Erucic acidCAS# 112-86-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 112-86-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281116.0 | Appearance | Powder |
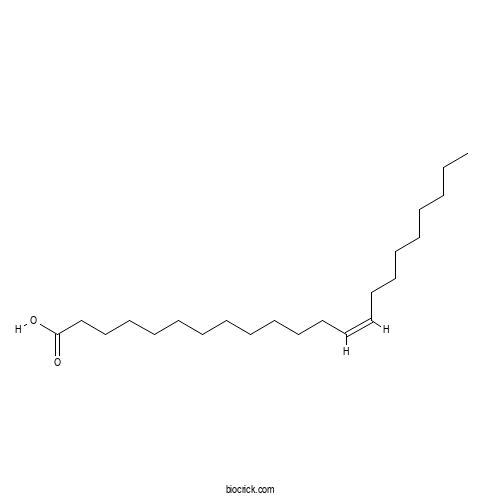
| Formula | C22H42O2 | M.Wt | 338.58 |
| Type of Compound | Aliphatics | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (Z)-docos-13-enoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DPUOLQHDNGRHBS-KTKRTIGZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H42O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20-21-22(23)24/h9-10H,2-8,11-21H2,1H3,(H,23,24)/b10-9- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Erucic acid Dilution Calculator

Erucic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9535 mL | 14.7676 mL | 29.5351 mL | 59.0702 mL | 73.8378 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5907 mL | 2.9535 mL | 5.907 mL | 11.814 mL | 14.7676 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2954 mL | 1.4768 mL | 2.9535 mL | 5.907 mL | 7.3838 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0591 mL | 0.2954 mL | 0.5907 mL | 1.1814 mL | 1.4768 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0295 mL | 0.1477 mL | 0.2954 mL | 0.5907 mL | 0.7384 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Dihydrohelenalin
Catalog No.:BCX1489
CAS No.:34257-95-9
- 12-Hydroxyganoderenic acid B
Catalog No.:BCX1488
CAS No.:1309931-84-7
- Paroxetine Impurity A Hydrochloride salt
Catalog No.:BCX1487
CAS No.:1394842-91-1
- Fluvoxamine Impurity D
Catalog No.:BCX1486
CAS No.:61718-80-7
- Aceclofenac impurity I
Catalog No.:BCX1485
CAS No.:15362-40-0
- Monbarbatain A
Catalog No.:BCX1484
CAS No.:138711-55-4
- Gymconopin C
Catalog No.:BCX1483
CAS No.:844493-85-2
- (±)-Taxifolin
Catalog No.:BCX1482
CAS No.:24198-97-8
- Purpurogallin carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1481
CAS No.:5146-12-3
- Ganoderic acid Epsilon
Catalog No.:BCX1480
CAS No.:294674-05-8
- 20(S)-25-Hydroxyprotopanaxadiol
Catalog No.:BCX1479
CAS No.:66007-91-8
- 20(S)-25-Methoxyprotopanaxadiol
Catalog No.:BCX1478
CAS No.:66007-93-0
- ent-kauran-16β,17-diol
Catalog No.:BCX1491
CAS No.:16836-31-0
- Ginsenoside CY
Catalog No.:BCX1492
CAS No.:83480-65-3
- 7,4'-Di-O-methyltectorigenin
Catalog No.:BCX1493
CAS No.:13186-08-8
- 11-O-Syringylbergenin
Catalog No.:BCX1494
CAS No.:126485-47-0
- 12β-Acetoxycoccinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1495
CAS No.:125247-74-7
- 9-epi-6-Methoxygeniposidic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1496
CAS No.:1215178-87-2
- Denthyrsinin
Catalog No.:BCX1497
CAS No.:118169-17-8
- Confusarin
Catalog No.:BCX1498
CAS No.:108909-02-0
- Swertiaside
Catalog No.:BCX1499
CAS No.:96087-14-8
- Potentillanoside A
Catalog No.:BCX1500
CAS No.:1309589-79-4
- Homocapsaicin II
Catalog No.:BCX1501
CAS No.:71240-51-2
- Regaloside E
Catalog No.:BCX1502
CAS No.:123134-21-4
Morpho-Physiochemical Indices and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal the Role of Glucosinolate and Erucic Acid in Response to Drought Stress during Seed Germination of Rapeseed.[Pubmed:38542283]
Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 14;25(6):3308.
