6-MethylflavoneCAS# 29976-75-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 29976-75-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 689013.0 | Appearance | Powder |
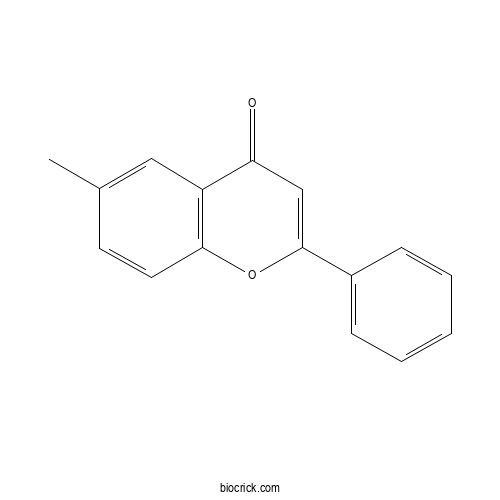
| Formula | C16O2H12 | M.Wt | 236.27 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 6-methyl-2-phenylchromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)OC(=CC2=O)C3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NOQJBXPAMJLUSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H12O2/c1-11-7-8-15-13(9-11)14(17)10-16(18-15)12-5-3-2-4-6-12/h2-10H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

6-Methylflavone Dilution Calculator

6-Methylflavone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.2324 mL | 21.1622 mL | 42.3245 mL | 84.6489 mL | 105.8111 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8465 mL | 4.2324 mL | 8.4649 mL | 16.9298 mL | 21.1622 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4232 mL | 2.1162 mL | 4.2324 mL | 8.4649 mL | 10.5811 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0846 mL | 0.4232 mL | 0.8465 mL | 1.693 mL | 2.1162 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0423 mL | 0.2116 mL | 0.4232 mL | 0.8465 mL | 1.0581 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cis-Ligupurpuroside B
Catalog No.:BCX0764
CAS No.:350588-96-4
- 3,4'-Dihydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX0763
CAS No.:14919-49-4
- Prosapogenin D
Catalog No.:BCX0762
CAS No.:103629-72-7
- Oleuropeinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0761
CAS No.:96382-90-0
- Mogroside VI B
Catalog No.:BCX0760
CAS No.:2149606-17-5
- Pulchinenoside E4
Catalog No.:BCX0759
CAS No.:1415553-83-1
- Mogroside VI A
Catalog No.:BCX0758
CAS No.:2146088-13-1
- Anemarrhenasaponin A2
Catalog No.:BCX0757
CAS No.:117210-12-5
- Ergothioneine
Catalog No.:BCX0756
CAS No.:497-30-3
- Dihydroferulic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0755
CAS No.:1135-23-5
- luteolin-7-O-gentiobiside
Catalog No.:BCX0754
CAS No.:70855-41-3
- Kuwanon T
Catalog No.:BCX0753
CAS No.:100187-66-4
- Methyl Vanillate
Catalog No.:BCX0766
CAS No.:3943-74-6
- L-Amygdalin
Catalog No.:BCX0767
CAS No.:29883-16-7
- 2α,6β,23-trihydroxyl oleanolic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0768
CAS No.:564-13-6
- Hirudonucleodisulfide B
Catalog No.:BCX0769
CAS No.:1072789-38-8
- Hederoside D2
Catalog No.:BCX0770
CAS No.:20853-58-1
- (Z)-9-Nonadecene
Catalog No.:BCX0771
CAS No.:51865-02-2
- 2-Hydroxycinnamicaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCX0772
CAS No.:3541-42-2
- Nardoguaianone K
Catalog No.:BCX0773
CAS No.:443128-65-2
- 2,3-dihydroxypropyl 9-octadecenoate
Catalog No.:BCX0774
CAS No.:251983-54-7
- 20-Deoxy,5-benzoyl-Ingenol
Catalog No.:BCX0775
CAS No.:54706-97-7
- Maltotriose
Catalog No.:BCX0776
CAS No.:1109-28-0
- Verrucosin
Catalog No.:BCX0777
CAS No.:83198-63-4
Inhibitory interaction of flavonoids with organic cation transporter 2 and their structure-activity relationships for predicting nephroprotective effects.[Pubmed:37057715]
J Appl Toxicol. 2023 Oct;43(10):1421-1435.
Organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2) is mainly responsible for the renal secretion of various cationic drugs, closely associated with drug-induced acute kidney injury (AKI). Screening and identifying potent OCT2 inhibitors with little toxicity in natural products in reducing OCT2-mediated AKI is of great value. Flavonoids are enriched in various vegetables, fruits, and herbal products, and some were reported to produce transporter-mediated drug-drug interactions. This study aimed to screen potential inhibitors of OCT2 from 96 flavonoids, assess the nephroprotective effects on cisplatin-induced kidney injury, and clarify the structure-activity relationships of flavonoids with OCT2. Ten flavonoids exhibited significant inhibition (>50%) on OCT2 in OCT2-HEK293 cells. Among them, the six most potent flavonoid inhibitors, including pectolinarigenin, biochanin A, luteolin, chrysin, 6-hydroxyflavone, and 6-Methylflavone markedly decreased cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity. Moreover, in cisplatin-induced renal injury models, they also reduced serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels to different degrees, the best of which was 6-Methylflavone. The pharmacophore model clarified that the aromatic ring, hydrogen bond acceptors, and hydrogen bond donors might play a vital role in the inhibitory effect of flavonoids on OCT2. Thus, our findings would pave the way to predicting the potential risks of flavonoid-containing food/herb-drug interactions in humans and optimizing flavonoid structure to alleviate OCT2-related AKI.
Inhibition of Bitter Taste from Oral Tenofovir Alafenamide.[Pubmed:33824185]
Mol Pharmacol. 2021 May;99(5):319-327.
Children have difficulty swallowing capsules. Yet, when presented with liquid formulations, children often reject oral medications due to their intense bitterness. Presently, effective strategies to identify methods, reagents, and tools to block bitterness remain elusive. For a specific bitter-tasting drug, identification of the responsible bitter receptors and discovery of antagonists for those receptors can provide a method to block perceived bitterness. We have identified a compound (6-Methylflavone) that can block responses to an intensely bitter-tasting anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) drug, tenofovir alafenamide (TAF), using a primary human taste bud epithelial cell culture as a screening platform. Specifically, TAS2R39 and TAS2R1 are the main type 2 taste receptors responding to TAF observed via heterologously expressing specific TAS2R receptors into HEK293 cells. In this assay, 6-Methylflavone blocked the responses of TAS2R39 to TAF. In human sensory testing, 8 of 16 subjects showed reduction in perceived bitterness of TAF after pretreating (or "prerinsing") with 6-Methylflavone and mixing 6-Methylflavone with TAF. Bitterness was completely and reliably blocked in two of these subjects. These data demonstrate that a combined approach of human taste cell culture-based screening, receptor-specific assays, and human psychophysical testing can successfully discover molecules for blocking perceived bitterness of pharmaceuticals, such as the HIV therapeutic TAF. Our hope is to use bitter taste blockers to increase medical compliance with these vital medicines. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Identification of a small molecule that inhibits bitter taste from tenofovir alafenamide may increase the compliance in treating children with human immunodeficiency virus infections.
Inhibition of Proinflammatory Cytokine Release by Flavones and Flavanones from the Leaves of Dracaena steudneri Engl.[Pubmed:33285592]
Planta Med. 2021 Mar;87(3):209-217.
The leaves of Dracaena steudneri yielded 6 new flavonoids-3,5,7-trihydroxy-6-methyl-3',4'-methylenedioxyflavone (1: ), 5,7-dihydroxy-3-methoxy-6-methyl-3',4'-methylenedioxyflavone (2: ), 3,5,7-trihydroxy-6-methoxy-3',4'-methylenedioxyflavone (3: ), (2S,3S)-3,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-3',4'-methylenedioxyflavanone (4: ), 4',5,7-trihydroxy-3,3',8-trimethoxy-6-Methylflavone (5: ), (2R) 7-hydroxy-2',8-dimethoxyflavanone (6: )-together with 13 known congeners. Their structures were established using spectroscopic and spectrometric methods including NMR, CD, and HRMS(n) measurements. The compounds were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory potential through measurement of the levels of cytokines IL-1beta, IL-2, GM-CSF, and TNF-alpha in the supernatant of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide. Flavones derivatives 1: -4: with a C-3'/4' methylenedioxy substituent led to a substantial increase in the production of IL-1beta and GM-CSF out of 4 pro-inflammatory cytokines relative to LPS control. Quercetin derivatives 5, 11,: and 13: with a hydroxyl group at C-4' inhibited the production of IL-2, GM-CSF, and TNF-alpha. The presence of a C-2/C-3 double bond in 14: was pivotal to the significantly stronger (0.4 to 27.5% of LPS control) inhibitory effect compared to its dihydro derivative 8: (36.2 to 262.7% of LPS control) against all tested cytokines. It is important to note that the inhibitory activity of 14: was substantially higher than that of the standard drug used, ibuprofen.
