134-21-4
- Hydroxylinderstrenolide
Catalog No.:BCX1503
CAS No.:20267-92-9
- Visamminol-3'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1504
CAS No.:2254096-98-3
- Tetrahydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCX1505
CAS No.:5234-70-8
- Fulvotomentoside A
Catalog No.:BCX1506
CAS No.:150107-44-1
Anti-colorectal cancer of Ardisia gigantifolia Stapf. and targets prediction via network pharmacology and molecular docking study.[Pubmed:36624500]
BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Jan 9;23(1):4.
BACKGROUND: Ardisia gigantifolia Stapf. (AGS), a Chinese folk medicine widely grows in the south of China and several studies reported that AGS could inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer, liver cancer, and bladder cancer cell lines. However, little is known about its anti-colorectal cancer (CRC) efficiency. METHODS: In the present study, a combination of MTT assay, network pharmacological analysis, bioinformatics, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation study was used to investigate the active ingredients, and targets of AGS against CRC, as well as the potential mechanism. RESULTS: MTT assay showed that three kinds of fractions from AGS, including the n-butanol extract (NBAGS), ethyl acetate fraction (EAAGS), and petroleum ether fraction (PEAGS) significantly inhibited the proliferation of CRC cells, with the IC(50) values of 197.24, 264.85, 15.45 microg/mL on HCT116 cells, and 523.6, 323.59, 150.31 microg/mL on SW620 cells, respectively. Eleven active ingredients, including, 11-O-galloylbergenin, 11-O-protocatechuoylbergenin, 11-O-Syringylbergenin, ardisiacrispin B, bergenin, epicatechin-3-gallate, gallic acid, quercetin, stigmasterol, stigmasterol-3-o-beta-D-glucopyranoside were identified. A total of 173 targets related to the bioactive components and 21,572 targets related to CRC were picked out through database searching. Based on the crossover targets of AGS and CRC, a protein-protein interaction network was built up by the String database, from which it was concluded that the core targets would be SRC, MAPK1, ESR1, HSP90AA1, MAPK8. Besides, GO analysis showed that the numbers of biological process, cellular component, and molecular function of AGS against CRC were 1079, 44, and 132, respectively, and KEGG pathway enrichment indicated that 96 signaling pathways in all would probably be involved in AGS against CRC, among which MAPK signaling pathway, lipid, and atherosclerosis, proteoglycans in cancer, prostate cancer, adherens junction would probably be the major pathways. The docking study verified that AGS had multiple ingredients and multiple targets against CRC. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation analysis showed that the binding would be stable via forming hydrogen bonds. CONCLUSION: Our study showed that AGS had good anti-CRC potency with the characteristics of multi-ingredients, -targets, and -signaling pathways.
A new bergenin derivative from the rhizome of Ardisia gigantifolia.[Pubmed:22991954]
Nat Prod Res. 2013;27(14):1242-5.
One new bergenin derivative, named 11-O-veratroylbergenin (1) along with five known bergenin derivatives, 11-O-(3'-O-methylgalloyl) bergenin (2), 11-O-Syringylbergenin (3), 11-O-Galloylbergenin (4), 4-O-Galloylbergenin (5) and bergenin (6) were isolated from Ardisia gigantifolia Stapf. Their structures were established on the basis of spectroscopic analysis, especially by means of 1D, 2D-NMR and HR-ESIMS analyses. Compounds 2, 4 and 5 showed significant 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free-radical scavenging activity with EC(5)(0) 9.7, 9.0 and 7.8 micromol L(-1), respectively. They showed more antioxidant activity than the positive control vitamin C (EC(5)(0) = 28.3 micromol L(-1)).
[Study on chemical constituents of rhizome of Ardisia gigantifolia].[Pubmed:22368857]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Dec;36(24):3463-6.
OBJECTIVE: To study the chemical constituents of the dried rhizome of Ardisia gigantifolia. METHOD: The 60% ethanol extract was extracted with EtOAc, and then separated and purified by column chromatography using silica gel and preparative HPLC. Their structures were identified on the basis of spectral analysis and physico-chemical properties. RESULT: Nine compounds were isolated and identified as 11-O-galloylbergenin (1), 11-O-Syringylbergenin (2), 11-O-protocatechuoylbergenin (3), 4-O-galloylbergenin (4), 11 -O-vanilloylbergenin (5), (-) -epicatechin-3-gallate (6), stigmasterol-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (7), (-) -4'-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl-beta-D-[6-O-(4"-hydroxy-3", 5"-dimethoxybenzoyl)] -glucopyranoside (8), and beta-sitosterol (9). CONCLUSION: Compounds 3, 4 and 7 were isolsted from the genus Ardisia for the first time, while compounds 1, 2, 5 and 6 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
[Studies on the chemical constituents of Ardisia crenata Sims].[Pubmed:2635600]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 1989 Dec;14(12):737-9, 762-3.
A new bergenin derivative isolated from the root of Ardisia crenata was determined to be 11-O-Syringylbergenin by spectral methods. Other compounds were identified as spinasterol, series fatty acids, beta-sitosterol-beta-D-glucoside, norbergenin and sucrose respectively. The last three were obtained for the first time from the genus of Ardisia.