The global expansion of rapeseed seed quality has been focused on maintaining glucosinolate (GSL) and Erucic acid (EA) contents. However, the influence of seed GSL and EA contents on the germination process under drought stress remains poorly understood. Herein, 114 rapeseed accessions were divided into four groups based on GSL and EA contents to investigate their performance during seed imbibition under drought stress. Our results revealed significant variations in seed germination-related traits, particularly with higher GSL and EA, which exhibited higher germination % (G%) and lower mean germination time (MGT) under drought stress conditions. Moreover, osmoregulation, enzymatic system and hormonal regulation were improved in high GSL and high EA (HGHE) versus low GSL and low EA (LGLE) seeds, indicating the essential protective role of GSL and EA during the germination process in response to drought stress. The transcriptional regulation mechanism for coordinating GSL-EA-related pathways in response to drought stress during seed imbibition was found to involve the differential expression of sugar metabolism-, antioxidant-, and hormone-related genes with higher enrichment in HGHE compared to LGLE seeds. GO enrichment analysis showed higher variations in transcription regulator activity and DNA-binding transcription factors, as well as ATP and microtubule motor activity in GSL-EA-related pathways. Furthermore, KEGG analysis identified cellular processes, environmental information processing, and metabolism categories, with varied gene participation between GSL, EA and GSL-EA-related pathways. For further clarification, QY7 (LGLE) seeds were primed with different concentrations of GSL and EA under drought stress conditions. The results showed that 200 mumol/L of GSL and 400 mumol/L of EA significantly improved G%, MGT, and seedling fresh weight, besides regulating stress and fatty acid responsive genes during the seed germination process under drought stress conditions. Conclusively, exogenous application of GSL and EA is considered a promising method for enhancing the drought tolerance of LGLE seeds. Furthermore, the current investigation could provide a theoretical basis of GSL and EA roles and their underlying mechanisms in stress tolerance during the germination process.
Allelochemicals-mediated interaction between algae and bacteria: Direct and indirect contact.[Pubmed:38437966]
Bioresour Technol. 2024 Apr;398:130525.
Secondary metabolites with bioactivity are allelochemicals. This study adopted direct contact (R0) and indirect contact (separated by 0.45 microm membrane, R1-A for algae, R1-S for sludge) to reveal the role of metabolites especially allelochemicals on interaction of bacteria and algae. Direct contact exhibited better nutrients removal than indirect contact, due to less antibacterial allelochemicals and oxidative stress. Bacterial signaling molecules were not detected. The major algae-derived allelochemicals were 13-Docosenamide, 9-Octadecenamide, n-Hexadecanoic acid, Erucic acid, octadecanoic acid, beta-sitosterol, and E,E,Z-1,3,12-Nonadecatriene-5,14-diol. Furthermore, presence of 13-Docosenamide and 9-Octadecenamide was associated with succession of Flavobacterium and suppression of nitrifying bacteria (Nitrosomonas, Ellin6067, and Nitrospira). Direct contact stimulated denitrifying bacteria Saccharimonadales and algae Scenedesmus, whereas indirect contact is friendly to Dechloromonas, Competibacter, nitrifying bacteria, algae Desmodesmus and Dictyosphaerium. This study highlights the essentiality of cell contact of bacteria-algae in establishing synergy, as cell contact mitigates antagonistic effect induced by metabolites.
Quantitative Analysis of Nervonic and Erucic Acids in Human Milk: Comparison with Infant Formula with Different Fat Sources and Nutritional Stages.[Pubmed:38432997]
J Oleo Sci. 2024;73(3):333-340.
This study aims to quantitatively analyze nervonic (C24:1 n-9) and erucic (C22:1 n-9) acids in human milk (HM) collected from Korean mothers, along with the infant formulas (IFs) with different fat sources and nutritional stages. The content of nervonic and Erucic acids in HM from Korean mothers were 2.13 and 2.81 mg/100 g, accounting for 0.06 and 0.08% of the total fatty acids (FAs), respectively. These acids in IFs based on fat from plant-oil formula were higher than those in IFs based on cow milk formula. The composition of Erucic acid in IFs based on cow milk formula and plant-oil formula increased with the nutritional stages, while nervonic acid only increased in IFs based on the plant-oil formula.