Involvement of selective GABA-A receptor subtypes in amelioration of cisplatin-induced neuropathic pain by 2'-chloro-6-methyl flavone (2'-Cl-6MF).[Pubmed:33221972]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2021 May;394(5):929-940.
Cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathic pain is a common adverse effect of chemotherapy. The present study evaluated the effects of 2'-chloro-6-Methylflavone (2'-Cl-6MF) at recombinant alpha1beta2gamma2L, alpha2beta1-3gamma2L, and alpha3beta1-3gamma2L GABA-A receptor subtypes expressed in Xenopus oocytes and subsequently evaluated its effectiveness in cisplatin-induced neuropathic pain. The results showed that 2'-Cl-6MF potentiated GABA-elicited currents at alpha2beta2/3gamma2L and alpha3beta2/3gamma2L GABA-A receptor subtypes. The potentiation was blocked by the co-application of flumazenil (a benzodiazepine (BDZs) site antagonist). In behavioral studies, mechanical allodynia was induced by intraplantar injection of cisplatin (40 mug/paw) in Sprague Dawley rats, and behavioral assessments were made 24 h after injection. 2'-Cl-6MF (1, 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg, i.p.), was administered 1 h before behavioral evaluation. Administration of 2'-Cl-6MF (30 and 100 mg/kg, i.p) significantly enhanced the paw withdrawal threshold and decreased mechanical allodynia. The standard drugs, gabapentin (GBP) at the dose of 70 mg/kg, and HZ 166 (16 mg/kg), i.p. also significantly enhanced the paw withdrawal threshold in mechanical allodynia. Pretreatment with pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) (15 mg/kg, i.p.) and flumazenil reversed the antinociceptive effect of 2'-Cl-6MF in mechanical allodynia indicating GABAergic mechanisms. Moreover, the binding mechanism of 2'-Cl-6MF was rationalized by in silico modeling tools. The 3D-coordinates of alpha2beta2gamma2L and alpha2beta3gamma2L were generated after homology modeling of the alpha2 subtype and 2'-Cl-6MF was at predicted binding sites of the developed models. The alpha2 model was compared with the alpha1 and alpha3 subunits via structural and sequence alignment. Molecular docking depicted that the compound binds efficiently at the neuromodulator binding site of the receptors. The findings of this study revealed that 2'-Cl-6MF ameliorated the manifestations of cisplatin-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Furthermore, we also conclude that GABAergic mechanisms may contribute to the antinociceptive effect of 2'-Cl-6MF. The molecular docking studies also confirm the involvement of the BDZs site of GABA-A receptors. It was observed that Ile230 of alpha2 stabilize the chlorophenyl ring of 2'-Cl-6MF through hydrophobic interactions, which is replaced by Val203 in alpha1 subunit. However, the smaller side chain of Val203 does not provide hydrophobic interaction to the compound due to high conformational flexibility of alpha1 subunit.
Vitex doniana Leaves Extract Ameliorates Alterations Associated with 7, 12-Dimethyl Benz[a]Anthracene-Induced Mammary Damage in Female Wistar Rats.[Pubmed:32223342]
Nutr Cancer. 2021;73(1):98-112.
Vitex doniana leaves are used traditionally in West Africa for the treatment of swellings and cancer. We investigated if Vitex doniana leaves extract could ameliorate 7, 12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)-induced mammary damage. Female Wistar rats aged 52 +/- 2 day were administered 80 mg/kg DMBA. After monitoring for 150 day, rats were administered 0, 50, 100, 200 mg/kg Vitex doniana and 20 mg/kg Tamoxifen for 14 day. Serum estrogen receptor-alpha, IL-1beta and TNF -alpha levels were determined using ELISA kits. Oxidative stress markers in mammary tissue homogenates were determined using standard spectrophotometric methods. Histopathological examination was done using hematoxylin and eosin staining and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression using immunohistochemistry. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was used to determine components present in the extract. Although tumors were not observed, significantly (p < 0.05) lower estrogen receptor-alpha, malondialdehyde, IL-1beta and TNF -alpha levels, significantly (p < 0.05) higher glutathione and catalase activity, attenuation of malignant epithelial hyperplasia and mild COX-2 expression were observed in rats administered Vitex doniana when compared to DMBA-induced untreated control. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of the V. doniana extract revealed the presence of 4,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-6-Methylflavone and vanillylamine, which are compounds with reported antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Collectively, treatment with Vitex doniana ameliorated some derangement observed in DMBA-induced rats.