Sesame bacterial wilt significantly alters rhizosphere soil bacterial community structure, function, and metabolites in continuous cropping systems.[Pubmed:38402727]
Microbiol Res. 2024 May;282:127649.
Bacterial wilt is the leading disease of sesame and alters the bacterial community composition, function, and metabolism of sesame rhizosphere soil. However, its pattern of change is unclear. Here, the purpose of this study was to investigate how these communities respond to three differing severities of bacterial wilt in mature continuously cropped sesame plants by metagenomic and metabolomic techniques, namely, absence (WH), moderate (WD5), and severe (WD9) wilt. The results indicated that bacterial wilt could significantly change the bacterial community structure in the rhizosphere soil of continuously cropped sesame plants. The biomarker species with significant differences will also change with increasing disease severity. In particular, the gene expression levels of Ralstonia solanacearum in the WD9 and WD5 treatments increased by 25.29% and 33.61%, respectively, compared to those in the WH treatment (4.35 log(10) copies g-1). The occurrence of bacterial wilt significantly altered the functions of the bacterial community in rhizosphere soil. KEEG and CAZy functional annotations revealed that the number of significantly different functions in WH was greater than that in WD5 and WD9. Bacterial wilt significantly affected the relative content of metabolites, especially acids, in the rhizosphere soil, and compared with those in the rhizosphere soil from WH, 10 acids (including S-adenosylmethionine, N-acetylleucine, and desaminotyrosine, etc.) in the rhizosphere soil from WD5 or WD9 significantly increased. In comparison, the changes in the other 10 acids (including hypotaurine, Erucic acid, and 6-hydroxynicotinic acid, etc.) were reversed. The occurrence of bacterial wilt also significantly inhibited metabolic pathways such as ABC transporter and amino acid biosynthesis pathways in rhizosphere soil and had a significant impact on two key enzymes (1.1.1.11 and 2.6.1.44). In conclusion, sesame bacterial wilt significantly alters the rhizosphere soil bacterial community structure, function, and metabolites. This study enhances the understanding of sesame bacterial wilt mechanisms and lays the groundwork for future prevention and control strategies against this disease.
[Analysis of contents of different kinds of fatty acids in carotid atherosclerotic plaques].[Pubmed:38281799]
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Jan 30;104(5):325-331.
Objective: To analyze the contents of different kinds of fatty acids in carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Methods: A total of 24 patients who underwent carotid endarterectomy at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University from October 2021 to September 2022 due to moderate and severe carotid artery stenosis were retrospectively enrolled, including 20 males and 4 females, with a median age[M(Q(1), Q(3))] of 68.5 (63.5, 72.3) years. According to the symptoms of cerebral ischemia, the patients were divided into a symptomatic group (12 cases) and an asymptomatic group (12 cases). Regarding the pathological characteristics, the patients were divided into a stable group (14 cases) and a vulnerable group (10 cases) according to carotid plaque pathology scores. The expression differences of different types of fatty acids in carotid plaques were analyzed by targeted fatty acid metabolomics technology based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-MS/MS) analysis. Results: In the 24 samples, the median amount of fatty acids [M (Q(1), Q(3))] was 1 113 (330, 5 897) ng/g. A total of 13 medium and long-chain fatty acids were detected, including saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids and polyunsaturated fatty acids. The content of saturated fatty acids was 584 (290, 9 888) ng/g, accounting for the highest proportion of 51.8%. The content of polyunsaturated fatty acids was 1 444 (393, 4 264) ng/g, accounting for 44.4%. The content of monounsaturated fatty acids was 2 793 (1 558, 3 247) ng/g, accounting for 3.8%. The contents of linoleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid and oleic acid in carotid plaques in the symptomatic group were 1 760 (581, 3 006), 682 (527, 886) and 2 081 (1 358, 2 907) ng/g, respectively, which were lower than those in the asymptomatic group 3 149 (2 226, 4 683), 1 423 (964, 2 270) and 3 178 (2 352, 3 993) ng/g (all P<0.05). The contents of linoleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid and oleic acid in carotid plaques in the vulnerable group were 1 537 (588, 2 921), 649 (477, 850) and 2 081 (1 129, 2 831) ng/g, respectively, which were lower than those in the stable group 3 149 (2 047, 4 416), 1 423 (940, 2 184) and 3 091 (2 201, 3 973) ng/g (all P<0.05). There were no significant differences in the contents of 11, 14-eicosadienoic acid, gamma-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, arachidonic acid, Erucic acid, margaric acid, pentadecanoic acid, stearic acid, dodecanoic acid and palmitic acid (all P>0.05). Conclusions: Saturated fatty acids are the main type in carotid plaques. The contents of oleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid and linoleic acid decrease in vulnerable plaques.
Transcriptome Profiling, Physiological and Biochemical Analyses Reveal Comprehensive Insights in Cadmium Stress in Brassica carinata L.[Pubmed:38279259]
Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 19;25(2):1260.
With the constant progress of urbanization and industrialization, cadmium (Cd) has emerged as one of the heavy metals that pollute soil and water. The presence of Cd has a substantial negative impact on the growth and development of both animals and plants. The allotetraploid Brasscia. carinata, an oil crop in the biofuel industry, is known to produce seeds with a high percentage of Erucic acid; it is also known for its disease resistance and widespread adaptability. However, there is limited knowledge regarding the tolerance of B. carinata to Cd and its physiological responses and gene expressions under exposure to Cd. Here, we observed that the tested B. carinata exhibited a strong tolerance to Cd (1 mmol/L CdCl(2) solution) and exhibited a significant ability to accumulate Cd, particularly in its roots, with concentrations reaching up to 3000 mg/kg. Additionally, we found that the total oil content of B. carinata seeds harvested from the Cd-contaminated soil did not show a significant change, but there were noticeable alterations in certain constituents. The activities of antioxidant enzymes, including catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX), were observed to significantly increase after treatment with different concentrations of CdCl(2) solutions (0.25 mmol/L, 0.5 mmol/L, and 1 mmol/L CdCl(2)). This suggests that these antioxidant enzymes work together to enhance Cd tolerance. Comparative transcriptome analysis was conducted to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the shoots and roots of B. carinata when exposed to a 0.25 mmol/L CdCl(2) solution for 7 days. A total of 631 DEGs were found in the shoots, while 271 DEGs were found in the roots. It was observed that these selected DEGs, which responded to Cd stress, also showed differential expression after exposure to PbCl(2). This suggests that B. carinata may employ a similar molecular mechanism when tolerating these heavy metals. The functional annotation of the DEGs showed enrichment in the categories of 'inorganic ion transport and metabolism' and 'signal transduction mechanisms'. Additionally, the DEGs involved in 'tryptophan metabolism' and 'zeatin biosynthesis' pathways were found to be upregulated in both the shoots and roots of B. carinata, suggesting that the plant can enhance its tolerance to Cd by promoting the biosynthesis of plant hormones. These results highlight the strong Cd tolerance of B. carinata and its potential use as a Cd accumulator. Overall, our study provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying heavy metal tolerance in B. carinata.
The functional divergence of homologous GPAT9 genes contributes to the erucic acid content of Brassica napus seeds.[Pubmed:38262947]
BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jan 24;24(1):69.
BACKGROUND: The early allopolyploid Brassica napus was a hybrid of two Brassica species, that had undergone a whole genome duplication event followed by genome restructuring, including deletions and small scale duplications. A large number of homologous genes appeared functional divergence during species domestication. Due to the high conservation of de novo glycerolipid biosynthesis, multiple homologues of glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases (GPATs) have been found in B. napus. Moreover, the functional variances among these homologous GPAT-encoding genes are unclear. RESULTS: In this study, four B. napus homologous genes encoding glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 9 (BnaGPAT9) were characterized. Although a bioinformatics analysis indicated high protein sequence similarity, the homologues demonstrated tissue-specific expression patterns and functional divergence. Yeast genetic complementation assays revealed that BnaGPAT9-A1/C1 homologues but not BnaGPAT9-A10/C9 homologues encoded functional GPAT enzymes. Furthermore, a single nucleotide polymorphism of BnaGPAT9-C1 that occurred during the domestication process was associated with enzyme activity and contributed to the fatty acid composition. The seed-specific expression of BnGPAT9-C1(1124A) increased the Erucic acid content in the transformant seeds. CONCLUSIONS: This study revealed that BnaGPAT9 gene homologues evolved into functionally divergent forms with important roles in Erucic acid biosynthesis.