Flavonoids from Mirabilis himalaica.[Pubmed:29421242]
Fitoterapia. 2018 Jun;127:89-95.
Six previously undescribed flavonoids, 2S-5-methoxy-6-methyl-7,2'-dihydroxyflavanone, 5,7,2'-trihydroxy-6-Methylflavone, 5,7,6'-trihydroxy-6-methylcoumaronochromone, 2,4',6'-trihydroxy-2'-methoxy-3'-methylchalcone, 6R,11-dimethoxy-9-hydroxyrotenoid, and 6R,11-dimethoxy-9-hydroxy-10-methylrotenoid, along with eight known flavonoids, including 2S-5-methoxy-6-methyl-7,4'-dihydroxyflavanone, not previously reported as a natural product, and seven rotenoids, boeravinone A, B, D, P, F, coccineone B, and mirabijalone E, were isolated from the ethyl acetate soluble fraction of Mirabilis himalaica roots. Their structures were established by the extensive spectroscopic analysis, including HRESIMS, UV, NMR and ECD. All compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities against three human cancer cell lines: A375 (melanoma), A549 (lung), and PLC (hepatoma).
The flavonoid, 2'-methoxy-6-methylflavone, affords neuroprotection following focal cerebral ischaemia.[Pubmed:29376464]
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 Jul;39(7):1266-1282.
Tonic inhibitory currents, mediated by extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors, are elevated at a delay following stroke. Flavonoids minimise the extent of cellular damage following stroke, but little is known about their mode of action. We demonstrate that the flavonoid, 2'-methoxy-6-Methylflavone (0.1-10 microM; 2'MeO6MF), increases GABA(A) receptor tonic currents presumably via delta-containing GABA(A) receptors. Treatment with 2'MeO6MF 1-6 h post focal ischaemia dose dependently decreases infarct volume and improves functional recovery. The effect of 2'MeO6MF was attenuated in delta(-/-) mice, indicating that the effects of the flavonoid were mediated via delta-containing GABA(A) receptors. Further, as flavonoids have been shown to have multiple modes of action, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of 2'MeO6MF. Using a macrophage cell line, we show that 2'MeO6MF can dampen an LPS-induced elevation in NFkB activity. Assessment of vehicle-treated stroke animals revealed a significant increase in circulating IL1beta, TNFalpha and IFgamma levels. Treatment with 2'MeO6MF dampened the stroke-induced increase in circulating cytokines, which was blocked in the presence of the pan-AKT inhibitor, GSK690693. These studies support the hypothesis that compounds that potentiate tonic inhibition via delta-containing GABA(A) receptors soon after stroke can afford neuroprotection.
Glycosylation of 6-methylflavone by the strain Isaria fumosorosea KCH J2.[Pubmed:28981527]
PLoS One. 2017 Oct 5;12(10):e0184885.
Entomopathogenic fungi are known for their ability to carry out glycosylation of flavonoids, which usually results in the improvement of their stability and bioavailability. In this study we used a newly isolated strain of the entomopathogenic filamentous fungus Isaria fumosorosea KCH J2 as a biocatalyst. Our aim was to evaluate its ability to carry out the biotransformation of flavonoids and to obtain new flavonoid derivatives. The fungus was isolated from a spider's carcass and molecularly identified using analysis of the ITS1-ITS2 rDNA sequence. As a result of biotransformation of 6-Methylflavone two new products were obtained: 6-Methylflavone 8-O-beta-D-(4"-O-methyl)-glucopyranoside and 6-Methylflavone 4'-O-beta-D-(4"-O-methyl)-glucopyranoside. Chemical structures of the products were determined based on spectroscopic methods (1H NMR, 13C NMR, COSY, HMBC, HSQC). Our research allowed us to discover a new species of filamentous fungus capable of carrying out glycosylation reactions and proved that I. fumosorosea KCH J2 is an effective biocatalyst for glycosylation of flavonoid compounds. For the first time we describe biotransformations of 6-Methylflavone and the attachment of the sugar unit to the flavonoid substrate having no hydroxyl group. The possibility of using flavonoid aglycones is often limited by their low bioavailability due to poor solubility in water. The incorporation of a sugar unit improves the physical properties of tested compounds and thus increases the chance of using them as pharmaceuticals.
Antidepressant, anticonvulsant and antinociceptive effects of 3'-methoxy-6-methylflavone and 3'-hydroxy-6-methylflavone may involve GABAergic mechanisms.[Pubmed:28943291]
Pharmacol Rep. 2017 Oct;69(5):1014-1020.
BACKGROUND: GABA(A) receptors have been implicated in the pathophysiology of depression, epilepsy and pain disorders. The purpose of this study was to investigate two novel synthetic flavones, 3'-methoxy-6-Methylflavone (3'-MeO6MF) and 3'-hydroxy-6-Methylflavone (3'-OH6MF), for their effect on GABA(A) receptors and subsequently investigate their antidepressant, anticonvulsant and antinociceptive effects. METHODS: Recombinant GABA(A) receptor subunits were expressed in Xenopus oocytes and a two electrode voltage clamp technique was used for electrophysiological studies. The antidepressant and anticonvulsant activities were determined using forced swim (FST) and tail suspension tests (TST) and bicuculline (BIC)-induced seizures respectively. Furthermore, the antinociceptive activity was determined using tail immersion and hot plate tests. RESULTS: 3'-MeO6MF and 3'-OH6MF potentiated GABA-induced currents through ternary alpha1-2beta1-3gamma2L and binary alpha1beta2 receptors indicating that the positive modulation by these flavonoids is not dependent on the gamma subunit. In behavioral studies, 3'-MeO6MF and 3'-OH6MF (10-100mg/kg, ip) exerted significant antidepressant like effects in the FST and TST. 3'-MeO6MF (10-100mg/kg) and 3'-OH6MF (30 and 100mg/kg) also exhibited significant anticonvulsant effects in BIC-induced seizures, and antinociceptive activity in tail immersion and hot plate tests (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Furthermore, the antidepressant and antinociceptive activities of 3'-MeO6MF and 3'-OH6MF were partially ameliorated by co-administration of BIC (3mg/kg) suggesting the involvement of GABAergic mechanisms. CONCLUSION: The findings of this study suggest that 3'-MeO6MF and 3'-OH6MF exhibited significant antidepressant, anticonvulsant and antinociceptive effects mediated via interactions with GABA(A) receptors.
The Direct Actions of GABA, 2'-Methoxy-6-Methylflavone and General Anaesthetics at beta3gamma2L GABAA Receptors: Evidence for Receptors with Different Subunit Stoichiometries.[Pubmed:26496640]
PLoS One. 2015 Oct 23;10(10):e0141359.
2'-Methoxy-6-Methylflavone (2'MeO6MF) is an anxiolytic flavonoid which has been shown to display GABAA receptor (GABAAR) beta2/3-subunit selectivity, a pharmacological profile similar to that of the general anaesthetic etomidate. Electrophysiological studies suggest that the full agonist action of 2'MeO6MF at alpha2beta3gamma2L GABAARs may mediate the flavonoid's in vivo effects. However, we found variations in the relative efficacy of 2'MeO6MF (2'MeO6MF-elicited current responses normalised to the maximal GABA response) at alpha2beta3gamma2L GABAARs due to the presence of mixed receptor populations. To understand which receptor subpopulation(s) underlie the variations observed, we conducted a systematic investigation of 2'MeO6MF activity at all receptor combinations that could theoretically form (alpha2, beta3, gamma2L, alpha2beta3, alpha2gamma2L, beta3gamma2L and alpha2beta3gamma2L) in Xenopus oocytes using the two-electrode voltage clamp technique. We found that 2'MeO6MF activated non-alpha-containing beta3gamma2L receptors. In an attempt to establish the optimal conditions to express a uniform population of these receptors, we found that varying the relative amounts of beta3:gamma2L subunit mRNAs resulted in differences in the level of constitutive activity, the GABA concentration-response relationships, and the relative efficacy of 2'MeO6MF activation. Like 2'MeO6MF, general anaesthetics such as etomidate and propofol also showed distinct levels of relative efficacy across different injection ratios. Based on these results, we infer that beta3gamma2L receptors may form with different subunit stoichiometries, resulting in the complex pharmacology observed across different injection ratios. Moreover, the discovery that GABA and etomidate have direct actions at the alpha-lacking beta3gamma2L receptors raises questions about the structural requirements for their respective binding sites at GABAARs.