Acer truncatum Bunge seed oil ameliorated oxaliplatin-induced demyelination by improving mitochondrial dysfunction via the Pink1/Parkin mitophagy pathway.[Pubmed:38205834]
Food Funct. 2024 Feb 5;15(3):1355-1368.
Dietary nutritional support for special populations is an effective and feasible method to improve the quality of life of patients and reduce medical pressure. Acer truncatum Bunge seed oil (ATSO) is widely recognized for its ability to promote nerve myelin regeneration. To evaluate the ameliorative effects of ATSO on chemotherapy-induced demyelination, a zebrafish model of chemotherapy-induced demyelination was established. The results showed that 100 mug mL(-1) of ATSO reversed tail morphology damage, axon degeneration, touch response delay, ROS level upregulation and the expression of myelin basic protein decrease in chemotherapy-induced zebrafish. In addition, the expression of myelin markers (including sox10, krox20, and pmp22) in oxaliplatin-induced cells was markedly reversed by ATSO and its active components (gondoic acid, Erucic acid, and nervonic acid). ATSO and its active components could reverse demyelination by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction. Conversely, linoleic acid and linolenic acid promoted demyelination by exacerbating mitochondrial dysfunction. Moreover, the Pink1/Parkin pathway was recognized as the main reason for ATSO and its active components improving mitochondrial function by activating mitophagy and restoring autophagic flow. Taken together, this study demonstrated that ATSO and its active components could be further developed as novel functional food ingredients to antagonize demyelination.
Identification of potential biomarkers for diabetic cardiomyopathy using LC-MS-based metabolomics.[Pubmed:38180052]
Endocr Connect. 2024 Jan 25;13(3):e230384.
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a serious complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) that contributes to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. However, the metabolic alterations and specific biomarkers associated with DCM in T2DM remain unclear. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive metabolomic analysis using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to investigate the plasma metabolite profiles of T2DM patients with and without DCM. We identified significant differences in metabolite levels between the groups, highlighting the dysregulation of various metabolic pathways, including starch and sucrose metabolism, steroid hormone biosynthesis, tryptophan metabolism, purine metabolism, and pyrimidine metabolism. Although several metabolites showed altered abundance in DCM, they also shared characteristics of DCM and T2DM rather than specific to DCM. Additionally, through biomarker analyses, we identified potential biomarkers for DCM, such as cytidine triphosphate, 11-ketoetiocholanolone, saccharopine, nervonic acid, and Erucic acid. These biomarkers demonstrated distinct patterns and associations with metabolic pathways related to DCM. Our findings provide insights into the metabolic changes associated with DCM in T2DM patients and highlight potential biomarkers for further validation and clinical application. Further research is needed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and validate the diagnostic and prognostic value of these biomarkers in larger cohorts.
Neuroprotective potential of erucic acid via inhibition of N2a cell lines and rotenone induced Parkinson's disease rat model.[Pubmed:38174534]
Indian J Pharmacol. 2023 Nov-Dec;55(6):376-384.
OBJECTIVE: The objective of this study was to investigate the potential for Erucic acid (EA), an omega-9 monounsaturated fatty acid, to act as a neuroprotective agent. MATERIALS AND METHODS: In this study, EA was investigated against N2a cell lines and a rotenone (ROT)-induced model of Parkinson's disease for its neuroprotective potential. The N2a cell line was incubated with fetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin supplemented with Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium, and the following assays were carried out: (i) MTT, (ii) biocompatibility, (iii) DCFDA, and (iv) diphenylamine. A cell morphology study was also performed. Further, ROT 1 mg/kg s.c. and EA 3 and 10 mg/kg p.o. were given to rats on a daily basis for 21 days, and the following parameters were assessed: (i) neurobehavioral studies, (ii) oxidative stress markers, (iii) neuroinflammatory markers, (iv) neurotransmitters, and (v) histopathological study. RESULTS: The cell viability assay revealed that EA showed protection against ROT-induced toxicity in N2a cells, which was confirmed by a cell morphology study. EA decreased oxidative stress and % DNA fragmentation significantly. EA also prevented ROT-induced motor impairment and altered levels of oxidative stress markers, neurotransmitters, and neuroinflammatory markers significantly. When compared to the ROT group, a histological investigation of the EA group showed partial neuronal loss with the existence of intact neurons in between the vacuolated gaps. CONCLUSION: This study revealed that EA possesses profound neuroprotective properties in in vitro and in vivo studies. Additional research can be carried out to study the mechanism of EA with respect to its neuroprotective potential.