The GABA A receptor subunits heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.[Pubmed:23373649]
Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013 Apr 1;13(5):744-8.
The gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor is composed of a variety of subunits and combinations and shows a characteristic distribution in the CNS. To date, 20 subunits of the GABA A receptor have been cloned: alpha1-6, beta1-4, gamma1-3, delta, pi, epsilon , Theta, and rho1-3. Oocyte of Xenopus laevis is one of the most frequently used heterologous expression systems, which are used to design and analyze specific combinations of GABA A receptor subunits. In oocytes, a certain GABA A receptor function is studied only by comparing the amplitude of the response to GABA and other drugs by physiological and pharmacological methods. According to the studies on Xenopus laevis oocytes, the alpha1beta2gamma2S receptor combination is mostly used. The alpha1-containing receptors mediate sedative and anticonvulsant acts. The results of studies on oocytes show that PKA, NKCC1, P2X3 receptors, and GABA A receptor-associated protein, etc., are existing systems that show different reactivity to the GABA A receptors. The GABA A receptor subunits contain distinct binding sites for BZDs, neurosteroids, general anesthetics, etc., which are responsible for the numerous functions of the GABA A receptor. A variety of other drugs, such as topiramate, TG41, (+)- and (-)-borneol, apigenin, and 6-Methylflavone could also have modulatory effects on the GABA A receptors. Some of the different models and hypotheses on GABA A receptor structure and function have been achieved by using the two-electrode voltage clamp method in oocytes.
A new antifungal and cytotoxic C-methylated flavone glycoside from Picea neoveitchii.[Pubmed:22901896]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Sep 15;22(18):5819-22.
A new C-methylated flavone glycoside, 5,7-dihydroxy-3-methoxy-6-C-methylflavone 8,4'-di-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (1), was isolated from the twigs and leaves of Picea neoveitchii Mast, together with eight known compounds, 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxy-3-methoxy-6-Methylflavone 8-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (2) kaempferol 3,4'-di-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), apigenin 7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (4), tiliroside (5), massonianoside B (6), umbeliferone 7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (7), dihydroconiferin (8) and gleditschiaside A (9). Their structures were elucidated on the basis of analyses of spectroscopic data. Compound 1 showed moderate antifungal activity against tested plant pathogens (Pyricularia grisea (Cooke) Sacc., Sclerotium rocfsii Sacc. and Alternaria mali Roberts), however, compounds 2 and 5 had obvious inhibitory effect against S. rocfsii and A. mali, respectively. Compounds 1, 2, 3 and 9 also exhibited potent cytotoxicity against Spodoptera litura Fabricius cells.
In vitro cytotoxic activity of novel protoflavone analogs - selectivity towards a multidrug resistant cancer cell line.[Pubmed:22753749]
Anticancer Res. 2012 Jul;32(7):2863-9.
BACKGROUND: Protoapigenone (PA), a natural flavonoid possessing an unusual p-quinol moiety on its B ring, is a prospective novel lead compound against cancer currently in development, together with WYC0209, a potent synthetic PA analog. Structure activity relationships (SAR) concerning different 1'-O-alkyl side-chains were also studied on two sets of derivatives. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Fifteen 1'-O-alkyl protoflavone derivatives were synthesized from genkwanin or 4'-hydroxy-6-Methylflavone, thirteen of which are new compounds. All compounds were tested for their cytotoxic effect on four human cancer cell lines, such as HepG2 and Hep3B (hepatic), A549 (lung) and MDA-MB-231 (breast) cell lines, with doxorubicin as a positive control. All compounds, as well as PA, WYC0209 and fourteen of their previously reported analogs were also tested on a multidrug-resistant (MDR) sub-cell line of L5178 mouse T-cell lymphoma and on its parental counterpart (PAR). RESULTS: In general, derivatives bearing a free hydroxyl group at C-1' exerted the strongest activities, while C-1'-substituted compounds were found to be much weaker. Derivatives of 6-Methylflavone exhibited mild, but statistically significant selectivity towards the MDR cell line. CONCLUSION: The results are in agreement with our previous findings for fundamental SAR of protoflavones. 6-Methylated protoflavones may serve as valuable leads for developing selective compounds against MDR cancer. Identical activity of other derivatives on the PAR and MDR cell lines suggests that cancer cells cannot exhibit resistance to protoflavones by ABCB1 efflux pump overexpression.