Carcass composition and physicochemical and sensory attributes of breast and leg meat from native Mexican guajolote (Meleagris g. gallopavo) as influenced by sex.[Pubmed:38111389]
Arch Anim Breed. 2023 Nov 20;66(4):341-355.
The aim of the study was to compare carcass composition and physicochemical and sensory attributes of breast and leg meat from native Mexican guajolote (Meleagris g. gallopavo) as influenced by sex. For this, slaughter weight and carcass characteristics of male (n = 8) and female (n = 8) guajolotes raised traditionally under extensive systems with similar housing and feeding conditions were recorded. Also, physical characteristics, proximate composition, the fatty acid profile, and sensory attributes were determined in breast and leg meat using standard procedures. The results showed that males had higher (P<0.001) slaughter weight, hot and cold carcass weights, and dressing percentage, as well as carcass part weights, while females had higher (P<0.001) abdominal fat weights than males. The lightness (L*), yellowness (b*), and drip loss values of breast meat, as well as redness (a*) and water-holding capacity values of leg meat, were significantly (P<0.05) influenced by sex. Male breast meat had higher (P<0.05) moisture content, crude protein, Erucic acid (C22:1n9), summation operator MUFAs (total monounsaturated fatty acids), summation operator UFAs (unsaturated fatty acids), summation operator DFAs (desirable fatty acids), summation operator UFA / summation operator SFA (total saturated fatty acid) ratio, summation operator PUFA (total polyunsaturated fatty acid) / summation operator SFA ratio, and chewiness scores than females. Likewise, leg meat from males showed higher (P<0.05) ash content, myristic acid (C14:0), palmitic acid (C16:0), stearic acid (C18:0), oleic acid (C18:1n9c), palmitoleic acid (C16:1n7), summation operator SFAs, summation operator OFAs (odd fatty acids), thrombogenic index, and atherogenic index, whereas females had high fat content. In conclusion, it would be suggested that, from a nutritional point of view, the meat from male guajolotes was preferable to the meat from females.
Effects of Supplementing Growing-Finishing Crossbred Pigs with Glycerin, Vitamin C and Niacinamide on Carcass Characteristics and Meat Quality.[Pubmed:38066986]
Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 24;13(23):3635.
The objective of this study was to determine the influence of supplementing the diet of growing-finishing pigs with glycerin and/or a mixture of vitamin C and niacinamide on carcass traits and pork quality. Eighty-four weaned piglets with an initial average body weight of 20.35 +/- 2.14 kg were assigned, at random, to four groups for a 103-day feeding experiment: control; glycerin-supplemented group; vitamin C and niacinamide-supplemented group; and glycerin, vitamin C and niacinamide-supplemented group. At the end of the experiment, three pigs/group were randomly selected and slaughtered, and samples were collected for analysis. The results indicated that supplementing crossbred pigs with glycerin, vitamin C and niacinamide simultaneously increased the redness (a*) value (p < 0.05), glycerol content (p < 0.01) and myristoleic acid content (p < 0.01) in the longissimus dorsi and tended to increase the level of flavor amino acids, linoleic acid, linolenic acid and Erucic acid, as well as the percentage and density of type I myofibers in the longissimus dorsi and the semimembranosus muscle. Glycerin had an influence (p < 0.01) on the Erucic acid content in the longissimus dorsi and the semimembranosus muscle, and vitamin C and niacinamide had an interaction effect (p < 0.05) on the redness (a*) value of the longissimus dorsi. Glycerin, vitamin C and niacinamide supplementation in the diet of crossbred pigs improved the color, flavor and nutritional value of pork, which contributed to an increased intent to purchase this product.
Review of the potential pharmacological role of erucic acid: a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid.[Pubmed:38060041]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 7.
This comprehensive review aims to provide an overview of the pharmacological properties of Erucic acid (EA) and highlight areas that require further research. EA is an omega-9 fatty acid found in certain vegetable oil, such as rapeseed oil has demonstrated favourable effects in rodents, including ameliorating myocardial lipidosis (fat accumulation in the heart muscle), congestive heart disease, hepatic steatosis (fat accumulation in the liver), and memory impairments. These findings have prompted regulatory bodies to establish limits on EA content in food oils. The studies were performed on rodents and led to caution on ingesting the EA at high levels. Moreover, EA is frequently utilized as a nutritional supplement for the treatment of adrenoleukodystrophy, myocardial disease, and memory improvement. The review of the article indicated that EA improves cognitive function, has a part in Huntington's disease, interacts with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, inhibits elastase and thrombin, has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumour properties, and inhibits influenza A virus. This article elucidates the pharmacological effects of EA, an omega-9 fatty acid.
Morphological, Biochemical, and Molecular Characterization of Exotic Brassica Germplasm.[Pubmed:38046330]
ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 14;8(47):44773-44783.
Oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) is an important oilseed crop. We examined the diversity of germplasm expressed at three distinct levels (i.e., morphological, biochemical, and DNA levels). In this study, 150 B. napus L. accessions with three check varieties were provided by Bioresources Conservation Institute. The germplasm was grown in field conditions for data collection of 15 quantitative and nine qualitative agro-morphological traits. The result indicated that for 15 quantitative agro-morphological traits, the highest coefficient of variation was recorded for plant height and days to flowering initiation. For nine qualitative traits, most of the accessions have a spatulate leaf, brown color seeds, yellow flowers, and erect silique attitude. The best adoptable genetically diverse exotic Brassica germplasms were selected, i.e., accessions 24178, 24881, 24199, 24214, 24242, and 24192. Based on biochemical analysis for high oil content and high oleic acid content, chakwal sarsoon and accession 24192 were selected. For high oleic and linoleic acids, accession 24181 performed best, for low Erucic acid accessions 24177 and 24195. Based on molecular (SSR) markers, the top 50 selected genotypes were evaluated with 30 SSR markers. The 47 genotypes with three check varieties were clustered in six major groups; the coefficient of similarity ranged between 0.18 and 1.00. Based on SSR data, the germplasms accession 24178 and Abasin were the most diverse genotypes. These genotypes have the capacity and could be used in future breeding programs. High genetic variations were investigated through the SSR among the studied genotypes of Brassica napus L. The present study also concluded that SSR is a better technique for intraspecific genetic diversity. Other modern techniques should be applied such as SNIP for the investigation of a high level of genetic diversity among crop plants in the future.
Genomics of predictive radiation mutagenesis in oilseed rape: modifying seed oil composition.[Pubmed:37921406]
Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Mar;22(3):738-750.
Rapeseed is a crop of global importance but there is a need to broaden the genetic diversity available to address breeding objectives. Radiation mutagenesis, supported by genomics, has the potential to supersede genome editing for both gene knockout and copy number increase, but detailed knowledge of the molecular outcomes of radiation treatment is lacking. To address this, we produced a genome re-sequenced panel of 1133 M(2) generation rapeseed plants and analysed large-scale deletions, single nucleotide variants and small insertion-deletion variants affecting gene open reading frames. We show that high radiation doses (2000 Gy) are tolerated, gamma radiation and fast neutron radiation have similar impacts and that segments deleted from the genomes of some plants are inherited as additional copies by their siblings, enabling gene dosage decrease. Of relevance for species with larger genomes, we showed that these large-scale impacts can also be detected using transcriptome re-sequencing. To test the utility of the approach for predictive alteration of oil fatty acid composition, we produced lines with both decreased and increased copy numbers of Bna.FAE1 and confirmed the anticipated impacts on Erucic acid content. We detected and tested a 21-base deletion expected to abolish function of Bna.FAD2.A5, for which we confirmed the predicted reduction in seed oil polyunsaturated fatty acid content. Our improved understanding of the molecular effects of radiation mutagenesis will underpin genomics-led approaches to more efficient introduction of novel genetic variation into the breeding of this crop and provides an exemplar for the predictive improvement of other crops.