3-Hydroxy-2'-methoxy-6-methylflavone: a potent anxiolytic with a unique selectivity profile at GABA(A) receptor subtypes.[Pubmed:21924247]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Dec 15;82(12):1971-83.
Genetic and pharmacological studies have demonstrated that alpha2- and alpha4-containing GABA(A) receptors mediate the anxiolytic effects of a number of agents. Flavonoids are a class of ligands that act at GABA(A) receptors and possess anxiolytic effects in vivo. Here we demonstrate that the synthetic flavonoid, 3-hydroxy-2'-methoxy-6-Methylflavone (3-OH-2'MeO6MF) potentiates GABA-induced currents at recombinant alpha1/2beta2, alpha1/2/4/6beta1-3gamma2L but not alpha3/5beta1-3gamma2L receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. The enhancement was evident at micromolar concentrations (EC(50) values between 38 and 106 muM) and occurred in a flumazenil-insensitive manner. 3-OH-2'MeO6MF displayed preference for beta2/3- over beta1-containing receptors with the highest efficacy observed at alpha2beta2/3gamma2L, displaying a 4-11-fold increase in efficacy over alpha2beta1gamma2L and alpha1/4/6-containing subtypes. In contrast, 3-OH-2'MeO6MF acted as a potent bicuculline-sensitive activator, devoid of potentiation effects at extrasynaptic alpha4beta2/3delta receptors expressed in oocytes. The affinity of 3-OH-2'MeO6MF for alpha4beta2/3delta receptors (EC(50) values between 1.4 and 2.5 muM) was 10-fold higher than at alpha4beta1delta GABA(A) receptors. 3-OH-2'MeO6MF acted as a full agonist at alpha4beta2/3delta (105% of the maximal GABA response) but as a partial agonist at alpha4beta1delta (61% of the maximum GABA response) receptors. In mice, 3-OH-2'MeO6MF (1-100 mg/kg i.p.) induced anxiolytic-like effects in two unconditioned models of anxiety: the elevated plus maze and light/dark paradigms. No sedative or myorelaxant effects were detected using holeboard, actimeter and horizontal wire tests and only weak barbiturate potentiating effects on the loss of righting reflex test. Taken together, these data suggest that 3-OH-2'MeO6MF is an anxiolytic without sedative and myorelaxant effects acting through positive allosteric modulation of the alpha2beta2/3gamma2L and direct activation of alpha4beta2/3delta GABA(A) receptor subtypes.
Phenolic compounds from Selaginella moellendorfii.[Pubmed:21922662]
Chem Biodivers. 2011 Sep;8(9):1735-47.
Chemical investigation of the leaves and roots of Selaginella moellendorfii Hieron has resulted in the isolation and characterization of two new flavone glucosides, 7-O-(beta-glucopyranosyl(1-->2)-[beta-glucopyranosyl(1-->6)]-beta-glucopyranosyl)flavone-3',4',5,7-tetraol (1) and 7-O-(beta-glucopyranosyl(1-->2)-[beta-glucopyranosyl(1-->6)]-beta-glucopyranosyl)flavone-4',5,7-triol (2), two new biflavonoids, 2,3-dihydroflavone-5,7,4'-triol-(3'-->8'')-flavone-5'',6'',7'',4'''-tetraol (3) and 6-Methylflavone-5,7,4'-triol-(3'-->O-->4''')-6''-methylflavone-5'',7''-diol (4), two new lignans, (7'E)-3,5,3',5'-tetramethoxy-8 : 4'-oxyneolign-7'-ene-4,9,9'-triol (5) and 3,3'-dimethoxylign-8'-ene-4,4',9-triol (6), together with two known monolignans, four known lignans, and four known biflavonoids. Their structures were established by spectroscopic means and by comparison with literature values.


